What is Patch Management?
A Patch Management Overview with Explanations
-
 by
Lauren Ballejos
by
Lauren Ballejos
- Last updated
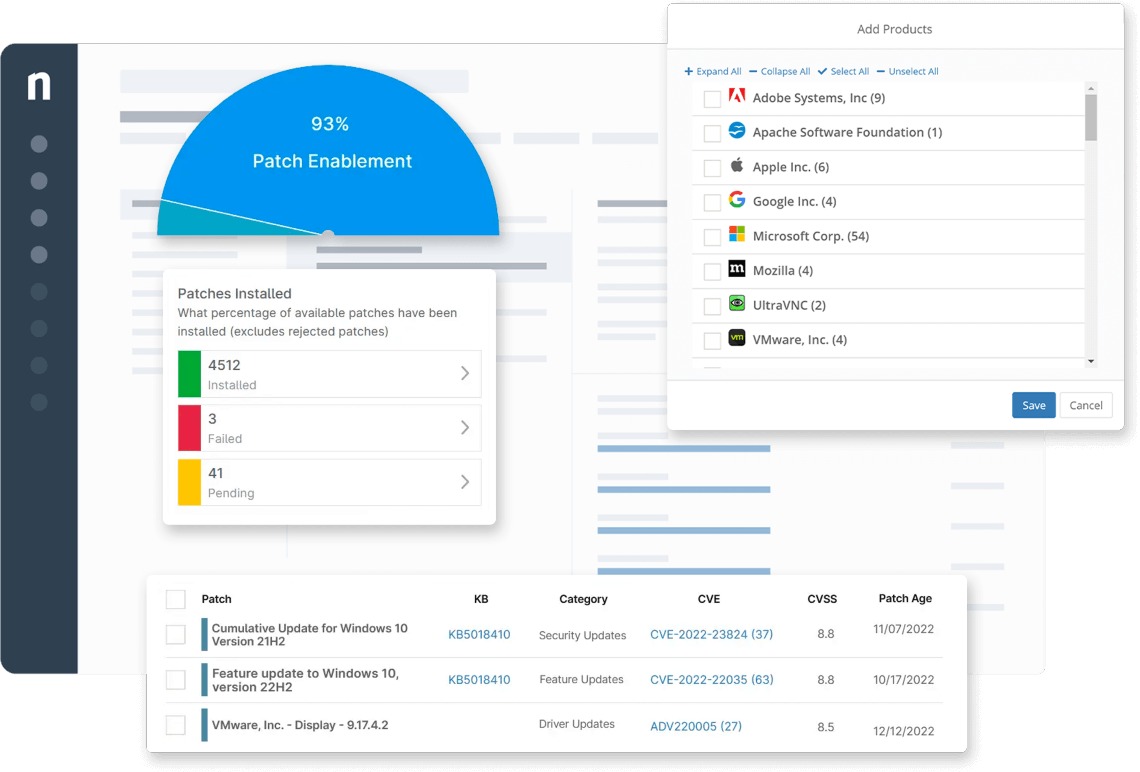
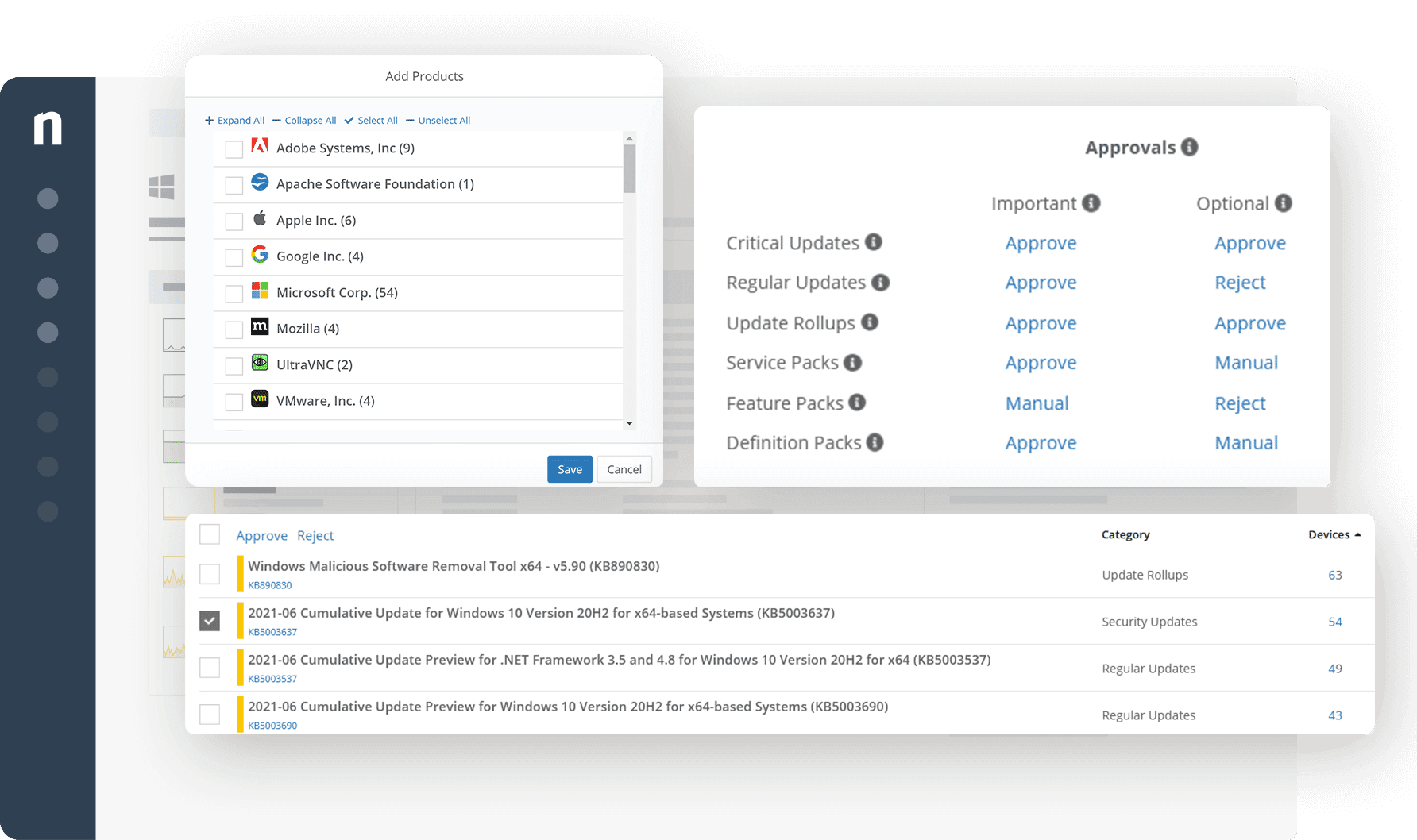
Since the number of malware attacks continues to rise every year, effective patch management is more important now than ever before. A Market Data Forecast report on the patch management industry claims that “the global patch management market size is forecasted to grow USD 1084 million by 2027 from USD 652 million in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 10.7% between 2022 and 2027.” Learn more about patch management and its multiple benefits in this overview.