This tutorial explains how to restart the explorer.exe process in Windows 10 and Windows 11. This will assist you in troubleshooting system issues (including freezing and slow responsiveness) as Explorer is responsible for displaying on-screen items such as the desktop, taskbar, Start menu, and file explorer windows.
Assist end-users securely with their Windows endpoint troubleshooting.
What you need to know about the Windows File Explorer/explorer.exe before you start
The File Explorer (formerly named Windows Explorer) explorer.exe process is the part of the Windows operating system that handles much of the graphical user interface, including the desktop environment and file manager. Because of this, if it crashes, freezes, or otherwise behaves unexpectedly, it can cause your system to become unresponsive. Restarting the explorer.exe process can resolve this without needing to fully reboot your system. It may also be necessary to restart explorer.exe to apply configuration changes or customizations.
Note that if the explorer.exe process crashes, or you stop it without restarting it, you will not be able to use your Windows PC, as the user interface will not be displayed (only a blank desktop will be shown until a new explorer.exe process is started). While restarting explorer.exe is a common and safe practice, it is still worth ensuring you regularly back up your vital data, as problems with explorer.exe may be a symptom of an underlying system issue or malware infection.
Each of the following methods can be used on its own to restart the explorer.exe process. These will work on any version of Windows 10 or Windows 11, and you should be able to restart explorer.exe without being logged in as an administrator: this is a task that any user should be able to do.
Restart explorer.exe using the Windows Task Manager
To restart the Windows File Explorer from the Windows Task Manager, follow these steps:
- Open the Task Manager by either pressing Ctrl + Alt + Delete and selecting Task Manager, or pressing Ctrl + Shift + Escape
- Select the Processes tab within the Task Manager
- Scroll through the list of processes and locate the Windows Explorer process (despite being renamed the File Explorer, the explorer.exe process is still named Windows Explorer in the Task Manager)
- Right-click the Windows Explorer process in the Task Manager and then click Restart in the context menu
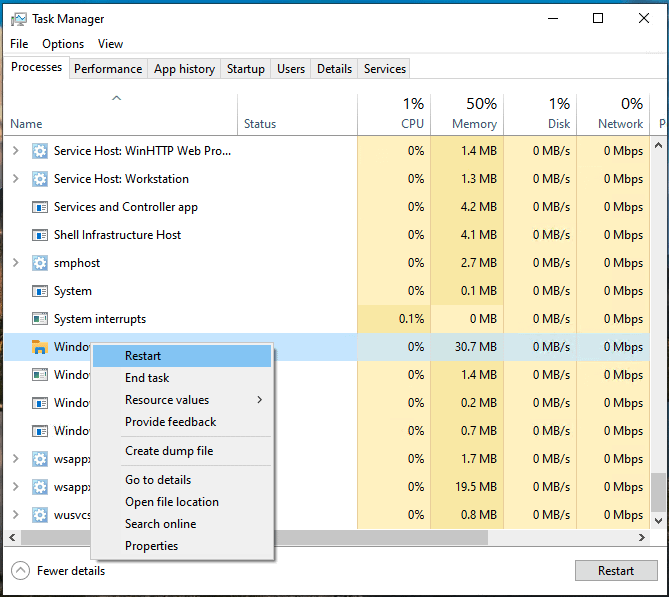
Note that when you restart the Windows File Explorer process, the Start menu, desktop icons, and other user interface elements will temporarily disappear until the process has started again. Any open File Explorer windows will also be closed.
