Mobile device management (MDM) is a software solution that allows IT teams to control, secure, and manage mobile devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Mobile device management is often a part of unified endpoint management (UEM), which is the practice of managing, monitoring, and securing devices from a single pane of glass. The purpose of MDM is to ensure that team members’ mobile endpoints and the confidential data they contain are used in a safe and secure manner. It also supports BYOD practices, which have gained popularity in recent years.
Why mobile device management is important
The main reason why mobile device management is important is because, without MDM, IT administrators would be unable to thoroughly secure and manage remote devices. According to C Solutions IT, “The use of mobile devices in business has crept up over the years, and now they handle about 80% of the workload in a typical office.” Because remote and hybrid work models were adopted by many companies in recent years, IT teams needed a way for team members to work safely and securely on remote endpoints, and sometimes on their own devices under a BYOD policy.
Remote and hybrid work isn’t going anywhere anytime soon. As a matter of fact, hybrid workforces are often considered the perfect mix between remote and on-premise models, and “the hybrid work model is expected to grow from 42% in 2021 to 81% in 2024.” Whether your organization uses a fully remote or hybrid work environment, you’ll need MDM to keep your remote devices and data safe.
Why MDM security is important for the public sector
No article about the importance of MDM would be complete without discussing its use in the public sector. In an article written by Open Access Government, businesses must consider MDM security to protect their sensitive information from being stolen by hackers. In particular, MDM solution can significantly reduce the risk of:
- Data privacy violations
- Data leaks
- Phishing attacks (or any of the other common types of cyber attacks)
- Mismanaged BYODs
- Malware
MDM in healthcare
Mobile device management is also an important strategy in the healthcare sector. In particular, MDM capabilities help healthcare leaders remain HIPAA compliant, and ensure that users do not share personal health information over an open system.
It is worth noting that most healthcare organizations prefer to work with an all-in-one endpoint management solution that offers HIPAA-compliant cloud backup services as well as MDM tools. This is especially important for healthcare agencies to maintain their data standards.
4 benefits of mobile device management software
Although security is an important function of MDM, this software solution also provides additional advantages for an organization. With effective MDM strategies, you can improve your IT security, efficiency, manageability, and support.
1) Strengthened security
MDM provides an extra layer of security for mobile devices. An organization that uses MDM can take preventative measures against cyberattacks, data leaks, unauthorized access, and more.
2) Enhanced efficiency
With MDM, technicians can easily deploy and manage updates to ensure that all mobile endpoints receive the latest software. This allows mobile device users to function more efficiently than before, thus boosting overall productivity.
3) Increased manageability
No matter where mobile devices are located, technicians can monitor and manage them remotely with MDM. Many MDM providers offer scalable solutions, allowing businesses to increase their remote workforce and manage a growing number of mobile devices with ease.
4) Improved support
Because MDM automates many time-consuming processes, it provides excellent support for IT teams. This reduces the need for IT administration so that technicians can focus their attention on other matters.
Why mobile device management is important for businesses
MDM is beneficial not only from a tech viewpoint but also from a business viewpoint. Because of this, MDM helps multiple departments within a business, not only IT and tech teams.
-
Costs
Since MDM supports the bring your own device (BYOD) practice, organizations with this software can save money and encourage employees to use their own mobile devices. However, even if an organization does not follow the BYOD practice, the cost of MDM is still worth it. It saves resources since it reduces endpoint downtime and ensures that all departments have up-to-date tools and information on their devices.
-
Workflow
The remote workforce grows larger and larger every year, so the number of mobile endpoints that businesses need to manage also increases. MDM gives employees the tools they need to function at peak productivity both inside and outside of the office.
-
Communication
Mobile devices allow teams around the world to communicate and work together. MDM ensures that these devices remain secure for fast and easy communication.
-
Compliance
Organizations that don’t use MDM struggle to keep all their mobile devices in compliance with legal requirements and IT standards. With an MDM solution that uses a single pane of glass display, organizations can ensure that all devices are in compliance from one screen.
How does mobile device management work?
TechTarget has the best in-depth explanation of how mobile device management (MDM) works. They clarify, “Mobile device management relies on endpoint software called an MDM agent and an MDM server that lives in the cloud. IT administrators configure policies through the MDM server’s management console, and the server then pushes those policies over the air to the MDM agent on the device. The agent applies the policies to the device by communicating with application programming interfaces (APIs) built directly into the device operating system.”
