Zero Day Vulnerability refers to a security flaw or weakness in software, hardware, or firmware that is unknown to the vendor or developer and has not been patched or mitigated. The term “zero-day” implies that developers have had zero days to address or fix the vulnerability because it is exploited by attackers on the same day it is discovered, leaving users vulnerable to attacks. Effective zero day vulnerability mitigation is crucial to protect systems from these immediate threats.
Zero-day vulnerabilities are particularly concerning because they are exploited by cyber attackers before the vendor has had a chance to release a patch or security update. This means that users and organizations are at risk of being targeted by malicious actors without any warning or protection.
Zero-day vulnerabilities can exist in distinct types of software, including operating systems, web browsers, applications, and even embedded systems. They can be exploited through various attack vectors, such as malicious websites, phishing emails, or infected files, to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive information, or execute malicious code on targeted systems.
Who Discovers Zero-Day Vulnerabilities?
Zero-day vulnerabilities can be discovered by several groups, including.
1. Security Researchers.
Ethical hackers, cybersecurity companies and security researchers actively search for vulnerabilities in software, hardware, and networks. When they discover a flaw, they often contact the vendor in confidence so that a patch can be developed before the flaw’s existence becomes widely known.
2. Bug Bounty Programs
Some companies and organizations offer bug bounty programs, which incentivize independent researchers to report security vulnerabilities, in exchange for monetary rewards, recognition, or other incentives.
3, Hackers
Some do it out of curiosity and passion, seeking recognition within the information security community. Others participate in bug bounty programs to earn rewards for their findings. In more clandestine scenarios, researchers may even sell their discoveries to the highest bidder.
4. Government Agencies
Intelligence agencies and government-sponsored organizations may engage in vulnerability research and discovery as part of their efforts to enhance national security, conduct cyber espionage, or develop offensive cyber capabilities.
5. Cybercriminals
Unfortunately, malicious actors, including hackers and cybercriminals, may also discover zero-day vulnerabilities through their illicit activities. These individuals may exploit zero-day vulnerabilities for personal gain, financial profit, or other malicious purposes.
What Can be Done to Mitigate Zero-Day Vulnerability?
To mitigate the risks associated with zero-day vulnerabilities, organizations should implement proactive security measures, such as user education and awareness, installing endpoint protection or endpoint detection and response software, zero trust segmentation, and intrusion detection systems. Additionally, prompt patch management and updates can help reduce exposure to known vulnerabilities and limit the impact of zero-day attacks.
What is Zero Trust Segmentation?
Zero Trust Segmentation is a security approach that builds upon the core principles of Zero Trust architecture and applies them specifically to network segmentation.
Here is a breakdown of the key concepts:
- Zero Trust Architecture: This is a security model that assumes no user, device, or connection is inherently trustworthy. Every attempt to access a resource requires verification, regardless of origin (inside or outside the network).
- Network Segmentation: This involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. This limits the potential damage if a security breach occurs, as attackers would be confined to the compromised segment and struggle to access other critical resources.
- Assume Breach: Zero Trust Segmentation operates under the assumption that a breach might already have occurred. It focuses on limiting lateral movement and isolating compromised devices or users to prevent them from accessing critical resources.
Zero Trust Segmentation is a powerful approach to network security that complements Zero Trust architecture by providing a layered defense against cyberattacks. It helps organizations create a more secure and resilient IT environment by minimizing the potential impact of security breaches.
How Can NinjaOne Help in Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Mitigation?
Once the vendor releases the patch, it´s crucial to promptly apply it to remediate the vulnerability. NinjaOne can help in the patch installation without delay, let’s go through the process. For our example, lets assume the software impacted is Windows and the new patch has been released.
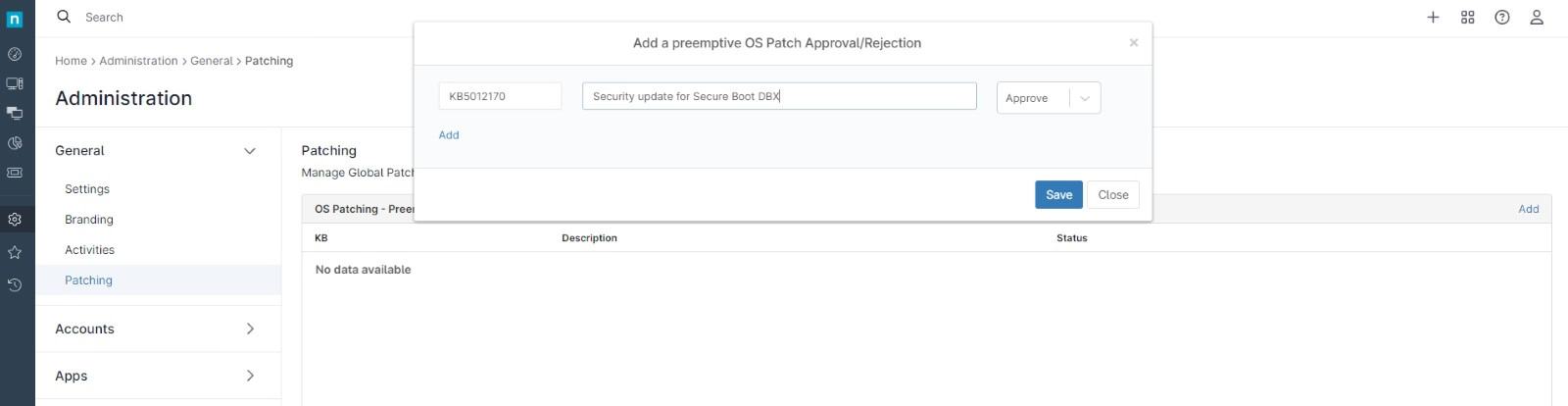
Once the new patch is tested and ready for distribution, let’s approve it globally, in other words, let’s whitelist it. Before that, you need to know the patch ID and description. Let’s assume in this example the following ID and description: KB5012170, Security update for Secure Boot DBX.
- Go to Administration, then General, then Patching, then click add at the right of the screen.
- A dialog box will open. Type the patch ID and description, from the drop-down at the right, select Approve.
- You can keep adding more patches, for that, click add at the left of the dialog box. If you´re done, click Save. (see screenshot below for reference)
Now, the patch is pre-approved for all the organizations in the tenant and the patch will be applied on all devices requiring it, in next scan window. Alternatively, you can run a manual scan to immediately apply the patch. For that, follow the next instructions.
- Go to Devices and using the filters, select only the devices that require this patch.
- Check mark them all.
- Click run, then OS update, then Scan.
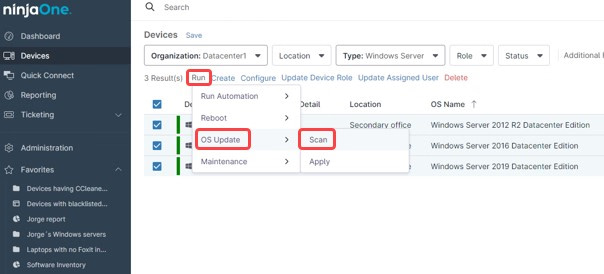
NinjaOne will send a scan order to all the selected devices. Once the scan is complete, send an Apply command to install the new found patch. This sequence should get the patch installed, which will probably require a reboot. Subsequently, you can confirm the patch installation by checking the installed patches or running a report.
It’ s a good practice to run this sequence after 6 hours to make sure the patch has been taken and troubleshoot if needed.
