57% of those who receive a cyberattack claim that the attack wouldn’t have happened had they simply applied an available patch. That’s a hard pill to swallow, especially when there are specific tools and software available to help simplify and streamline the patch management process. Windows patch management is vital for organizations with Windows endpoints to keep their devices updated and secured.
What is Windows patch management?
Windows patch management is the updating or fixing of Microsoft systems using patches created specifically for Windows devices. These patches work to harden devices, protect them from outside cyberattacks and threats, and ensure that the software functions properly and runs smoothly. Patch management software for Windows devices allows you to efficiently execute the patch management process.
Patch all your Windows endpoints and applications automatically and at scale to secure your IT estate.
→ Learn more about Windows Patch Management Software
or
Why Windows patch management is important
Practicing efficient Windows patch management does not only protect against vulnerabilities, it also ensure optimal device performance. Robust Windows patch management solutions can automatically assess and priotize critical patches over others based on the possible risks and negative effects or the likelihood of vulnerability exploitation.
What are the benefits of Windows patch management?
Protects against known Windows threats
Microsoft reports, “Attacks that impact customers’ systems rarely result from attackers’ exploitation of previously unknown vulnerabilities. Rather, they exploit vulnerabilities for which patches are available but not applied.” Efficient Windows patch management can help to quickly patch your Windows devices with available patches before attackers try to enter the system.
Preserves and supports Windows endpoints
Windows patch management helps you to save money and lower costs that are associated with the management and upkeep of your Windows endpoints, such as device support and repair. The patch management of Windows servers is also critical because of the far-reaching effects of a server endpoint.
Meet compliance requirements
To ensure your business maintains compliance, effective Windows patch management is critical. Whether your IT environment is made up of entirely Windows devices or has just a few, to meet compliance standards, every component in your IT environment needs to remain secure.
What is Patch Tuesday?
Patch Tuesday is the term used for Microsoft’s software patches and security updates. Patch Tuesday happens monthly on every second Tuesday.
The patches released on Patch Tuesday are typically to address vulnerabilities in Windows systems, specifically the desktop, and server. Additionally, the patches may update or fix other Microsoft software and applications, such as Azure or Microsoft Office.
What are the types of Windows patches?
Microsoft has multiple types of patches or updates, but the two most common types you will hear about are feature updates and quality updates:
1. Feature updates
Windows feature updates are when Microsoft adds new features to its existing products. These types of updates are released annually.
2. Quality updates
Windows quality updates are made up of four subtypes: security updates, critical updates, servicing stack updates, and driver updates. Quality updates are usually the updates that are released on Patch Tuesday, so they are largely security fixes, but they can also be non-security focused.
Does Microsoft have a patch management tool?
Microsoft’s free patch management tool is known as Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). WSUS is available on the Windows Server Operating system, and it is used to initiate and deploy patches to endpoints from the server.
This free patching tool may be beneficial if basic Windows patching is all you need, but it is lacking if you need more than that. WSUS uses push-style patching, which means that it just sends the patches directly to the endpoints regardless of their status. It can’t pull information from the endpoint so it doesn’t know what patches are missing or needed, and it doesn’t know if a patch was successfully applied to a system.
SCCM was the paid Microsoft endpoint management tool that was used in conjunction with WSUS. SCCM would manage devices while WSUS would patch those devices. SCCM is now a component of Microsoft Configuration Manager, which is part of the Microsoft Intune family of products. Microsoft Configuration Manager is their endpoint management product, and using this product you can manually or automatically deploy software updates.
What Is WSUS Patch Management?
WSUS is a free tool provided by Microsoft for managing patches and updates. It allows administrators to control which patches are approved for installation and deploy those updates at scale to specific devices.
As a free patch management tool, WSUS patch management can be a solid choice for businesses that only require basic Windows patching. WSUS uses push-style patching, which means that patches are directly sent to the endpoint devices regardless of their status. WSUS is unable to pull information from the endpoint, so it doesn’t know what patches are missing or needed or if a patch was successfully applied to a system.
Windows patch management challenges
If there’s one thing that IT teams can agree on, it’s that patching is hard! There are many patch management challenges that apply broadly, but three specific challenges of Windows patch management include:
1. Volume of Windows patches
Microsoft releases patches all the time, and there are a lot of them. It can be difficult to keep track of them all while efficiently applying them to your IT environment. Since patches are typically related to security, it’s critical to make sure you account for all the available Windows patches.
2. Broken Windows patches
Often the patches received for Windows devices may be broken, or the patches may inadvertently break stuff in other workflows. You need to be able to patch, but you also need to be able to revert back if you do break something.
3. Compliance management
For organizations that must follow industry regulatory standards, deploying patches consistently is vital to protect sensitive data. Having full visibility of patch status and when patches have been deployed helps with regulatory patch audits.
4. Patch prioritization
Assessing which Windows patches must be pushed out first can be challenging as it requires expert knowledge and analysis. A robust patch management software can simplify this process by automatically identifying crucial patches and deploying them at scale to address vulnerabilities.
