This step-by-step guide explains how to change Delivery Optimization cache drive for updates in Windows 10 and Windows 11. This allows you to move the location of where Windows Update Delivery Optimization cache files are stored to another drive so you can better manage your disk space. Instructions are included for using both Local Group Policy and the Windows Registry editor.
For a visual version of this guide, watch Change Delivery Optimization Cache Drive For Updates In Windows 10/11
How to change the Delivery Optimization cache folder in Windows 10/11 using the Local Group Policy Editor
The Local Group Policy Editor is accessible only in the Pro, Education, and Enterprise editions of Windows 10 and Windows 11 (if you’re using Windows Home, you’ll need to follow the steps to use the Registry Editor instead, as shown below).
Before you start, you’ll need to be logged in as an administrative user, and create a backup of your Local Group Policy Editor settings so that you can revert your changes if a mistake is made. You should also make sure that the drive you want to move the Windows Update Delivery Optimization cache data to has sufficient space.
Then, follow these steps to change the Delivery Optimization cache drive:
- Right-click on the Start button and select Run
- In the Run dialog, enter the command gpedit.msc and click OK to open the Local Group Policy Editor
- Navigate to Local Computer Policy\Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Delivery Optimization
- Open the Modify Cache Drive setting by double clicking on it
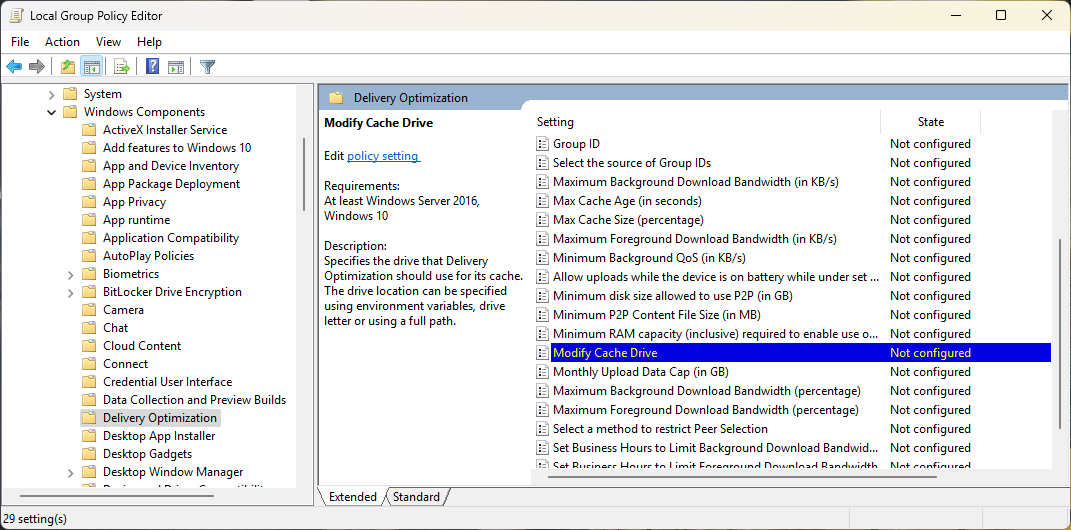
- Change the value of the setting to Enabled
- Enter the path to the new location for the Delivery Optimization cache folder — this can be a drive letter (e.g., D:), a full path to a subdirectory on that drive (e.g., D:\delivery_optimization_cache), or an environment variable (e.g., %SYSTEMDRIVE%)
- To return the Windows Update Delivery Optimization cache to its default location, change the value of the Modify Cache Drive setting to Not configured
- Press OK to save the change

Within the specified path, a new folder named DeliveryOptimization will be automatically created, containing the cache files. If it does not, check that the folder has permissions that will allow the system to read and write to it.
How to move the Delivery Optimization cache drive in Windows 10/11 using the Windows Registry Editor
The Windows Registry Editor is available in all editions of Windows 10 and Windows 11 (including Home). Before you continue, you will need to be logged in as an administrator, and create a backup of your Windows Registry settings so you can restore them if something goes wrong.
