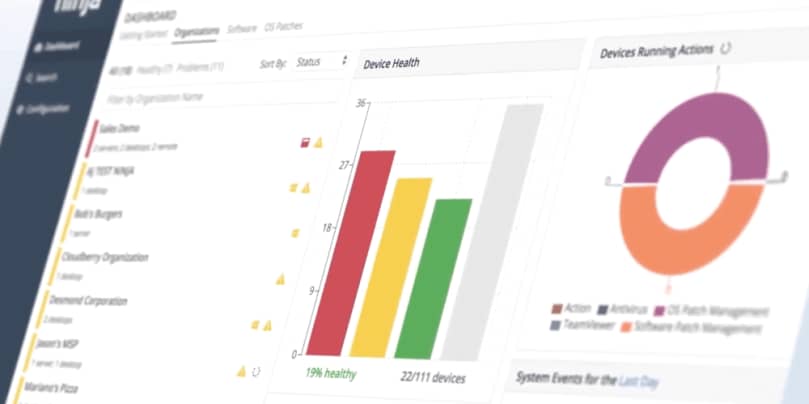
RMM is short for remote monitoring and management. RMM software is used to do two things: a) gather information from remote endpoints and networks to assess their health, and b) perform various remote IT management tasks on them without disruption.
As more organizations across sectors leverage RMM products to boost efficiency and benefit from its flexible and versatile services, it has become all the more important for you to understand how the software works and what you need to know before selecting the best RMM software for your organization.
Specifically for 2024, you need to consider the Cyber Defense Plan for Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) published last year by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). This is the first proactive plan developed by industry and government partners through the Joint Cyber Defense Collaboration (JCDC) to inform and protect the public against the malicious use of RMM and educate customers about the key factors to consider when choosing an RMM tool.
Who uses remote monitoring & management software?
RMM solutions are most widely used by managed services providers (MSPs). These professionals provide IT support to clients in different locations, and they need a fast, reliable way of doing that without having to be physically present in client offices providing on-site support.
With workforces becoming increasingly distributed, however, it’s also becoming more and more common to see internal IT departments also utilizing RMM tools, which makes sense since they combine many of the core functions of IT into a single solution.
Why do MSPs need RMM?
IT business leaders use RMM to proactively detect and resolve issues before they turn into bigger problems. This is important: Proactive monitoring is an essential feature of any good RMM.
→ Download your free Proactive IT Management Guide [PDF]
The right tool uses a unified IT management approach to deliver powerful risk monitoring and management all done in the background. This leads to improved IT network security, which contributes to strengthened customer satisfaction and consistent revenue.
Key takeaways
- RMM is a proactive technology that allows you to observe and maintain your IT infrastructure.
- The software reduces network complexities by offering multiple features from a single console.
- It helps MSPs provide better customer service and meet their SLAs on time.
- As more organizations use RMM, it is important to stay current with the latest cybersecurity plans and advisories released by CISA, the National State Agency (NSA), and the Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC).
The history of RMM
The original way IT teams dealt with issues as they occurred follows the break/fix model. When hardware or software, broke or malfunctioned, technicians would have to go on-premise to investigate what caused the problem and eventually resolve the issue, which could take a lot of time. The break/fix model also lacked contracts or subscriptions to provide technicians with a steady income, and customers lacked continuous support from technicians. Break/fix was a lose-lose situation for both end users and service providers.
Then RMM software was introduced, which enabled technicians to actively monitor and manage IT assets from a completely different location. Rather than providing reactive services, technicians could proactively work to fix issues that arise. RMM software gives technicians the information and tools they need to provide preventative maintenance for their users’ IT assets.
Are you interested in transitioning from the break/fix model to managed services?
Download this guide today to get started.
Key capabilities of RMM software
RMM solutions offer an array of functionality, but in essence, IT pros use them to get three core jobs done:
- Real-time remote monitoring and alerting: RMM solutions can monitor the health and performance of individual systems and entire networks 24/7. IT pros can be alerted to potential issues before they become disruptive problems, create automated workflows to deal with those alerts, and generate reports that provide clear visibility into network activity, asset inventory, compliance, and the direct value of IT support.
- Behind-the-scenes remote maintenance and remediation: With RMM software, technicians can deploy software, manage updates, run scripts, and remotely connect to machines to troubleshoot and fix problems without interrupting the end user.
- Automating routine IT management: RMM software unlocks the ability to streamline IT workflows and automate a wide variety of common IT tasks, from installing patches to running scripts to creating and responding to tickets with predetermined policies and actions.
In addition to these core capabilities, RMMs are also commonly used to deploy and actively manage third-party endpoint security products and backup solutions.
With all that functionality, it’s no surprise that most MSPs consider their RMM to be their most critical application.
