As digital payment systems grow more popular, so do the threats against them. If your organization accepts, processes, stores, or transmits credit card data in any form, you must follow a set of security standards known as Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance.
In this comprehensive guide, we discuss what PCI compliance means, why it matters (especially for MSPs with clients in the financial industry), how to become compliant, and what happens if you don’t follow the rules.
What this article will cover:
- What is PCI compliance?
- PCI DSS v.4.0: What’s new and which version should you follow?
- Who must follow PCI compliance?
- Why is PCI compliance important?
- The 7 core principles of PCI DSS
- What is PCI Compliance Certification
- How to become PCI compliant?
- PCI compliance requirements
- PCI compliance checklist
- What happens if you’re not compliant with PCI DSS?
- Benefits of PCI compliance
- Challenges with PCI compliance
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is PCI compliance?
PCI compliance refers to the adherence to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), a set of security standards designed to protect sensitive payment card information during transactions. These standards were established by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), which was founded by major credit card companies such as Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover, and JCB International to ensure the secure handling of cardholder data.
Established in 2006, PCI DSS, or simply PCI, helps maintain account security throughout the entire transaction process, increases control around cardholder data to reduce credit card fraud and improve compliance management.
PCI DSS v.4.0: What’s new and which version should you follow?
PCI DSS 4.0, released in March 2022, is the latest version of the standard. It represents a significant evolution from PCI DSS 3.2.1, as it introduces a more flexible and customized approach to meeting and maintaining compliance. As such, it places a stronger emphasis on continuous security and better addresses modern threats.
You can see all the changes in the official PCI Document Library, but some key changes include:
- Customized validation: Organizations can implement alternative controls to meet security objectives as long as they can justify their effectiveness.
- Expanded authentication requirements: Stronger requirements for multi-factor authentication (MFA) across administrative and remote access points.
- Improved encryption and key management: Tighter controls on how sensitive data is encrypted, stored, and transmitted.
- Enhanced testing frequency: Encourages more frequent testing and real-time security validation.
⚠️ PCI DSS 3.2.1 was officially retired in March 2024. Organizations must comply with 4.0 now.
Who must follow PCI compliance?
PCI compliance is often associated with retail brands or e-commerce businesses, but its scope is much broader.
PCI compliance affects:
- Merchants: This includes any business or organization that accepts card payments, whether that’s online, in-store, over the phone, or through mobile apps. Even small merchants with low transaction volumes must comply with PCI DSS requirements to ensure the security of customer cardholder data.
- Service providers: Companies that store, process, or transmit cardholder data on behalf of others, such as payment processors, data centers, or hosting providers, are considered service providers and must follow PCI standards.
- Managed service providers (MSPs): MSPs that manage the IT infrastructure of clients who handle cardholder data are also subject to PCI DSS requirements. Even if they don’t directly process card payments, they often have access to systems and networks that do, which makes compliance critical.
- IT professionals: Anyone in charge of configuring or managing networks, endpoints, or servers in a payment environment must ensure their systems meet PCI requirements, from firewalls to encryption protocols.
- Software vendors and developers: If you develop point-of-sale (POS) systems, e-commerce platforms, or payment-related applications, you must ensure your software meets PCI DSS requirements. A vulnerability in your software could expose thousands of businesses to risk.
- Third-party payment processors: While many businesses outsource payment handling to third-party services, like Stripe, Square, or PayPal, these providers themselves must maintain PCI compliance. Additionally, merchants who use these services still retain shared responsibility for data protection.
⚠️ It’s worth noting that PCI DSS is an international security standard. This means that it is not limited to any specific country or region and is applied worldwide.
Why is PCI compliance important?
Much has been said about data being the new currency in this digital age. But what about data on currency? The importance of PCI compliance goes far beyond regulatory checkboxes. It helps organizations:
- Safeguard sensitive payment data against breaches and theft.
- Build trust with customers, clients, and partners by showing commitment to data protection.
- Avoid fines and penalties that can be financially devastating.
- Prevent legal consequences and reputational harm from data breaches.
- Improve security posture by aligning with widely accepted best practices.
With the exponential rise in digital transactions, ensuring the security of sensitive cardholder data is paramount. Adhering to PCI compliance prevents data breaches, reduces the risk of financial loss, and bolsters customer trust. Customers are more likely to do business with organizations that prioritize data security.
Furthermore, compliance with PCI DSS is mandatory for any organization that handles cardholder data. One of the standards under PCI is PA-DSS, which ensures that vendors that develop payment applications for third parties do not store sensitive credit card information. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and penalties and the potential loss of the ability to process card payments. Thus, PCI compliance is crucial in maintaining an organization’s reputation, financial stability, and customer relationships.