Make sure the drive you will move the delivery optimization cache to has sufficient space, and then follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Start button and then click Run
- Copy and paste the command regedit.msc into the Run dialog and press the Enter key to open the Windows Registry Editor
- Find the Registry Key located at Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\DeliveryOptimization (you can copy and paste this path into the navigation bar in the Registry Editor)
- If the DeliveryOptimization key doesn’t exist at this location, navigate to Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows and then select Edit > New > Key from the toolbar and name the new key DeliveryOptimization
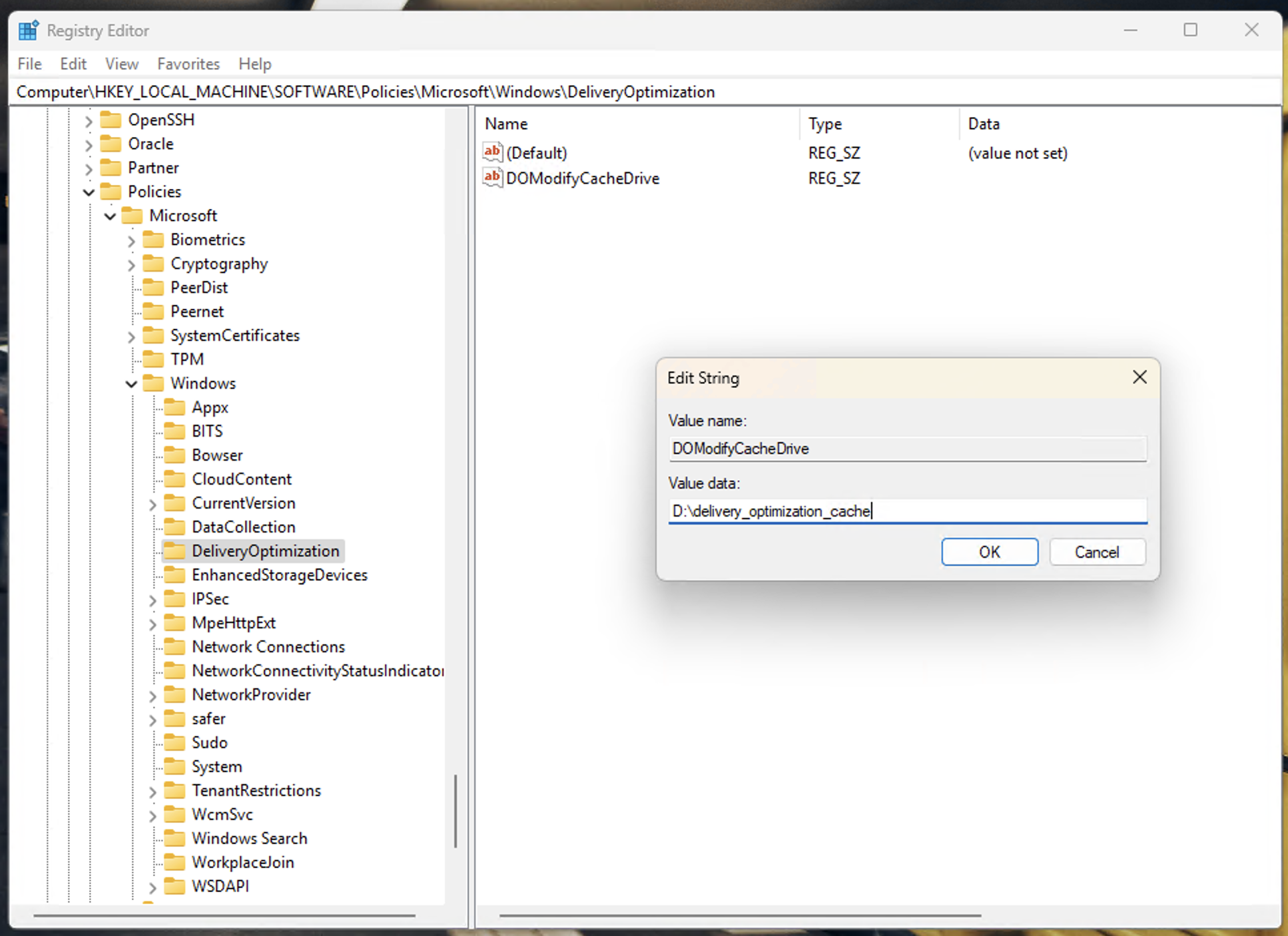
- Within the DeliveryOptimization key, create the value DOModifyCacheDrive if it does not yet exist by selecting Edit > New > String Value from the toolbar
- Double-click on the DOModifyCacheDrive value to edit it
- In the Value data: field, enter the path you want to contain the delivery optimization cache folder: set it to a drive letter (e.g., D:), the path to a subdirectory on that drive (e.g., D:\delivery_optimization_cache), or use an environment variable (e.g., %SYSTEMDRIVE%)
- To restore the delivery optimization cache folder to its default location, delete the DOModifyCacheDrive value by right-clicking on it and selecting Delete
- Press OK to save the change and close the Registry Editor
You will need to reboot your Windows device for changes made in the Registry Editor to take effect. Once your PC has rebooted, a new folder named DeliveryOptimization will be automatically created at the specified path, in which the delivery optimization cache files will now be stored. If the cache folder does not appear at this location, check that the folder has the correct permissions applied.
