Microsoft Edge’s Sleeping Tabs feature helps devices conserve system resources by hibernating inactive tabs. While useful, this feature may unintentionally interrupt critical web apps that need constant activity. To mitigate this, administrators can exclude a site from sleeping tab functions.
This guide walks through different methods to effectively manage the list of sites excluded from Edge’s Sleeping Tabs.
Methods of managing Sleeping Tabs’ exclude site list
Whether you’re tweaking the settings on your own device or rolling out an organizational policy, the five methods below should let you exempt specific websites from the Sleeping Tab features.
📌 Prerequisites: To use any of the methods listed, you will need:
- Microsoft Edge version 88 or above
- Windows 11, or a supported OS
📌 Recommended deployment strategies:
Click to Choose a Method | 💻 Best for Individual Users | 💻💻💻 Best for Enterprises |
| Method 1: Browser Settings | ✓ | |
| Method 2: Registry Editor | ✓ | |
| Method 3: Command Prompt | ✓ | |
| Method 4: PowerShell | ✓ | |
| Method 5: Group Policy Editor | ✓ |
Method 1: Modifying your browser settings
With this method, you can add or remove a website from your list of excluded sites. Modifying your browser settings is relatively straightforward, risk-free, and doesn’t need any special requirements such as administrative privileges.
📌 Use Case: This method is best for users on unmanaged or personal systems.
(A) Adding a website to your exclude list
- Go to edge://settings/system
- Select Performance.
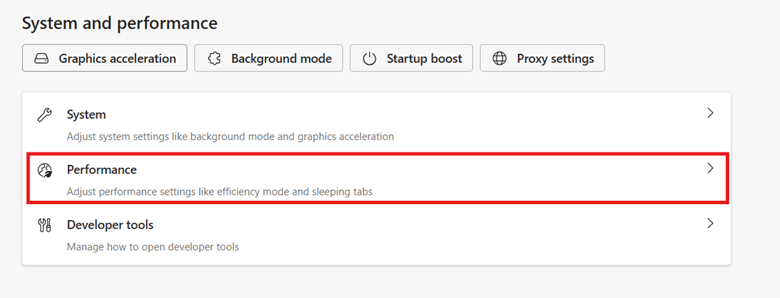
- To add a website to your excluded list, look for Never put these sites to sleep and click the Add button.
- Type in the site URL (e.g., https://intranet.company.local) and click Add.
(B) Removing a website from your exclude list
To remove a website from the list, tap on the three dots beside the site you want to delete and select Remove.
When using this method, all changes will immediately apply.
Method 2: Changing the list using Registry Editor
Using the Registry Editor provides users with a more granular approach to managing Microsoft Edge’s Sleeping Tabs features. With this method, IT administrators can choose between modifying a user’s specific settings or modifying the settings for all users on a device.
📌 Use Cases: Modifying the registry is ideal for:
- Manual configuration for small environments
- Local testing
- Quick fix during support sessions if the Group Policy Editor is unavailable
📌 Prerequisites: You will need administrator privileges for this method to work.
⚠️ Warning: Editing the registry can cause system issues. Create a backup before proceeding. Read more about the potential consequences of registry misconfigurations in the Things to look out for section.
To deploy this method, follow these steps:
- Press Windows key + R, type “regedit”, and tap Enter to open Registry Editor.
- Navigate to your desired path.
- If you’re modifying only for the current user, go to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge.
- For all users, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge.
- If the key is not present, create one.
- Create or edit a String Value (REG_SZ) and name it SleepingTabsExcludeURLs
- Enter URLs separated by commas or semicolons.
- It should look like so: https://intranet/,https://app.local/
- Save your changes and restart Microsoft Edge.
Method 3: Using Command Prompt to edit the list of excluded sites
📌 Use Cases: Using Command Prompt is ideal for administrators applying script-based changes.
📌 Prerequisites: You’ll need administrator privileges to use this method.
To use this method, open Command Prompt as an administrator and execute the following commands:
To set exclusions per user:
reg add “HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge” /v SleepingTabsExcludeURLs /t REG_SZ /d “https://intranet.com/;https://app.local/” /f
For system-wide deployment (all users on a device):
reg add “HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge” /v SleepingTabsExcludeURLs /t REG_SZ /d “https://intranet.com/;https://app.local/” /f
Restart Microsoft Edge after executing these commands to apply changes.
⚠️ Warning: Syntax is important when using Command Prompt. Ensure that your commands are correct before executing them. Read more about potential consequences of incorrect commands in the Things to look out for section.
Method 4: Automating with PowerShell
📌 Use Cases: PowerShell is a great alternative to using the Command Prompt or Registry Editor. It’s also the ideal method for automating this configuration across an organization.
