Active Directory (AD) is the heart of user management in most Windows-based networks. It acts as a central repository for user accounts, computers, groups, and other objects, enabling administrators to efficiently manage and secure their network resources.
This guide will explore various aspects of Active Directory user management, from understanding its core features to leveraging tools like NinjaOne for streamlined operations.
How to Manage Users in Active Directory without NinjaOne
Traditionally, administrators have relied on the Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) console or PowerShell cmdlets to manage users in AD. While these tools offer a comprehensive set of features, they can be cumbersome for large-scale operations or repetitive tasks.
- ADUC Console: The ADUC console provides a graphical interface for managing users, groups, and computers. It allows administrators to perform common tasks such as creating users, resetting passwords, and modifying group memberships.
- PowerShell: PowerShell offers a powerful command-line interface for automating and scripting AD user management tasks. Administrators can use cmdlets to perform bulk operations, generate reports, and delegate administrative tasks.
How to Manage Users in Active Directory with NinjaOne
NinjaOne simplifies Active Directory user management by centralizing essential tasks. Easily enable/disable accounts, reset passwords, manage password policies, set expiration dates, and edit group memberships – all from one platform, saving time and reducing errors.
Locating Active Directory Domain Controllers
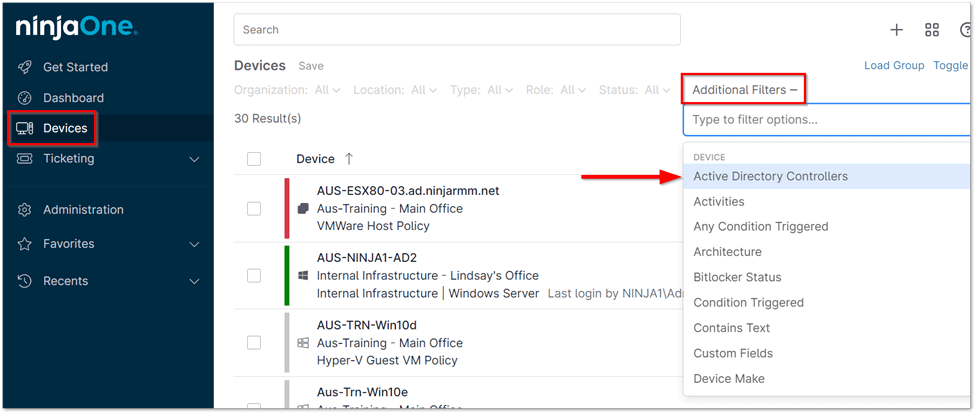
Active Directory Domain Controllers can be located using the filter in the Devices tab.
- Access Devices Tab: Select the ‘Devices’ tab from the left-hand navigation menu.
- Apply Filter: Click the ‘Additional Filters‘ button located at the top of the page, then choose the ‘Active Directory Controllers’ filter from the available options.
Managing Active Directory users
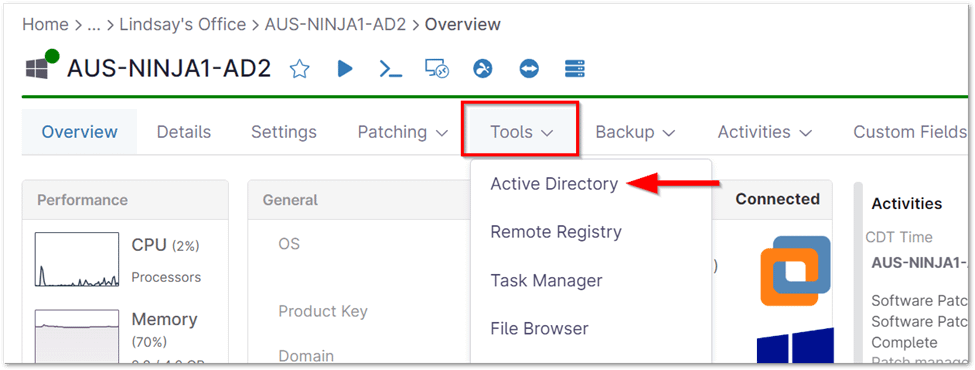
- Access Device Dashboard: Navigate to the NinjaOne device dashboard corresponding to the desired Active Directory domain controller.
