Ratings
Baramundi
Naverisk
Overall
4.8
Meets Requirements
9.2
905 responses
Ease of Use
9.3
912 responses
Ease of Setup
9.4
804 responses
Ease of Admin
9.5
80 responses
Quality of Support
9.4
876 responses
Ease of Doing Business with
9.6
808 responses
Product Direction (% positive)
Based on G2 Spring 2024
Competitors
Baramundi
Product Summary
Baramundi is a unified endpoint management software provider that allows IT teams to manage their endpoints from anywhere with an internet connection. Its solution features Windows management and patch management for Microsoft and other third-party applications.
Use Cases
- Automated software deployment:
Baramundi allows you to deploy software faster and at scale. - Compliance scans:
Baramundi software regularly runs compliance scans to ensure that all your software and applications are up-to-date. - Asset inventory:
Baramundi keeps an accurate, real-time inventory of all your managed hardware and software.
Shortcomings
- Scripting:
Baramundi could add to its script library or its ability to create custom scripts. - Support for macOS devices:
Baramundi is limited in macOS support, especially in patch management and remote access. - Static dashboards:
Baramundi’s dashboard is not as intuitive as expected.
Naverisk
Product Summary
Naverisk is an IT services platform that consolidates remote monitoring and management (RMM), professional services automation (PSA), and service desk tools into one solution. With Naverisk, technicians can easily manage and monitor the entire IT environment. Tools such as patch management, alerts, and automation ensure that endpoints remain up-to-date, and efficient.
Use Cases
- Remote monitoring:
Naverisk monitors devices and servers in real time, allowing technicians to diagnose and remediate problems early. - Endpoint management:
Naverisk allows users to manage devices from a single console, keeping them updated and secure. With integrations, technicians can access remote devices. - Automation:
Technicians can code policies to automate routine IT tasks and workflows with open-source scripting.
Shortcomings
- Search feature issues:
Users have reported that the search function does not work well, making navigating the platform difficult. - Outdated interface:
Naverisk’s GUI has been described as lacking. Others are asking for more GUI customization to address this. - Steep learning curve:
Naverisk reviews say that the product requires time and resources to learn, and users can get lost when trying to navigate the platform.
NinjaOne
Why your peers choose us over Baramundi and Naverisk
NinjaOne sets itself apart with its exceptional customer reviews, usability and comprehensive integration options, positioning it ahead of its competitors. The platform’s interface is expertly crafted for both quick adoption and ease of use, vital for dynamic IT environments. This focus on user experience doesn’t compromise its robust feature set, which is designed to boost operational efficiency, an area where many competitors struggle.
In terms of integration, NinjaOne shines by offering extensive compatibility with a wide array of third-party applications, an area where other RMM solutions often have limitations. This makes it a more adaptable choice for varied IT ecosystems. Furthermore, NinjaOne’s scalability and performance consistency, even in large network scenarios, mark it as a superior option. Enhanced by advanced, customizable reporting tools, NinjaOne emerges as a leading choice for IT professionals seeking a dependable, efficientRMM platform.
