This guide covers the options you can enable to set a data usage limit in Windows 10 and Windows 11. This will let you reduce the amount of internet data you use, which is especially useful when on mobile connections with high data usage fees. Configuring data usage on Windows also helps performance on slow internet connections by preventing background services from using your connection while you’re trying to work, play, or stream media.
Do more with your Windows endpoint by leveraging NinjaOne.
Start a free trial of the Top-Rated endpoint management
Step-by-step guide to setting data usage limits for Windows 10 and Windows 11
The following settings allow you to control how some of Windows’ features and apps utilize internet bandwidth, allowing you to set limits and reduce the amount of data they use.
Setting a connection as metered
Setting a network connection to metered in Windows 10 and Windows 11 signals to the operating system, as well as some applications, that they should reduce the amount of internet data they use by disabling or reducing some functionality (like automatic updates or online file syncing).
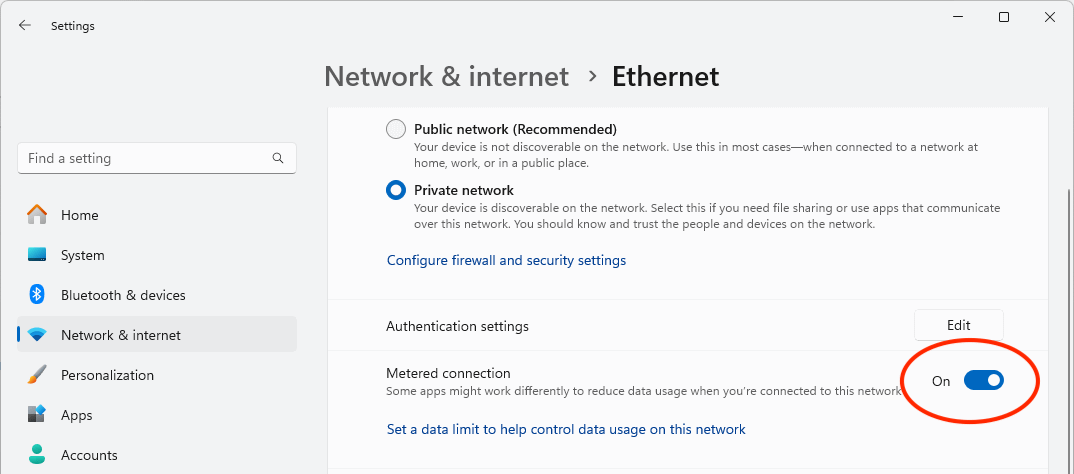