- Open Active Directory Tool: Within the dashboard, expand the ‘Tools’ tab and select the ‘Active Directory’ option.
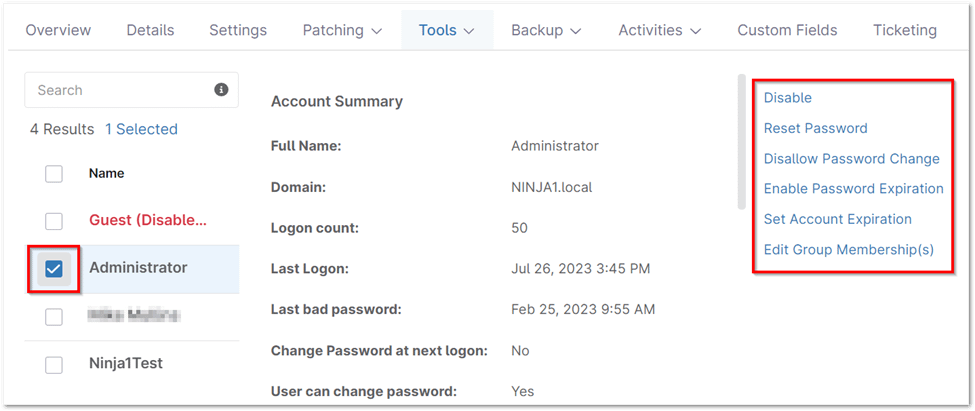
User Management Actions
The following user management actions are available within the Active Directory tool:
- Enable/Disable: Activate or deactivate the user account based on its current state. A confirmation prompt will appear upon completion.
- Reset Password: Set a new password for the user, with the option to enforce a password change at the next login or unlock the account if currently locked due to failed login attempts.
- Require/Do Not Require Password Change: Enforce or remove the requirement for the user to change their password. A confirmation prompt will appear upon completion.
- Allow/Disallow Password Change: Permit or prevent the user from changing their own password. A confirmation prompt will appear upon completion.
- Enable/Disable Password Expiration: Activate or deactivate password expiration for the user account. A confirmation prompt will appear upon completion.
- Set Account Expiration: Specify a date and time for the account to expire. If expiration is set, an additional option to “Disable Account Expiration” will be available.
- Edit Group Membership(s): Select the group(s) to which the user should belong.
Benefits of Using NinjaOne for Active Directory User Management
- Centralized Management: Manage supported Active Directory user tasks from a single platform, eliminating the need to switch between multiple tools.
- Simplified Interface: NinjaOne’s intuitive interface makes it easy to perform user management tasks.
- Remote Management: Manage Active Directory users from anywhere with an internet connection.
Strategies for Active Directory User Management with NinjaOne
- Secure Access Control: Reset passwords, enforce password policies, and manage account lockouts to enhance security.
- Group Management: Easily manage group memberships to control access to resources and simplify permissions management.
- Delegation: Delegate specific administrative tasks to users or groups to improve efficiency.
Best Practices for Active Directory User Management
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your Active Directory environment.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies and encourage users to change their passwords regularly.
- Least Privilege Principle: Grant users only the minimum level of access required.
- Group-Based Access Control: Utilize group-based access control to simplify permissions management and improve security.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of your Active Directory environment.
Examples of Using NinjaOne for Active Directory User Management
- Password Management: Reset user passwords, enforce password change requirements, and unlock accounts locked due to failed login attempts.
- Group Membership: Modify a user’s group memberships to grant or restrict access to specific resources and permissions.
- Account Control: Enable/disable user accounts, and set password expiration and requirements as needed.