This guide details the steps that are required in the case of re-enrollment after device wipe for Windows devices . It covers re-provisioning for previously enrolled devices in Microsoft Intune and remediation of failed or incomplete onboarding.
MSPs and internal IT administrators need to be able to re-enroll Windows PCs and mobile devices as part of the device lifecycle: often, devices considered lost and subsequently wiped are then found and need to be remotely re-provisioned, or devices need to be re-purposed for new users.
In some cases, devices may need to be freshly provisioned to apply new policies or respond to data loss, malware, or misconfiguration. Being able to do this without having to return hardware to base reduces downtime and manual labor.
Prerequisites for re-enrolling devices in Intune
To manage device enrollment in the endpoint lifecycle, you will need administrator access to Microsoft Intune Admin Center (previously known as Microsoft Endpoint Manager).
To re-enroll a device in Intune after it has been wiped, it must be running Windows 10 or Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, or Education, and have an Intune license assigned to either the device or user. The device must also have been enrolled or eligible for Azure AD Join, Hybrid Join, or Autopilot.
Before wiping any device or removing it from management control, ensure that any important data on it has been backed up as it will not be recoverable.
What happens when you wipe a device in Intune? What is the difference between retire and wipe, and fresh start?
When re-enrolling a device after it has been wiped, keep in mind that Windows Autopilot Reset will retain the device identity and re-apply its configurations, while Intune Fresh Start reinstalls Windows and removes apps (re-enrolling with Intune when the user signs in). Device Wipe removes all user data and configurations (you can elect to retain enrollment and the associated user account, however). Retiring removes data and settings and unmanages the device, but does not factory reset it.
When repurposing hardware, ensure that Azure AD and Intune records are correctly managed to avoid duplication or stale entries.
Wiping a device from Intune and retaining its Autopilot profile
To wipe a device from Intune and retain its Autopilot profile, log into the Microsoft Intune Admin Center and then:
- Navigate to Devices > Windows > All devices
- Select the target device and then click Wipe
- Choose to optionally wipe the device, but keep the enrollment state and the associated user account
- The device will restart and retain only the optional information selected when initiating the wipe
It is critical that you do not retire a device (easily confused with wiping it due to interface similarities) from the Intune Admin Center unless it’s being fully decommissioned, or you will lose management control.
Manual reset on a device using “Reset this PC”
If the Intune wipe action fails or the device is offline, you can manually wipe the device and re-enroll it by following these steps:
- On the Windows device, open the Settings app and navigate to Settings > System > Recovery
- Click Reset this PC and then choose Remove everything (select cloud download or local reinstallation based on whether you want a completely fresh installation of Windows downloaded from Microsoft, or to use files already on the device)
- Once the device has finished resetting, it will either re-trigger Autopilot provisioning or, if this fails, require manual rejoin via Azure AD
To remove devices that have failed to be fully removed from the Intune Admin Center, they can be removed from the specific device pane. Note that many mobile device management (MDM) platforms support automatic remediation of devices that have broken enrolment, rather than requiring manual intervention.
Advanced repair with Registry cleanup for enrollment artifacts
In some cases, device enrollment may be corrupted and needs to be purged manually by deleting information from the Windows Registry. This is done by managing the following keys using the Windows Registry Editor:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Enrollments\
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Enrollments\Status\
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\CloudDomainJoin
Once the relevant registry values have been deleted, the device must be rebooted, and the enrollment process must be triggered by running the following command prompt command:
dsregcmd /join
or, in PowerShell:
Start-Process “C:\Windows\System32\DeviceEnroller.exe” -ArgumentList “/c /AutoEnrollMDM”
This removes stale tokens and resets the enrollment pipeline.
Re-enrollment with Autopilot for post-wipe provisioning
To re-enroll with Autopilot after a device wipe, ensure the device ID is already registered in Autopilot, then:
- Connect the device to the Internet
- The Autopilot profile will be automatically pulled from Intune
- The device will go through Azure AD Join, Intune enrollment, and the ESP (Enrollment Status Page)
- Apps, policies, and scripts will then be re-applied automatically
You can verify success in the Intune interface, or by running dsregcmd /status on the device.