To set your currently connected network as metered, follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start button and select Settings
- Navigate to Network & Internet
- Click Properties next to your network connection
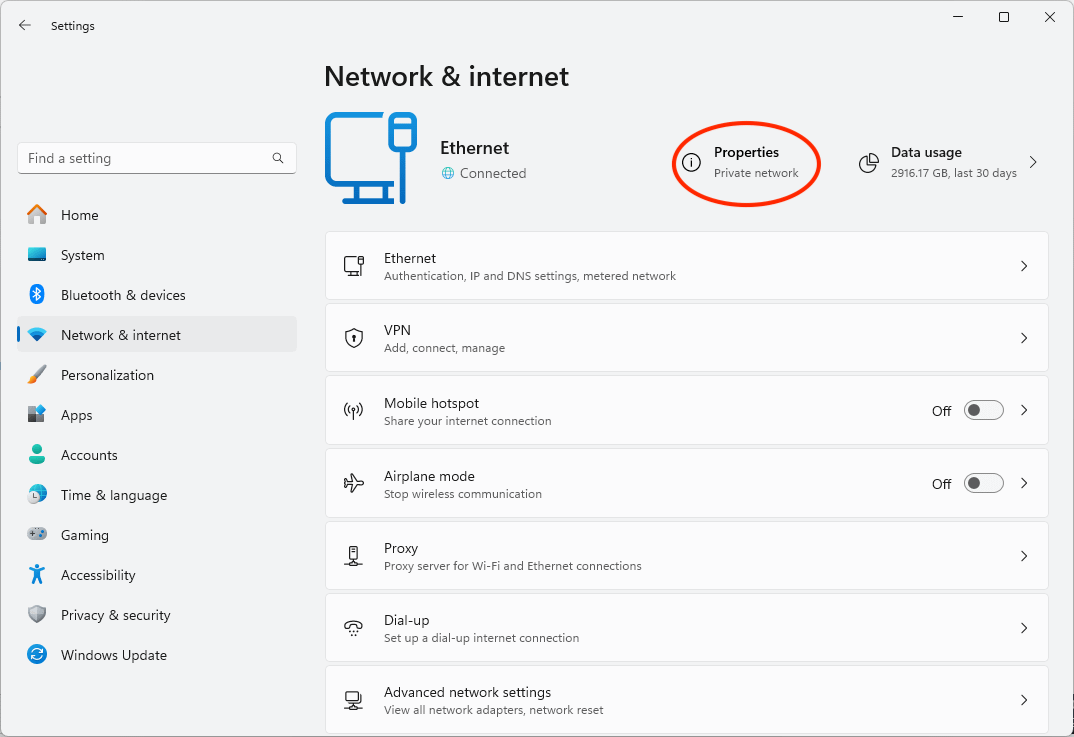
- Toggle Metered connection to On
Setting a data usage limit (data cap)
You can set a data usage limit on metered connections. This will cut off your connection once that limit is reached. This is useful when tethering, and you are approaching your mobile provider’s limit (which can often lead to hefty fees if you go over their limit).
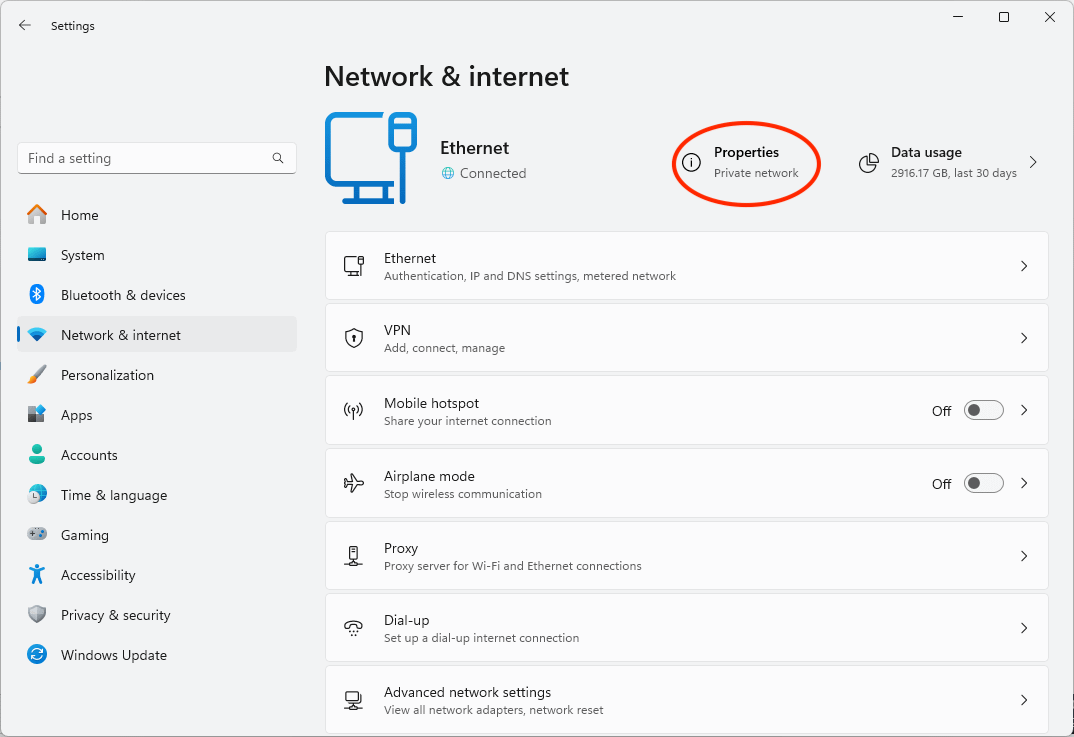
- Navigate back to Network & Internet Settings
- Click on Data usage (next to the Properties button you clicked to change your connection to be metered)
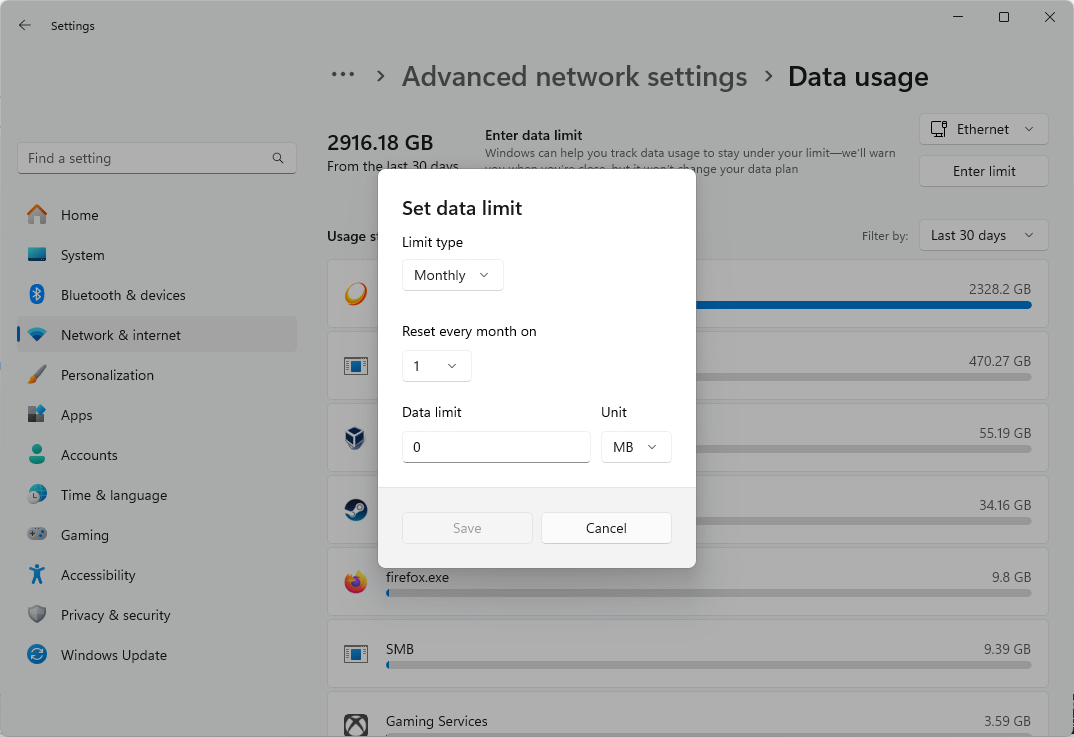
- Select the connection you want to set the data limit for from the dropdown next to Enter data limit
- Click Enter limit to enter a data usage limit
Managing background data for Microsoft Store apps
Apps running in the background may continue to use data without you realizing it. In Windows 10, you can control which apps run in the background by following these steps:
- Open the Settings app
- Navigate to Privacy & Security
- Scroll down to the App permissions section, and click on Background apps
- Toggle Let apps run in the background to Off, or choose which individual apps you do not want to run in the background
The steps differ slightly if you’re using Windows 11:
- Open the Settings app
- Navigate to Apps
- Click on Installed apps
- Find the app you want to restrict from running in the background, click on the options button (…) next to it, and select Advanced options
- Change Let this app run in the background to Never
Temporarily disabling Windows Update
Windows update can download a significant amount of data, and should be disabled if you’re concerned about data usage while traveling. You can disable Windows Update temporarily by following these steps:
- Open the Settings App
- Navigate to Update & Security (Windows 10) or Windows Update (Windows 11)
- Select Pause updates to pause the updates for a week
You can also resume updates or extend the amount of time updates will be paused from this screen.
Note that if you have set your connection to metered, Windows Update will be paused by default.