The 7 core principles of PCI DSS
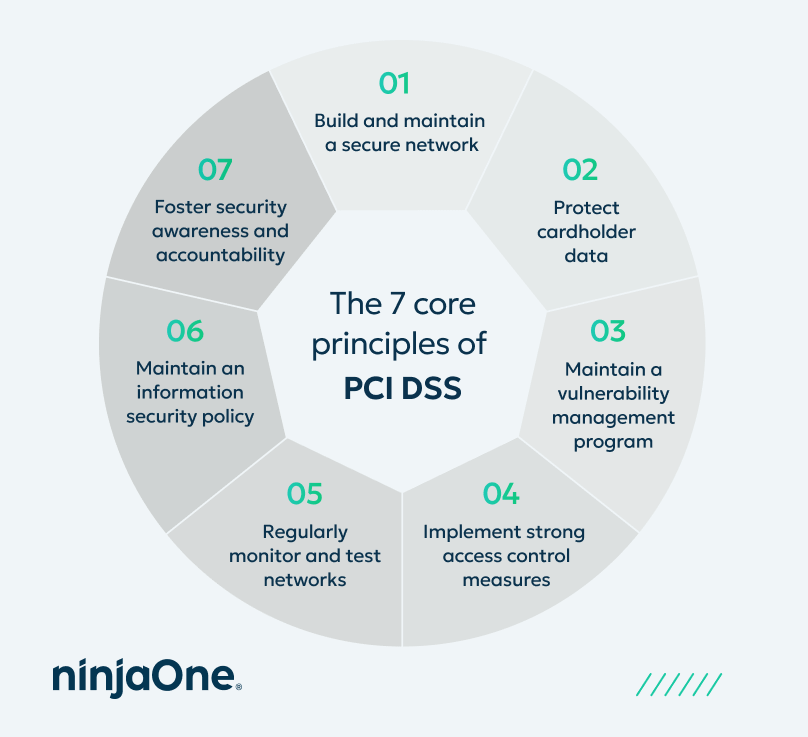
PCI DSS is built on a set of foundational principles that support the development of a secure environment for cardholder data. We’ve listed seven of them.
1. Build and maintain a secure network
Routers and firewall configurations form the first line of defense against cyber criminals. This principle emphasizes preventing unauthorized access to cardholder data environments by securing network entry points and infrastructure.
2. Protect cardholder data
Cardholder data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Protecting this data ensures that even if it is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it cannot be used maliciously.
3. Maintain a vulnerability management program
Regular updates to antivirus software, operating systems, and applications help defend against known threats. A structured approach to vulnerability management minimizes the risk of exploitation due to outdated or unpatched systems. You can also consider a vulnerability management and mitigation tool like NinjaOne to help you quickly identify and resolve endpoint patching issues.
4. Implement strong access control measures
Only authorized personnel should be able to access cardholder data. Access controls should be based on the principle of least privilege, with mechanisms such as role-based permissions in place to limit access.
5. Regularly monitor and test networks
Ongoing monitoring and testing networks help identify potential breaches early. Logging, vulnerability scans, and penetration testing provide visibility and help organizations verify that security controls are functioning as intended. We recommend reading this guide, “Penetration Testing vs Vulnerability Scanning” as an additional resource.
6. Maintain an information security policy
A documented, organization-wide policy sets the tone for a culture of security. This principle requires organizations to formalize and communicate their security practices, roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
7. Foster security awareness and accountability
Security is not just a technical issue—it requires constant vigilantism. Training staff, assigning responsibility, and establishing a chain of accountability ensure that PCI compliance is a shared responsibility across the organization. We recommend checking out this guide, “How to Create a Modern Cybersecurity Strategy for IT Departments”, for more information.
What is PCI Compliance Certification
PCI compliance certification is a validation provided by an external auditor that your business complies with the PCI DSS standard. The certification process involves an assessment of your business’s network and systems, policies, procedures, and other relevant areas. Upon completing this assessment, your business receives a certificate of compliance.
PCI compliance requirements
PCI DSS comprises 12 requirements for managing customer payment card information that can be organized into six control objectives:
1) Build and Maintain a Secure Network and Systems:
1.1. Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data.
1.2. Do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters.
2) Protect Cardholder Data:
2.1. Protect stored cardholder data.
2.2. Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks.
3) Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program:
3.1. Protect all systems against malware and regularly update antivirus software or programs.
3.2. Develop and maintain secure systems and applications.
4) Implement Strong Access Control Measures:
4.1. Restrict access to cardholder data by business need-to-know.
4.2. Identify and authenticate access to system components.
4.3. Restrict physical access to cardholder data.
5) Regularly Monitor and Test Networks:
5.1. Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data.
5.2. Regularly test security systems and processes.
6) Maintain an Information Security Policy:
6.1. Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel.
PCI compliance checklist
We’ve created a checklist to help you achieve PCI compliance. We’ve organized it into key phrases, covering all technical, administrative, and procedural requirements. While not exhaustive, it should serve as a great jumping-off point for your MSP.