Benefits of remote monitoring & management software
Under the right conditions and management, RMM can help IT providers completely transform their operations, making them more efficient, more effective, and — in the case of MSPs — more profitable. Here are a few of the benefits of using RMM software that IT providers value most:
- Complete visibility and control from a central location: That makes it possible for even small MSPs or IT departments to support, secure, and manage large numbers of systems no matter where they’re located.
- Comprehensive IT management via a single pane of glass: Thanks to integrations with endpoint security, backup, PSA, and other software, RMM dashboards can serve as a central control panel, dramatically cutting down on the number of screens techs and admins have to toggle back and forth between during the day.
- Automation makes support scalable: Streamlining and automating workflows frees techs from time-consuming manual tasks and empowers them to support more users and endpoints.
- Proactive rather than reactive support: RMM software allows service providers to escape the disruptive cycle of constantly putting out fires, and instead helps them get ahead of potential issues and avoid downtime and disruption altogether (find out how the right RMM can help you transition from providing break/fix support to generating recurring revenue with managed services).
“NinjaOne gives us the ability for just a few technicians to manage hundreds of endpoints from anywhere in the world with real-time insight.”
— Nate Davis, Crossroad IT
See the benefits of a modern RMM for yourself: Start a free trial
Real-world uses of RMM
- Software and technology. RMM is essential to any digital transformation, helping tech companies improve support outcomes, drive end-user productivity, and secure endpoints. Advania, a well-known MSP, uses Ninja’s RMM tool to manage over 2,000 servers and provide more flexible IT services to its customers.
- Healthcare. Centralized device management is priceless in the healthcare industry. The right RMM tool can improve the stability, reliability, and security of your healthcare IT assets in a centralized IT management console. NinjaOne, for example, helped Horizon Home Care & Hospice easily manage 1,000 endpoints in under two weeks without disrupting their frontline caregivers.
- State and Local Government. Many state and local governments use RMM to centrally monitor, patch, and manage their entire IT portfolio. The City of North Adams was able to save $20,000 and over 20 hours per month in manual labor with NinjaOne’s RMM.
- Financial. RMM protects financial institutions from cyber-attacks, hardening their endpoints and automating various tasks. For example, Heritage Credit Union uses NinjaOne RMM to manage over $200 million in assets and provide excellent service to the residents of British Columbia’s Kootenay Region.
- Education. Schools and universities can improve faculty and staff productivity with a powerful RMM tool that can centralize and automate IT management. NinjaOne helped Park University manage over 1,000 devices through automation, saving over 150 hours per year in manual intervention.
Key takeaways:
- Any good remote monitoring software helps you remotely monitor and manage your endpoint devices in real time.
- These processes are ideally automated and deployed in the background so that your end users are never affected.
- An RMM tool offers end-to-end visibility from a single pane of glass so that your IT technicians can easily observe, analyze, and act on the health and performance of different endpoints in your IT network.
- Various industries use RMM for monitoring and managing their IT environments.
How does remote monitoring & management software work?
RMM works by deploying RMM agents onto endpoint devices, which include desktops, laptops, servers, tablets, smartphones, workstations, and Internet-of-things (IoT) devices. The agent enables technicians and those using the RMM software to get real-time data on how endpoints are performing, manage devices, deploy and apply patches, automate repeatable tasks, and more.
Evaluating remote monitoring & management software: Key criteria
As with any software, evaluating RMM options is highly dependent on specific needs and priorities. Most RMMs offer many of the same core features, but reliability and performance can vary. While one tool may excel in some areas, it may lag behind in others. That’s one of the reasons why it’s so important to take advantage of free trials to see for yourself whether an RMM’s strong suits match up with your top needs.
In addition to product features, RMM users also factor in crucial things like ease of use, product stability, and customer support.
RMM feature requirements
- Monitoring and alerting: In addition to workstations and servers, a good RMM should be able to monitor SNMP devices such as routers, switches, firewalls, printers, and more. Cloud monitoring, including application servers and websites, is another capability to look for, and all monitoring data should be delivered as close to instantaneously in real-time. Alerting should be easy to set up and customize, with options to receive alerts via SMS or email and/or have them create tickets in your ticketing system.
- Remote management tool: Speed and reliability are the two big factors here. Many RMMs provide remote access via integration with third-party software such as TeamViewer or Splashtop, and performance can vary. Other options include Connectwise ScreenConnect (formerly ScreenConnect) and establishing connections over cloud-enabled RDP.
- Patch management tool: An RMM should be able to help automate patching for Windows, as well as third-party applications, allowing techs and admins to easily schedule updates on off hours to avoid disrupting end users.
- Reporting: There should be a wide variety of reliable reports you can easily generate, from detailed patch compliance and asset inventory reports to network performance overviews and high-level executive summaries.