Group Policy and hybrid join for re-enrollment of domain-joined devices
In hybrid environments, post-wipe re-enrollment requires the use of Group Policy and Azure AD Connect.
Confirm that the Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > MDM Group Policy Object is applied to the device, and enable the Automatic MDM enrollment using default Azure AD credentials setting and configure the credentials to use.
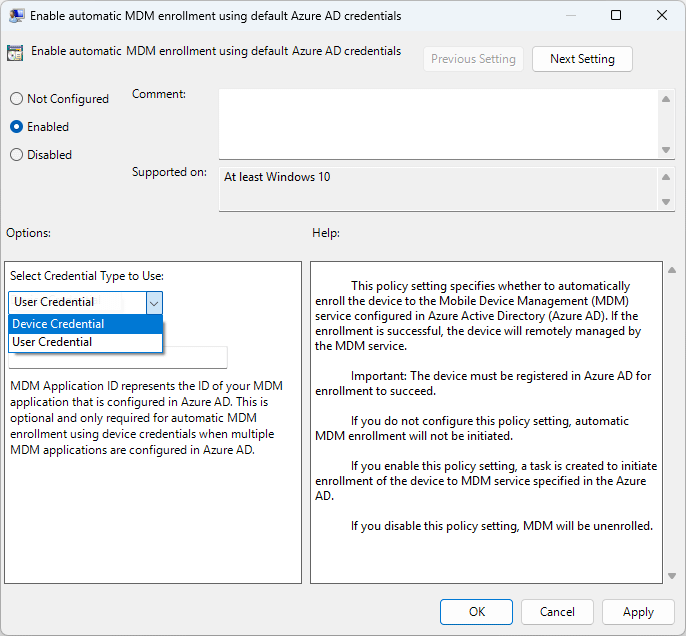
Then, when the device is joined to your Active Directory domain post-wipe, it will be re-enrolled. You can also trigger re-applying Group Policy Objects by running gpupdate /force and rebooting your device.
PowerShell automation for re-enrollment
You can use the following PowerShell commands in your scripts for bulk or remote device re-enrollment, or for self-healing and remediation.
Optionally reset/wipe the device without user approval/intervention by running:
systemreset -factoryreset
Trigger device join with the command:
dsregcmd /join
The following PowerShell command will enroll the device with Intune:
Start-Process “C:\Windows\System32\DeviceEnroller.exe” -ArgumentList “/c /AutoEnrollMDM”
You can use the Microsoft Graph API to verify enrollment:
Get-MgDeviceManagementManagedDevice | Where-Object {$_.DeviceName -eq “Device123”}
Scripting device wipes, re-enrollment, and remediation reduces the need for manual device reconfiguration, and can be automated using MDM and deployment tools.
Device re-enrollment troubleshooting
There are several common steps that you can take to troubleshoot device enrolment after it has been wiped:
| Issue | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Enrollment fails after wipe | Device record still present in Intune | Delete old device from Intune and Azure Active Directory |
| ESP hangs post-reset | App dependency or sync delay | Disable blocking apps or extend timeout |
| Autopilot profile not applied | Device not assigned to dynamic group | Reassign or manually assign profile |
| MDM enrollment token invalid | Registry not cleared | Delete Enrollments and reboot |
When troubleshooting, you can examine the logs located in the Windows Event Viewer at:
Microsoft > Windows > DeviceManagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider
Microsoft > Windows > User Device Registration
You can also find information in the Windows Registry key located at:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Enrollments\
NinjaOne enables and automates Intune remediation and re-enrollment
Mobile Device Management (MDM) by NinjaOne gives you a complete toolset to manage, support, and secure your end user devices. It provides zero-touch enrolment, as well as tools for automating reset scripts for remote devices, clearing broken enrollment states, tracking devices’ enrolment status, and providing centralized reporting and alerting for devices that fall out of management. Devices can be tagged, wiped, and reprovisioned entirely remotely, with role-specific deployment workflows.
For MSPs managing thousands of devices, NinjaOne ensures lifecycle consistency with minimal manual intervention for common tasks such as post-wipe remediation and re-enrollment, allowing you to easily bring devices back under control and maintain compliance and security posture.