Essentially, mobile device management tools function similarly to many remote monitoring and management (RMM) solutions. They use an RMM or MDM agent that’s placed on the endpoint that allows IT teams to control, connect, and communicate with the endpoint.
Many business leaders use trusted endpoint management software, like NinjaOne, to monitor, manage, and secure their mobile devices. With an all-in-one solution, you can quickly and simply manage your mobile devices from your NinjaOne dashboard.
For example, once you open your NinjaOne dashboard, you will see all your managed devices, from your personal computers to your mobile devices.
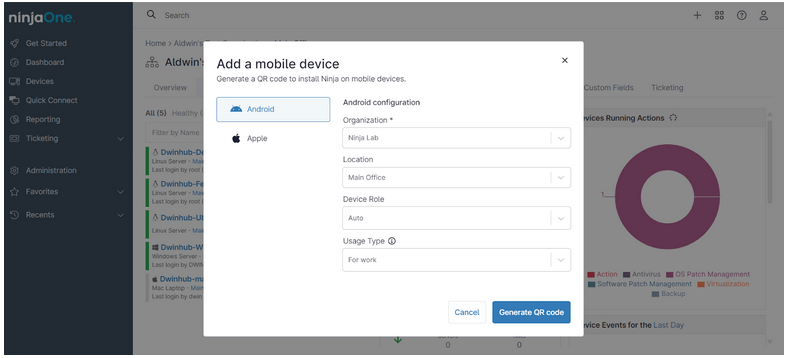
You can then add a new mobile device by pressing the (+) in the upper right corner.
Once you’ve added a mobile device, you should be able to see it on your RMM dashboard.
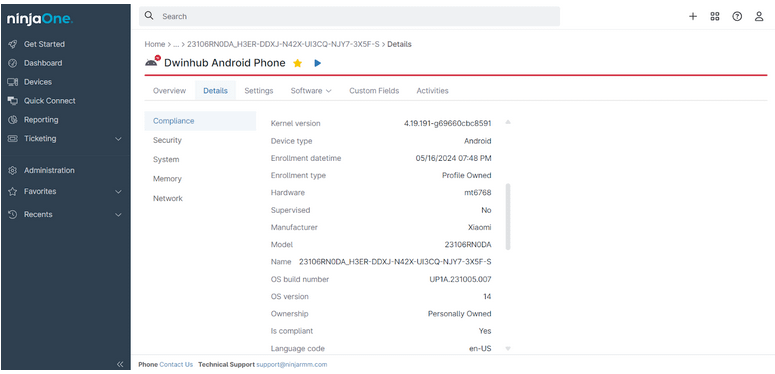
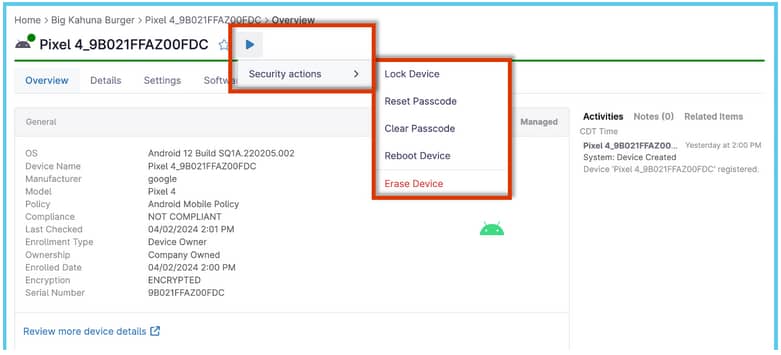
Once on the dashboard, you can see all other details about the mobile device.
What are the main components of mobile device management?
Although MDM’s main purpose is security, it also has many other core functions. The main components of a mobile device management solution are:
- Access management
Access management, or IAM, is an IT security framework that uses policies, tools, and procedures to manage user access within an IT environment.
- Device and application security
Device and application security is critical for protecting an organization’s confidential data from cyber threats.
- Data security
In addition to protecting devices and their applications, it’s also important to safeguard the data itself from theft, damage, or corruption.
- Device tracking
Device tracking helps prevent endpoints from being lost, stolen, or misplaced, which could turn into a serious security issue.
Endpoint monitoring and management enable IT professionals to ensure that devices remain secure, up-to-date, and functioning at peak performance.
IT automation helps IT teams save time and resources by reducing manual workloads and automating tedious tasks.
