Remote access is a means to extend network accessibility by establishing a connection over a server. It allows users to manage and view the system from remote locations when they’re not able to connect physically. In short, remote access allows users to access their systems and IT infrastructure just by using an internet connection or telecommunication protocol. Remote access is essential for IT departments who work remotely or manage multiple locations, as well as MSPs who manage a variety of clients.
What is remote access?
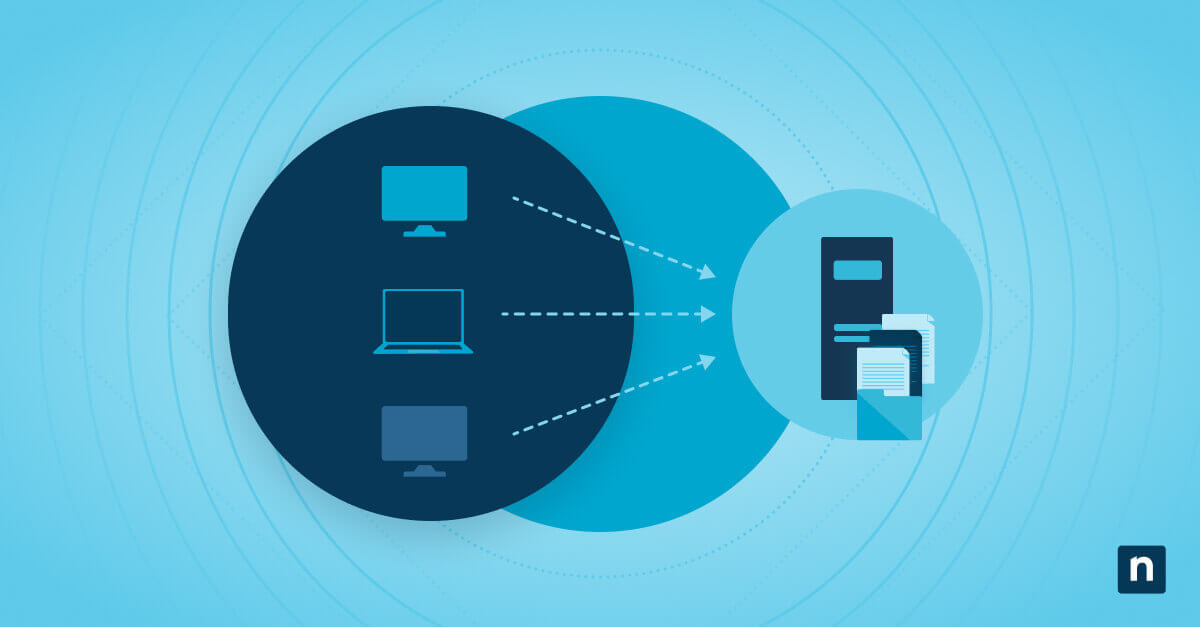
Remote access is a method of connecting to IT services, applications, or data from a location other than where that asset is kept. This connection allows users to access a network or computer remotely via the internet or other means — i.e. to make changes to a server while outside the physical location of the hardware.
Remote access allows for the monitoring, maintenance, and control of devices as long as they are connected to the same network. This empowers IT professionals to troubleshoot issues without being in the same physical location as the device or system with the problem.
Remote access can also be used to access files without having them sent via email or other means. Remote access tools allow users to define who has the rights to files and folders, as well as organize users into different categories for setting group access privileges.
Remote access plays a key role in many business continuity plans and disaster recovery strategies as well. In the event that office staff are displaced from their usual workplace due to natural disasters or other circumstances, these employees can continue to work from home. For this reason, remote access also makes life easier for vendors and contractors, both inside and outside of disaster recovery scenarios.
How does remote access work?
Remote access is typically achieved through a combination of hardware and software working in tune with a network connection. Many years ago (before the advent of the modern internet) remote access was available through terminal simulations managed using a hardware modem linked to a telephone network.
These days, secured remote access is usually provided by secure software called VPN, or Virtual Private Network. It is used to communicate between hosts via a wired interface network or an internet/wi-fi connection.
Using remote access, a cloud VPN can connect any number of private networks to the VPN server. This allows outside users (such as remote workers) to connect to the primary network using security protocols that encrypt data traffic before it reaches the destination over the internet.
In this and other use cases, the organization can employ a remote desktop so the user can link the network and applications remotely. Remote desktop software is integrated into the operating system of the remote host and allows the applications to execute in a remote method on a network server. In turn, the user can safely use cloud applications from any location on any device, further protecting their activity with different authentication techniques depending on the network configuration.
What are the benefits of remote access?
There are numerous benefits that remote access provides for businesses, especially since remote and hybrid workforces have grown considerably in recent years. When properly implemented, remote access will:
-
Increase productivity
When employees are able to work from any location and at any time, they are able to increase productivity and efficiency.
-
Improve employee satisfaction
With remote access, employees gain more flexibility over their work environment and devices, which leads to greater employee satisfaction.
-
Reduce costs
Remote access allows businesses to support remote and hybrid workforces, thus reducing the need for expenses such as offices, facility equipment, and even travel. Although the remote access tools themselves have a cost, it’s much lower than the various expenses companies pay without it.