Completely stop and start explorer.exe from the taskbar
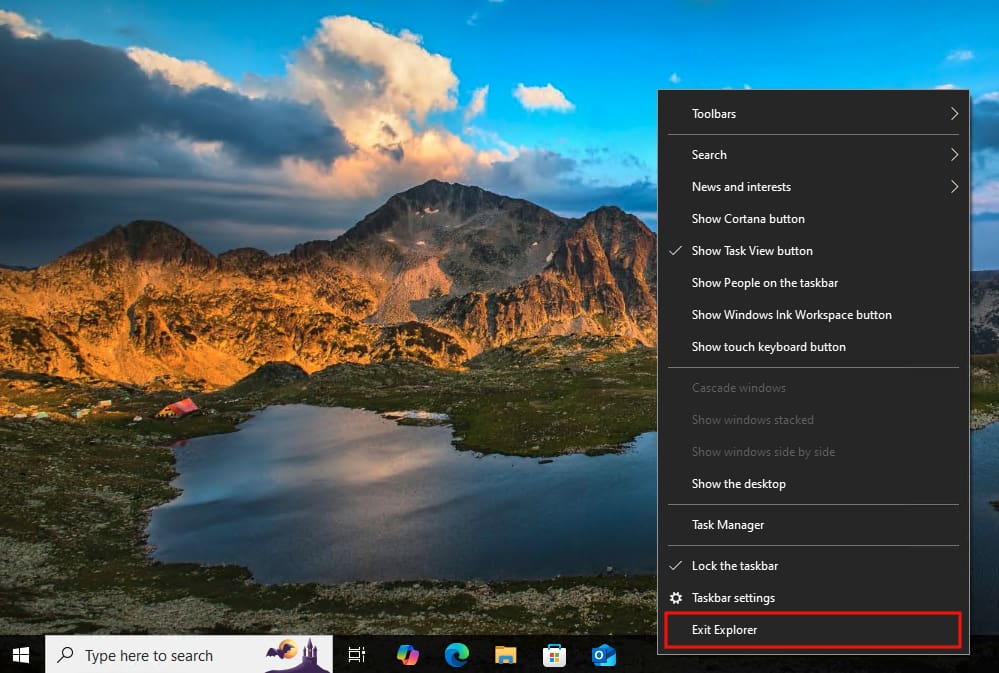
You can stop explorer.exe using the context menu available from the Windows taskbar:
- Hold both the Ctrl and Shift keys while right-clicking on an empty part of the Windows taskbar
- Select Exit Explorer from the context menu that appears
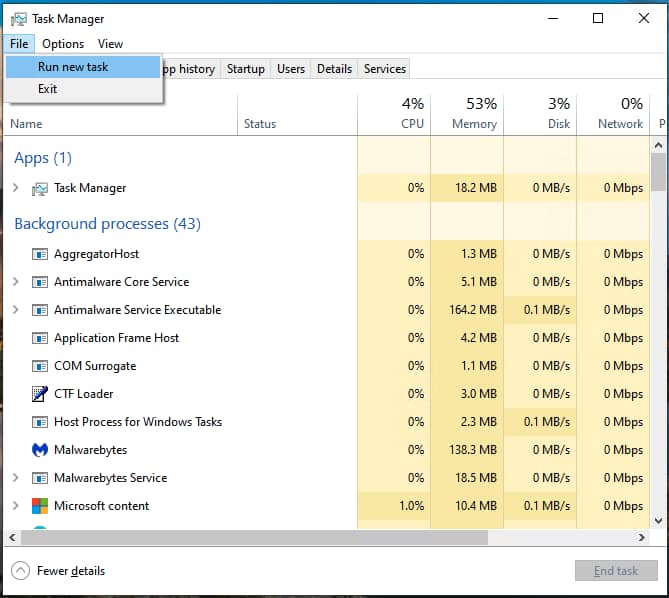
You will then need to manually restart the File Explorer process:
- Open the Task Manager by either pressing Ctrl + Alt + Delete and selecting Task Manager, or pressing Ctrl + Shift + Escape
- Click File > Run new task from the toolbar
- Enter the command explorer.exe and press OK to launch a new File Explorer process
Reset explorer.exe from the Command Prompt or PowerShell
Open the Command Prompt or PowerShell and enter the following command to stop the Windows File Explorer process:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe
Then, enter the following command to restart explorer.exe:
start explorer.exe
You can add both of these commands to a batch script to automate them.
Restart explorer.exe via PowerShell
The following single-line command will only work in PowerShell, and will stop and then restart the explorer.exe process:
Stop-Process -Name explorer -Force; Start-Process explorer
This command can be added to a PowerShell script for automation.
Troubleshooting issues with restarting the Windows File Explorer
If the Windows File Explorer fails to stop or properly relaunch using the above methods, you can try fully rebooting your system. If you continue to have issues with Windows Explorer, you should check for corrupt system files using sfc /scannow, as well as checking for Windows updates and performing a malware scan. You should also evaluate any recently installed software that could be leading to system instability.
Remotely assisting users with Windows File Explorer issues in the enterprise
Without the right tools, helping resolve issues with Windows 10 and Windows 11 PCs can be frustrating for both the end user and support agents.
NinjaOne Remote allows you to manage and control Windows, Mac, and Linux devices so that you can directly help users and diagnose and resolve problems. By delivering tools such as chat, file transfers, and remote terminal sessions, You can ensure that your users’ issues are fully understood and completely resolved—all via industry-standard encrypted remote access from your own desktop or mobile devices.
Automate tasks and ensure uniform policies across your Windows fleet.
Watch a demo or start a free trial of NinjaOne
FAQ
Does restarting explorer.exe affect other programs?
No. Using the above methods will only restart the explorer.exe process.
Is it safe to restart explorer.exe on Windows 10 and Windows 11?
Yes, this is a common troubleshooting method used by IT professionals and regular users.
Can restarting the Windows File Explorer be scripted?
Yes, restarting explorer.exe can be scripted using batch scripts or PowerShell.
What should you do if restarting explorer.exe does not resolve issues?
If the Windows File Explorer fails to relaunch after being restarted, you can manually start it from the Task Manager or Run dialog. You can also try verifying system files from the command line or Windows Recovery Environment.