- Tech support
In today’s world of technology, IT support is more necessary than ever before, and MDM allows IT support teams to troubleshoot and resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
- Content management
Using MDM, organizations are able to securely manage and distribute content across on-premise, remote, or hybrid IT environments.
What information can MDM see from a device?
MDM can gather a lot of information from a device, but it can’t access everything. Information that MDM administrators can access includes the OS version, device model, device health information, device location, applications, network information, and security policies. MDM does not grant access to more personal data, such as personal emails, texts, files photos, browser history, contacts, financial information, et cetera.
The reason MDM is set up this way is so that it benefits both the organization and the device user. The goal of MDM is to protect and manage devices and any data related to an organization or its projects while respecting the device owner’s privacy and personal information.
Bring your own device (BYOD) & mobile device management (MDM)
As mentioned above, MDM is set up in a way that protects and secures devices and organizational data while respecting the device owner’s privacy and personal information. Because of this, MDM goes hand-in-hand with bring your own device (BYOD), which is a practice that allows team members to bring and use their personal devices for work. BYOD not only saves a business’s resources, but it also allows team members to use devices that they are familiar with and comfortable with, so it’s a win-win situation for all.
Mobile device management best practices
1) Automate routine tasks
An MDM should make managing mobile devices an easier and more efficient process, and IT automation is one way to do just that. Automate device updates, reports, and other routine tasks to save time and effort.
2) Follow all security practices
While implementing an MDM solution will contribute to security efforts, IT teams should not forget about other IT security best practices, such as access control protocols and strong passwords. The best way to ensure that devices remain safe and secure is to follow all security best practices while using an MDM tool.
3) Use MDM with BYOD
BYOD policies should be clear and easy for employees to understand. If your organization decides to adopt BYOD, be sure to implement MDM as soon as possible for optimal security.
What is the difference between MDM and RMM?
MDM and RMM are similar software solutions, but they do have some differences. Some of the main differences to remember as you choose a solution include:
MDM vs. RMM functions
The purpose of MDM strategies and solutions is to provide IT leaders with insight into mobile endpoints and allow them to administer devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, to team members. The purpose of RMM strategies and solutions is to provide insight into an entire IT infrastructure (which includes servers, networks, and workstations) and all its assets.
In other words, MDM allows IT teams to administer and manage mobile devices while protecting the data on these mobile endpoints, and RMM allows IT teams to manage and monitor their entire IT portfolio and provide remote support to other team members.
MDM vs. RMM benefits
As mentioned above, MDM improves security, efficiency, compliance, visibility, and IT support. RMM reduces IT costs and complexity while improving visibility, support, efficiency, security, and asset productivity. Since MDM and RMM both provide various benefits for an organization, it’s best to use them together to create a secure and efficient IT infrastructure.
MDM vs. RMM solutions
Now that you know more about MDM and RMM, you’re probably wondering how to choose the best solution for your business. RMM is an essential software solution for organizations and IT teams of all sizes, so it should definitely be on your list of software to purchase. However, since MDM is necessary for the safety and security of mobile endpoints, organizations that use mobile devices should also consider using MDM.
In fact, the way to get the most out of these software solutions is to use them together. With MDM and RMM, you can create a safe and secure IT environment that is also efficient and productive.
Conclusion
Since the usage of mobile devices in the workplace is on the rise, you can expect many more organizations to use MDM solutions in the near future. If your IT team needs a way to manage, control, and secure mobile devices, MDM is currently the best solution on the market. Whether you implement a BYOD policy or use your organization’s own devices, implement MDM to ensure that all mobile devices, and your business’s data, remain in the right hands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why do people use mobile device management?
One of the primary purposes of MDM is to monitor, manage, and protect mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, in a single platform. Besides strengthening the security posture of a company’s IT network, it also enables employees to use their own devices to work more productively and efficiently.
Business leaders use MDM as part of a more comprehensive RMM to manage and secure their various endpoint devices.
2. Is mobile device management worth it?
There is no one answer to this question, as it depends on how you define “it.” MDM is definitely important today, as more workforces become more remote and distributed. Given the ever-evolving cyber landscape, it is important that you use software that can minimize the risk of your devices being infected by malware or other viruses.
Nevertheless, MDM may not be suitable for companies that do not use many mobile devices or follow a BYOD policy. If you use more laptops and servers, it may be a better option to implement an RMM, instead, which typically has MDM capabilities as well.
3. What is an MDM server?
An MDM server is the way IT teams manage mobile devices. Server hosting can be on-premises or cloud-based.