5. Application of Windows patches
You need to make sure your Windows endpoints are patched and patched quickly. The generally heterogeneous nature of IT environments also means that no one is starting from the same place. Within an environment, you may have very different versions of Windows, which complicates the patch management application process. The patch management lifecycle of your Windows devices is also something you need to take into account when determining how to effectively apply Windows patches.
6. Lack of device visibility
Without being able to see the patch status and history of all the devices in a Windows environment, IT administrators will not be able to monitor missed Windows patches which could lead to exploitable vulnerabilities and possible performance issues. To address this, consider utilizing Windows endpoint management tools to monitor and manage all your devices in real-time and identify any critical patching failures.
How to automate Windows patch management
Windows patch management can be automated using policies on third-party patching software. Automation features help to streamline and speed up your patch management process.
When you set up a patching policy you can determine:
- When you want to identify patches
- When you want to deploy them
- What types of patches you want to approve and deploy automatically
Windows patch management best practices
Ensure the security and stability of your device systems with these best practices for Windows patch management:
-
Regular Scheduling
Establish a consistent schedule for applying patches. Since Microsoft typically releases patches on “Patch Tuesday”, plan your patch deployment schedules around these dates.
-
Automation
Leverage IT automation software to streamline the patch management process. Automation tools can detect missing update, schedule consistent distribution of patches and updates, simplify compliance with industry regulations, and more.
-
Continuous monitoring
Monitor and scan the assets in your IT environment to detect signs of vulnerability or instability and deploy the proper updates fast
-
Backup your devices
Utilize a backup solution so that you can backup your Windows systems before applying any patches. In some rare instances, something can go wrong in the patching process and jeopardize the safety of sensitive business data.
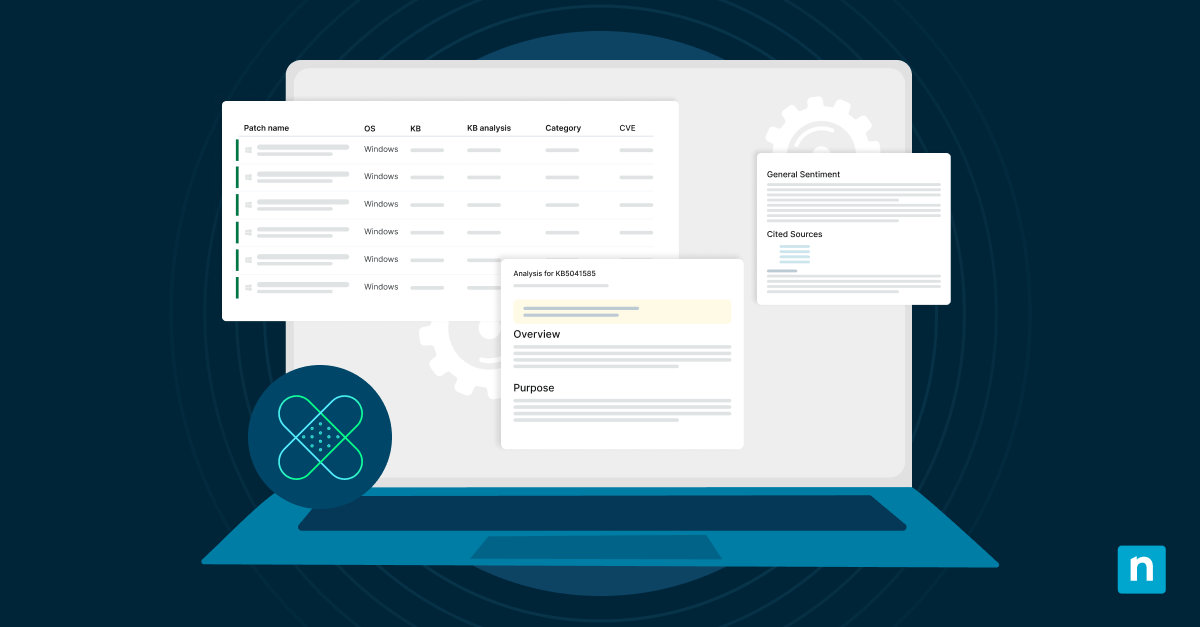
Automated Windows patch management with NinjaOne
Windows handles patch management natively but doesn’t give you visibility, control, or the ability to ensure that you’re patched in a timely manner. Additionally, a lot of patching tools are designed to be used on a network, which doesn’t work well for remote employees who require a remote solution.
NinjaOne provides Windows patch management software to help you more effectively patch your Windows devices. It provides features such as automated remote patch management, a patch status dashboard, and compliance reporting. NinjaOne also allows you to leverage a WSUS server by pulling patches directly from the Microsoft cloud, ensuring you don’t miss any available Windows patches. Start increasing the efficiency of your Windows patch management and sign up for a free trial today.
Windows Patch Management FAQs
-
Why is a Windows patch necessary?
Windows patches are essential for multiple reasons such as addressing security vulnerabilities, resolving software bugs, introduce new features or enhancements.
-
What is automated Windows patching?
Automated Windows patching involves using IT automation software to automatically detect, download, test, and install updates to reduce the manual workloads, ensure timely and consistent distribution of patches, and minimize human errors associated with manual patching.