What is Windows Update Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 and Windows 11?
Windows Update Delivery Optimization is a feature of Windows 10 and Windows 11 that allows your PC to download updates from nearby PCs that have previously installed the same update.
It also allows your device to supply previously downloaded updates to other Windows devices. This is done to speed up the update process and to reduce the amount of internet bandwidth required to keep multiple PCs on the same network up-to-date. Once one Windows PC has downloaded an update, it can be shared with other devices on the same network and doesn’t need to be downloaded from Microsoft’s servers twice.
Delivery Optimization covers Windows Updates, as well as downloads and updates for apps installed from the Microsoft Store. It does not affect updates for applications installed via other methods.
Understanding the Windows Update Delivery Optimization cache
For Delivery Optimization to work, update files need to be stored locally after they have been installed so that other local devices can access them. This is the Delivery Optimization cache, which by default is stored on your system drive (usually C:).
Though they’re only kept for a short duration, cached files can take up a bit of disk space, which can impact the performance and usability of your PC if your primary disk is running low on space. While it’s possible to turn off Delivery Optimization completely, if you have multiple Windows devices (for example, in an office), or a slow or metered internet connection, you may want to move the Delivery Optimization cache folder to a different drive instead.
You can clear the Windows Update Delivery Optimization cache using the built-in Windows Disk Cleanup utility, without having to move the cache or disable the feature.
Managing Windows and Software Updates in Education and Enterprise
Delivery Optimization can greatly speed up the deployment of Windows Updates and Microsoft Store apps in corporate networks by reducing the number of PCs that need to download update files directly from Microsoft’s servers.
Mobile management (MDM) by NinjaOne can further improve the efficiency and speed of update deployments for software not covered by Windows Update Delivery Optimization, and also allows you to test updates before they are widely deployed. This ensures defective updates don’t reach your users, and that compatibility with your other software is ensured before they are installed.
Policies and scripts, including those for managing where Delivery Optimization files are stored, can be centrally managed and rolled out to end-user devices, and remote assistance can be offered to users across Windows 10/11, Apple, Android, and Linux devices.
FAQ
Can I disable Delivery Optimization altogether?
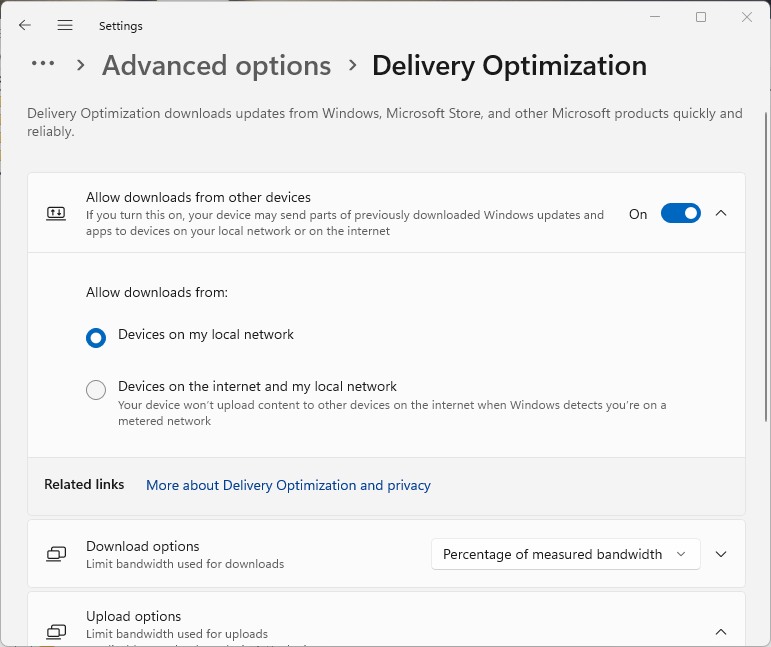
Yes, Windows Update Delivery Optimization can be disabled by opening the Windows Settings app and navigating to Settings > Windows Update > Advanced Options > Delivery Optimization > Allow downloads from other devices (Windows 11) or Settings > Updates & Security > Delivery Optimization > Allow downloads from other PCs (Windows 10) and toggling the option to off.
Does changing the cache drive affect update speed?
No, changing the drive will not impact the speed or behavior of Windows Update Delivery Optimization.
Will the settings persist after a major Windows update?
Yes, the settings to change the Delivery Optimization cache drive should persist after a major Windows update (but will not survive reformatting/completely resetting your system or installing a different version of Windows).
Is it safe to move the Windows delivery optimization cache?
Yes, it is safe to move the delivery optimization cache to a different drive, and there are no negative side effects (other than using space on the specified drive for the cache files).