📌 Prerequisites: To use this method, you need to have administrator privileges.
(A) To apply to the current user
New-Item -Path “HKCU:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge” -Force | Out-Null
Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKCU:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge” -Name “SleepingTabsExcludeURLs” -Value “https://intranet.com/;https://app.local/” -Type String
(B) To apply system-wide
New-Item -Path “HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge” -Force | Out-Null
Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge” -Name “SleepingTabsExcludeURLs” -Value “https://intranet.com/;https://app.local/” -Type String
Method 5: Deploying changes via Group Policy Editor
📌 Use Case: The Group Policy Editor is best used for:
- Enterprise-wide deployment with central control
- Standardization of Edge performance behavior across devices
📌 Prerequisites: To use the Group Policy Editor, you will need:
- Administrator privileges
- Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, or Education edition
⚠️ Important: This method will not work on Home editions of Windows 11.
To employ changes via Group Policy Editor:
- Press Win + R, type gpedit.msc, and click OK to open the Group Policy Management Console.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration or User Configuration > Preferences > Windows Settings > Registry.
- Create a new Registry Item:
- Action: Update
- Hive: HKLM or HKCU
- Key Path: Software\Policies\Microsoft\Edge
- Value Name: SleepingTabsExcludeURLs
- Value Type: REG_SZ
- Value Data: URL list separated by semicolons
- Apply GPO to your target users or organizational units.
- Restart Edge to see updated exclusions.
⚠️ Things to look out for
| Risks | Potential Consequences | Reversals |
| Improper URL formatting | The website may not be added to the excluded list, or it may still be affected by the Sleeping Tabs feature. | Remove the incorrect URL and add the correct one. Make sure to include the protocol and trailing slash in the new URL. |
| Not restarting Microsoft Edge | Changes won’t be applied, no matter which method you used. | Simply restart Microsoft Edge to ensure changes are applied. If you’ve restarted Microsoft Edge, but changes have still not been applied, check out possible solutions in the Troubleshooting section. |
| Registry misconfiguration: Configuring the wrong registry path (HKLM vs HKCU) | System instability or policy misapplication | Recover your registry backup or undo the change manually. |
| Using the wrong syntax in the Command Prompt | Policy error | Use reg delete or overwrite with the correct value. |
Other considerations when modifying the excluded list for sleeping tabs
Aside from common issues during deployment, users also need to keep the following points in mind:
Typecase and formatting of URLs
Whichever method you choose to use, be careful of how you format URLs. When adding excluded sites, remember that URLs must be formatted with the protocol and trailing slash to match correctly.
HKLM vs HKCU usage
Most of the methods listed above allow administrators to modify the settings for the current user or all the users on a device. Before making any changes, ensure that you’re using the correct path (especially if you’re modifying the registry). Using HKLM means that you will be modifying the system, while HKCU means modifying the settings for a specific user.
Troubleshooting: Changes aren’t reflecting even after restarting Microsoft Edge
If the excluded list hasn’t been updated even after restarting Edge, ensure that you deployed the steps of your chosen method correctly. First, refer to the Methods of managing the Sleeping Tabs exclude site list and the Things to look out for sections.
💡 Note: If you used the Group Policy Editor to edit the exclude list, you can also force a policy change to update the exclusion list. Do this by running gpupdate /force. In fact, it’s a good practice to use this after a policy change.
If changes still aren’t reflected, there may be conflicting policies within your system or organization.
How do I stop tabs from going to sleep in Edge?
For some users and organizations, having sleeping tabs may not be efficient. In such cases, disabling the Sleeping Tab feature is the way to go.
The fastest way to disable the feature is by modifying the browser settings. Open Microsoft Edge settings, navigate to System and Performance > Performance and find Save resources with sleeping tabs.
Simply toggle the feature off to prevent all tabs from sleeping.
Maximize your resources while browsing with Microsoft Edge Sleeping tabs
The Sleeping Tabs feature is useful, especially for users who need to complete resource-intensive tasks. Modifying your list of excluded websites ensures that critical sites remain active, while resources are conserved elsewhere. With the methods above, both end-users and IT administrators can easily modify the setting as needed.
Related topics:
- How to Enable or Disable “Add Profile” in Microsoft Edge
- How to Enable or Disable Vertical Tabs in Microsoft Edge in Windows 11
- How to Enable or Disable InPrivate Browsing in Microsoft Edge in Windows 11
- How to Enable or Disable Restore Pages Dialog Prompt in Microsoft Edge in Windows 11
- How to Disable Microsoft Edge from Launching at Startup in Windows