- Scripting: The ability to launch and schedule scripts (with the appropriate privileges) is critical to unlocking automation opportunities and increasing efficiency.
- Integrations: In addition to backup, remote access, and endpoint security products, RMMs are expected to integrate with tools like Professional Services Automation (PSA) solutions, documentation software, and more.
Other key criteria
- Ease of setup: This can vary significantly, with some RMMs requiring considerable implementation training and fees. In fact, there is an entire ecosystem of implementation consultants that have sprung up around particular legacy RMM options. In contrast, other RMMs are designed to be intuitive and cut down drastically on ramp-up time and costs.
- Ease of ongoing administration: The true cost of any software isn’t limited to the licensing fee — you also have to factor in the time, effort, and level of expertise necessary to manage it.
- Stability and reliability: With RMMs serving as a central management portal, any downtime can be extremely disruptive and detrimental.
- Customer support: How important is it for you to have access to responsive, knowledgeable support?
The importance of RMM customer support
Customer support is a crucial factor to consider when choosing RMM software. Since RMMs serve as a central management portal, any downtime can be extremely disruptive and detrimental to your operations. Having access to responsive, knowledgeable support can make a significant difference in quickly resolving issues and minimizing disruptions. Additionally, the ease of setup and ongoing administration can vary significantly between RMMs, further underlining the importance of quality customer support.
RMM software ratings
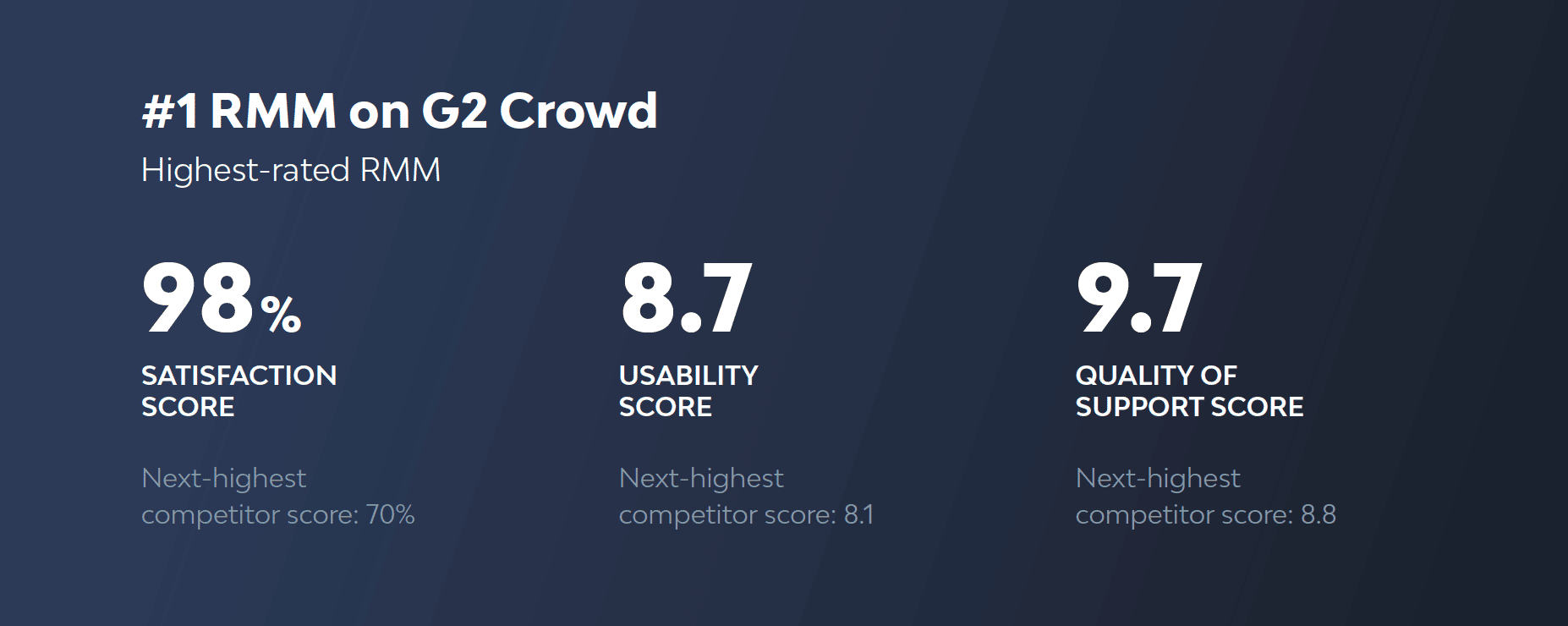
NinjaOne ranks as one of the top easiest to use in RMM software by G2 Crowd and as the emerging favorite by Capterra.