Disabling Microsoft Store updates
Updating apps from the Microsoft store will also be disabled when your connection is metered. You can also manually disable automatic app updates by following these instructions:
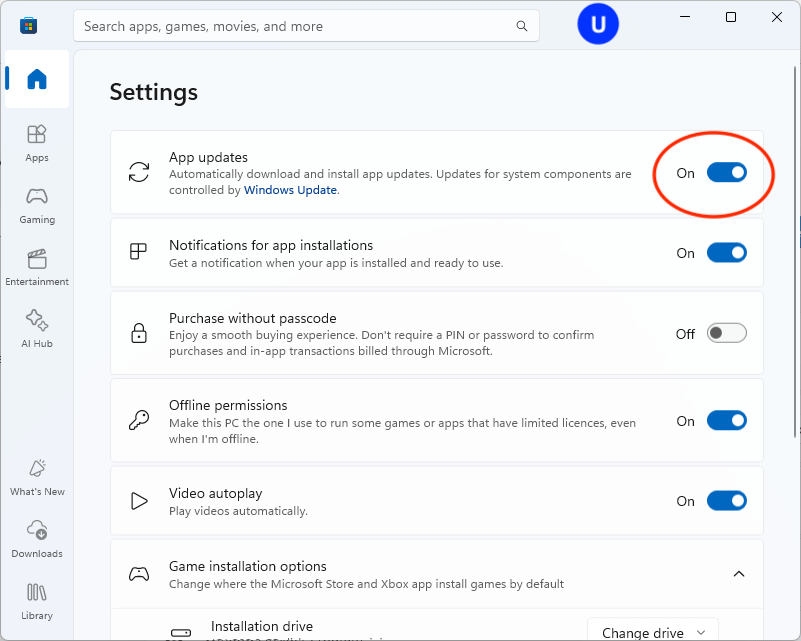
- Open the Microsoft Store from the Start menu
- Click on your user icon at the top right of the window and click Settings
- Toggle App updates to Off
Disabling settings sync
Windows lets you back up your settings online to your Microsoft account. This can be disabled to reduce data usage.
On Windows 10:
- Open Settings app and navigate to Accounts
- Click Sync your settings in the sidebar
- Toggle Sync settings to Off
On Windows 11:
- Open the Settings app and click on Accounts
- Scroll down to Account settings and click on Windows backup
- Click on Remember my preferences and toggle off the preferences that you don’t want to sync online
Pausing OneDrive
Windows pauses OneDrive by default when on a metered connection. You can confirm that this is the case in OneDrive’s settings:
- Open Windows File Explorer
- Right click on OneDrive in the sidebar (there may be more than one if you have multiple accounts configured)
- In the right-click menu, click on OneDrive and then Settings
- Ensure Pause syncing when this device is on a metered network is enabled
Monitoring data usage in Windows 10 and Windows 11
If you notice unexpected data use, you can monitor the bandwidth consumption of Windows features and other apps in Windows 10 and Windows 11:
- Open Network & internet in the Settings app
- Click Data usage
- Scroll through the list of apps to see their usage
- Scroll to the bottom of the list to find the button to reset usage statistics
FAQ
Can I set a limit for mobile hotspots?
Yes, you can set data limits for each internet connection individually. The connection to limit can be specified when setting data limits in the Network & Internet section of the Settings app.
Does the data usage limit reset automatically?
Yes, you can configure the interval the data usage limit resets (for example, by setting a 10GB limit to reset every 30 days if that’s what your mobile carrier provides you).
How accurate is the Windows 10 and Windows 11 data usage tracker?
Windows tracks data usage accurately for the individual device.
Gain a comprehensive observability of your Windows devices.
Learn more about NinjaOne for Windows or watch a demo
Monitoring and managing Windows data usage in enterprise environments
Businesses often look to monitor and limit data usage on Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices to reduce the costs of providing internet connectivity to employees working remotely. Unexpected data usage can also be a sign of malware, or that an employee is misusing company resources.
NinjaOne provides a complete Remote Monitoring and Management platform that gives you deep insights into how your organization’s Windows, Apple, and Android devices are used, including bandwidth usage. You can also deploy policies to control application behavior and reduce bandwidth consumption while monitoring for potential cybersecurity threats.