What they're saying
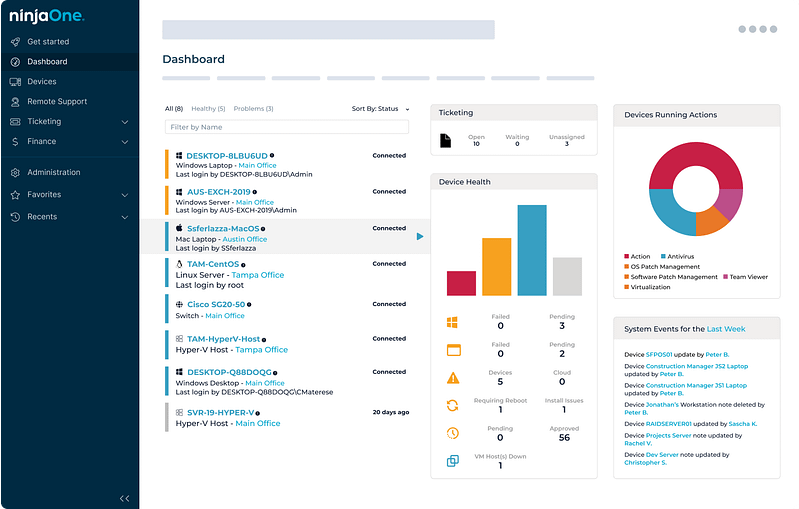
Watch a Demo of the #1 IT Management Software on G2
Related resources
Baramundi
Baramundi vs JumpCloud
Baramundi vs Miradore
Baramundi vs Jamf
Baramundi vs Moki Total Control
Baramundi vs SureMDM
Baramundi vs GFI Languard
Baramundi vs Mosyle
Baramundi vs Esper
Addigy vs Baramundi
Baramundi vs Sophos Mobile
Baramundi vs Kandji
Baramundi vs Cisco Meraki
Baramundi vs BMC Helix Client Management
Baramundi vs SOTI MobiControl
Baramundi vs IBM Security MaaS360
Baramundi vs Pandora FMS
Baramundi vs Scalefusion
Baramundi vs SysAid
Baramundi vs VMware Workspace One
Baramundi vs Kace
Baramundi vs Syxsense
Action1 vs Baramundi
Baramundi vs SuperOps
Matrix42 vs Baramundi
Baramundi vs LogicMonitor
Baramundi vs Goverlan
Auvik vs Baramundi
Automox vs Baramundi
Atera vs Baramundi
Baramundi vs SyncroMSP
Baramundi vs Kaseya VSA
Baramundi vs Connectwise Automate
Baramundi vs PRTG Network Monitor
Baramundi vs Bravura Optitune
Baramundi vs Microsoft Intune
Baramundi vs ManageEngine Endpoint Central
Baramundi vs LogMeIn
Baramundi vs N-able N-central
Baramundi vs N-able N-sight
Baramundi vs Veeam
Baramundi vs Panorama9
Baramundi vs Naverisk
Baramundi vs SolarWinds Dameware
Baramundi vs Tanium
Baramundi vs Lansweeper
Baramundi vs BigFix
Arcserve vs Baramundi
Baramundi vs Pulseway
Baramundi vs Ivanti
Baramundi vs IT Glue
Acronis vs Baramundi
Baramundi vs GoTo Resolve
Baramundi vs Baramundi
Bacon Unlimited vs Baramundi
Baramundi vs ITarian
Baramundi vs Hexnode
Baramundi vs Datto
Naverisk
JumpCloud vs Naverisk
Miradore vs Naverisk
Jamf vs Naverisk
Moki Total Control vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs SureMDM
GFI Languard vs Naverisk
Mosyle vs Naverisk
Esper vs Naverisk
Addigy vs Naverisk
Kandji vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs Sophos Mobile
Cisco Meraki vs Naverisk
BMC Helix Client Management vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs SOTI MobiControl
IBM Security MaaS360 vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs Pandora FMS
Naverisk vs Scalefusion
Naverisk vs SysAid
Naverisk vs VMware Workspace One
Kace vs Naverisk
Action1 vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs Syxsense
Naverisk vs SuperOps
Matrix42 vs Naverisk
GoTo Resolve vs Naverisk
Level vs Naverisk
Bacon Unlimited vs Naverisk
ITarian vs Naverisk
Hexnode vs Naverisk
Baramundi vs Naverisk
Automox vs Naverisk
Auvik vs Naverisk
Goverlan vs Naverisk
LogicMonitor vs Naverisk
Atera vs Naverisk
LogMeIn vs Naverisk
ManageEngine Endpoint Central vs Naverisk
Microsoft Intune vs Naverisk
Bravura Optitune vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs PRTG Network Monitor
Connectwise Automate vs Naverisk
Kaseya VSA vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs SyncroMSP
Naverisk vs SolarWinds Dameware
Naverisk vs Panorama9
Naverisk vs Veeam
Datto vs Naverisk
N-able N-sight vs Naverisk
N-able N-central vs Naverisk
Acronis vs Naverisk
IT Glue vs Naverisk
Ivanti vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs Pulseway
Arcserve vs Naverisk
BigFix vs Naverisk
Naverisk vs Tanium
Lansweeper vs Naverisk