The following ratings were collected from third-party review sites G2 Crowd and Capterra. The “-” indicates the particular data point was either unavailable at the time of collection, or the product did not meet our cutoff of having three or more reviews.
Comparison of RMM software solutions for MSPs (G2)
| Category | NinjaOne | Hexnode | Pulseway | GoTo Resolve | OptiTune | Auvik | SyncroMSP | Action1 | Atera | Naverisk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 4.8 out of 5 (1,035) | 4.6 out of 5 (189) | 4.5 out of 5 (57) | 4.4 out of 5 (412) | 4.3 out of 5 (5) | 4.6 out of 5 (297) | 4.5 out of 5 (126) | 4.9 out of 5 (149) | 4.6 out of 5 (409) | 4.7 out of 5 (63) |
| Has the product been a good partner in doing business? | 9.6 | 9.2 | 9.0 | 8.8 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 9.4 | 9.5 |
| Quality of Support | 9.4 | 9.3 | 8.5 | 8.7 | 10 | 8.8 | 8.3 | 9.8 | 9.1 | 9.6 |
| Ease of Admin | 9.3 | 9.1 | 9.0 | 8.9 | 9.4 | 8.7 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 9.0 | 9.2 |
| Ease of Use | 9.3 | 9.0 | 9.2 | 9.0 | 9.3 | 8.7 | 8.9 | 9.6 | 9.2 | 9.1 |
Comparison of RMM software solutions for MSPs (Capterra)
| Category | NinjaOne | Hexnode | Pulseway | GoTo Resolve | OptiTune | Auvik | SyncroMSP | Action1 | Atera | Naverisk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 4.8 out of 5 (201) | 4.7 out of 5 (114) | 4.7 out of 5 (181) | 4.5 out of 5 (197) | 4.3 out of 5 (14) | 4.7 out of 5 (71) | 4.7 out of 5 (75) | 4.9 out of 5 (83) | 4.6 out of 5 (341) | 4.8 out of 5 (90) |
| Ease of Use | 4.8 | 4.6 | 4.7 | 4.5 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 4.6 |
| Customer Service | 4.8 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.8 |
| Features | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 4.5 |
| Value for Money | 4.7 | 4.6 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5.0 | 4.7 | 4.8 |
| Likelihood to Recommend | 92% | 90% | 90% | 85% | 82% | 88% | 91% | 96% | 89% | 91% |
See our deep-dive analysis of the best RMM software solutions.
See why IT pros are choosing NinjaOne RMM
Ratings via G2 Crowd
NinjaOne was founded with a mission to help IT providers accomplish more by simplifying their workdays. We believe RMM platforms should make things easier, not more complicated. That’s why we’re dedicated to providing a more modern solution that combines powerful functionality, intuitive ease of use, and unbeatable support. Start a free trial today.
Key takeaways
- Choose an RMM that matches your unique business environment.
- While all RMM vendors offer the same core functionalities, they may differ in speed, reliability, and features.
- It is highly recommended that you take advantage of the free trials most providers offer. This will help you personally understand how a specific tool can benefit your company.
- When considering the features and functions of a specific RMM, it is also worth noting your current IT budget and how that aligns with the cost of RMM software.
Keep up-to-date with the leading IT trends for 2024.
FAQs
What is the difference between RMM and MDM?
Mobile device management (MDM) helps companies monitor and secure the mobile devices used by their end-users. RMM, on the other hand, helps IT pros monitor and manage the endpoints in their IT environment and offers additional features such as remote access. This MDM vs RMM guide offers a more in-depth view of when to use each (or both) to manage devices for distributed workforces.
What is the difference between RMM and UEM?
Both RMM and unified endpoint management (UEM) enable IT teams to monitor, manage, and secure endpoints. RMM software is key for MSPs since it allows them to remotely deliver IT services to their clients’ IT environments. UEM software also provides this capability but includes additional tools and features, such as MDM. The main distinction is who uses them. RMMs are used by MSPs, and UEMs are more common in larger businesses and enterprises.
Is RMM safe?
When used and configured correctly, RMM tools can be a powerful way to secure your and your clients’ IT networks. Ideally, look for an RMM platform that offers robust security features and regularly updates its software based on customer feedback. It’s worth noting that—for the most part—security risks are created by how RMM is used (or misused).
What is the best RMM in the market today?
While there is no one “best” solution for all companies, NinjaOne ranks the highest in the best RMM software in 2024, after compiling data from leading review sites, such as G2 and Capterra.
What is NinjaOne RMM?
NinjaOne has been the #1 rated RMM on G2 for years and with good reason. It offers a powerful and lightweight solution that helps MSPs worldwide deliver radical efficiency from day one. Designed by IT for IT, NinjaOne is the go-to solution for over 20,000 customers worldwide.