- Scoping and discovery
- Identify where cardholder data is received, processed, stored, and transmitted
- Document all systems, devices, and personnel involved in handling cardholder data
- Determine compliance requirements
- Identify your PCI DSS merchant level based on transaction volume
- Determine which Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) applies to your organization
- Engage a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) if required
- Schedule vulnerability scans with an Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV), if applicable
- Implement security controls
- Install and maintain firewalls to protect cardholder data
- Encrypt cardholder data during transmission across open or public networks
- Store cardholder data securely and limit storage duration
- Deploy and maintain anti-malware and antivirus solutions
- Keep all systems and applications up to date with patches
- Restrict access to cardholder data on a “need to know” basis
- Monitoring and testing
- Track and log all access to network resources and cardholder data
- Monitor logs daily for anomalies or unauthorized access
- Conduct regular penetration tests and vulnerability scans
- Test security systems and processes at least quarterly
- Policy and training
- Create a formal information security policy and review it annually
- Train employees and contractors on PCI DSS responsibilities and security awareness
- Maintain documented procedures for incident response. We’ve created an MSP Ransomware Response Planning Checklist if you want a more in-depth discussion.
- Assign personnel to oversee compliance responsibilities
- Validation and reporting
- Complete and submit the applicable Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ)
- Retain compliance documentation and scan results for audit purposes
- Schedule annual reviews and re-assessments to maintain compliance
What happens if you’re not compliant with PCI DSS?
Noncompliance with PCI can lead to:
- Fines and penalties: Non-compliant organizations may face hefty fines that can reach hundreds of millions of dollars, depending on their size, the number of customers affected, and the length and degree of non-compliance.
- Increased transaction fees: Payment processors may impose higher transaction fees on businesses that are not PCI-compliant. These fees are a way for banks to offset the increased risk of dealing with non-compliant merchants.
- Reputation damage: A publicized security breach can severely damage your brand reputation and erode customer trust. Customers are more likely to abandon companies that fail to protect their personal and financial information.
Benefits of PCI compliance
Enhanced security
PCI compliance provides enhanced security by setting strict standards that help businesses protect their customer’s data. It ensures that businesses have the necessary safeguards to prevent data breaches, maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
Customer trust
A PCI-compliant business shows customers that their data is taken seriously and handled securely. This builds trust, vital for customer retention and loyalty, and can lead to increased business over time.
Avoidance of penalties
Non-compliance with PCI standards can result in substantial fines and penalties from payment card providers. By being PCI compliant, businesses can avoid these financial pitfalls, ensuring uninterrupted operations and financial stability.
Competitive advantage
In a competitive marketplace, being PCI compliant can provide a significant edge. Customers who are aware of data security will prefer to do business with a company that is PCI compliant, thereby potentially attracting more customers and increasing market share.
Regulatory compliance
PCI compliance ensures that businesses align with regulations set forth by governmental and regulatory bodies. This can prevent potential legal issues and aid in smoother business operations, contributing to the organization’s overall success.
Challenges with PCI compliance
Complexity
The PCI DSS framework includes hundreds of technical and administrative requirements. Even with the checklist we created and detailed above, it can still be overwhelming. Understanding which requirements apply and how to properly implement them can require extensive planning.
Resource limitations
Smaller businesses may lack the financial and personnel resources to dedicate to PCI compliance. To remain compliant, you may need to hire several consultants and invest in security tools, which can be costly.
Changing environments
IT environments are rarely static, so we can’t expect compliance standards to remain so as well. Cloud migrations, new applications, and shifting architectures can all expand and change PCO scope. The changes demand continuous monitoring and re-evaluation to ensure compliance isn’t accidentally violated.
Third-party risks
Many organizations rely on vendors and service providers to manage parts of their cardholder data environment. It’s crucial you know that your vendor is also PCI-compliant to reduce the risk of breaches. There is a misconception that outsourcing payment processing fully transfers PCI responsibilities to the provider. In reality, merchants are still responsible for ensuring that cardholder data is protected throughout their environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is PCI compliance required by law?
No, PCI DSS is not a law, but it is mandated by major credit card brands and enforced by acquiring banks and payment processors. Failure to comply can still lead to significant financial and operational penalties.
- How often do I need to validate PCI compliance?
Validation requirements depend on your merchant level. Higher levels must conduct quarterly network scans by an ASV and an annual audit.
- Does using a third-party processor make me PCI-compliant?
No. While using a PCI-compliant third-party processor may reduce your PCI score, it does not eliminate your company’s personal responsibility. You still must ensure your systems and practices meet applicable PCI DSS requirements.
- Do small businesses need to comply with PCI DSS?
Yes. All businesses that accept credit card payments, regardless of size or volume, must comply with PCI DSS.
- What is the difference between PCI DSS 3.2.1 and PCI DSS 4.0?
PCI DSS 4.0 introduces a more flexible, risk-based approach. It allows organizations to use customized security strategies to meet their PCI objectives.
The value of PCI compliance
PCI compliance is crucial to running any business with credit card transactions. It ensures the secure handling of sensitive information, protects against potential financial losses, and enhances customer trust. While achieving compliance might seem daunting, the benefits far outweigh the effort. Businesses should view PCI compliance as not a burden but an essential component of their overall business strategy.