-
Strengthen security
When implemented properly, remote access helps IT teams detect and remediate threats quickly and efficiently, so it becomes an asset to security efforts rather than a hindrance.
What are the risks associated with remote access?
While there are many benefits of remote access, it does come with some risk. Remote access, by its very nature, can be an entry point for cyber threats. Many threats and vulnerabilities emerge when two devices are connected remotely. That said, using the right endpoint protection methods, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and security software will go a long way toward making remote access a safe way to connect two devices.
These layered security tools will help eliminate the risk of intrusions from threats like Trojans. These malicious attacks can easily get from one device to another undetected because they often appear harmless. Likewise, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) can gain access to a machine and provide control to a threat actor outside of the network. They can then gain access to files and typically will gain complete control of the device.
As in most cases, users will also need to be careful that malicious files and viruses aren’t spread accidentally through files sent from one computer to the other. It’s common for ransomware, spyware, and other malware to spread this way; once the threat is disseminated, it can be very difficult to contain.
Types of remote access and remote access protocols
Although there are many different remote access protocols, you’ll find that three types of remote access are most common:
- Virtual private network (VPN)
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- Virtual network computing (VNC)
VPNs, VNCs, and RDPs allow users to gain access and have full control over a computer or other device via a remote network, while most other protocols place limitations on how much can be done via remote.
-
Virtual Private Network
A VPN provides users with the ability to send and receive data between devices or via a private network that is extended over a public network. This method requires both computers to be connected to the same VPN and use the same access software.
-
Remote Desktop Protocol
RDP is a Microsoft program that provides a graphical interface to connect with another computer via a network connection. The user simply runs the RDP client software to connect to another computer running the RDP software.
-
Virtual Network Computing
VNC provides a graphical system for sharing desktops between users. This is useful when one user, such as an IT helpdesk agent, needs to take control of another user’s computer as if it’s their own. This allows the remote user to control everything as if they were the one sitting at the keyboard while also allowing the local user to see what they are doing on their own screen.
-
Internet Proxy Servers
Internet proxy servers add a server as a go-between, allowing users to connect with another computer within the proxy server environment. Both computers connect to the same proxy server serving as an intermediary, at which point one user can gain access to the other’s computer.
-
Other Types of Remote Access
Different methods of remote access allow for different levels of control and data sharing. The following methods are types of remote access with limited (often very limited) permissions:
- Cellular internet service is a type of data sharing wherein a wireless connection is created between mobile devices
- Cable broadband users typically share bandwidth with other users, even to the point that their home router also serves as a public wifi hotspot for the provider
- A digital subscriber line (DSL) uses a telephone network to share data
- Local-area network/wide-area network (LAN/WAN) involves creating an encrypted network that connects users who sign in to it
- Vendor privileged access management (VPAM) is a network-sharing protocol controlled by an outside vendor that limits connection privileges
- Various desktop-sharing software/tools allow users to share their desktop with several other people at once
- Private access management (PAM) limits remote user access to certain files and apps on a network
Remote access best practices for keeping your network secure
Regardless of the protocol used, it is important to remember that your computer will be exposed to outside users when using remote access or remote management. The open doorway for file transfers allows not only for snooping or data theft but the possibilities for the transfer of malware can increase exponentially. To help alleviate this increased risk, here are several remote access best practices to ensure security and IT stability.
- Use an endpoint protection solution: Endpoint security software will make sure each device participating in the remote connection is safe. Endpoint protection measures can include several layers of security, including firewall, antivirus, and even password management functions.
- Always use a secure connection: Public wifi can be an open invitation to intruders. A secure, trusted connection should always be used to create a direct link that excludes unauthorized users.
- Password hygiene: Use strong passwords with at least ten characters and a combination of numbers, symbols, and letters. Change your passwords regularly and do not reuse passwords between applications.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever you can: Multi-factor authentication, most often a system that verifies your identity using a text message, adds an extra layer a hacker would need to negotiate to gain access. You can set up MFA for Office 365 and other tools that might contain important data.
- Set up account lockout policies: Entering the wrong password a certain number of times should bar them from trying to connect again. This measure helps defend against brute force attacks and password-cracking tools.
- Stay on top of patches: Keeping your software updated will keep your computer safe from malicious viruses or malware that is designed to exploit known vulnerabilities. Patch management is a key part of all cybersecurity plans.
- Limit use of the service: The more users are allowed to use the remote access tools, the more risk. Limit usage of remote access only to users who need it to perform their jobs. Always remove old, unnecessary user access privileges as quickly as possible.
Conclusion
Remote access can give you the means to connect to another person’s computer and use it as if you were sitting in front of it yourself. It can also allow for file sharing between computers and facilitates quick, seamless troubleshooting for remote IT professionals.
Various remote access protocols — such as a virtual private network (VPN), virtual network computing (VNC), or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) — make these connections possible. While there are native security features in most types of access software, the very act of directly connecting two devices creates new security challenges that must be addressed.
It is critical to put advanced security measures in place whenever you use remote access. Some best practices include encryption, strong passwords, MFA, and limiting the number of users who can use the service. It’s also recommended that you use purpose-built endpoint security software like NinjaOne to harden your entire IT environment against intrusion. NinjaOne is a complete suite for remote monitoring and management at scale, and its included security features ensure that you can get the most from remote access without sacrificing your safety.