Looking to launch or improve your MSP sales process for 2024? This guide covers examples and tips that will give you a massive jumpstart.
On the face of it, now is a great time to be an MSP. The MSP market continues to grow every year — it’s expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.4% from 2022 to 2030 according to Grand View Research. That means plenty of new business and sales opportunities, right? Maybe. But for who?
Even though the market is growing, it’s also becoming more competitive. Without a defined and structured sales process, opportunities have a tendency to remain ad hoc at best and, at worst, slip through the cracks. Additionally, MSPs can miss out on chances to make iterative improvements by defining exactly what is and isn’t working, and then adjusting their approaches accordingly. This post will provide a detailed overview of what a structured MSP sales process looks like along with tips for optimizing your operations so that you can start winning more deals.
What does the MSP sales process look like? 4 Steps
Today, businesses never purchase anything on a whim. Instead, they follow a straightforward process to ensure that they receive the product or service they require. A simplified MSP sales process includes these four steps:
1) Lead generation
Lead generation is the process of attracting potential customers to your business. Marketing efforts contribute significantly to this step by making leads aware of and interested in your services. Leads can be captured by prospects coming to your website and filling out a form, receiving registration lists for virtual or in-person events, conducting your own research via platforms like LinkedIn, or by purchasing lead lists.
See our post “19 MSP Lead Generation Ideas that Don’t Require Being In-Person” to start building up your list.
2) Lead qualification
Qualification is the process of ensuring that leads can become potential customers. Good leads are interested in a business’s services and are in a position to actually purchase, while poor leads have little to no interest in a business or are unable to sign up for its services. For example, poor leads could be businesses that are located outside of your service area, or small businesses that are under your minimum required number of seats. To ensure that you don’t spend your time and money chasing poor leads, it’s best to qualify prospects using a lead qualification tool as early as possible in the sales process.
3) Discovery and demonstration
The purpose of this step is to assess the prospect’s needs and map them to how your services can improve their business.
In addition to collecting basic technical information about their environment, during this step, it’s also important to ask the prospect to reaffirm their pain points and encourage them to connect their own dots between the business impact of those pain points and the corresponding value your solution is going to provide.
This will help you pave the way for establishing a budget while confirming that your price range and the prospect’s expectations are in the same ballpark.
4) Deal
The final step in a MSP sales process is to close the deal. In this step, you present a detailed proposal outlining your services, including billing terms and your managed services agreement.
Every interaction you have with a prospect during your sales process needs to be tightly focused on progressing them from one stage to the next. Otherwise, you’ll either find yourself wasting your time or leaving unnecessary openings for the prospect to have uncertainty and doubt and shop elsewhere.
Speaking of time…
How long should an MSP sales process take?
How many steps and how long this takes will vary. It can depend a lot on the types of clients you’re dealing with, the number of decision-makers, red tape, etc.
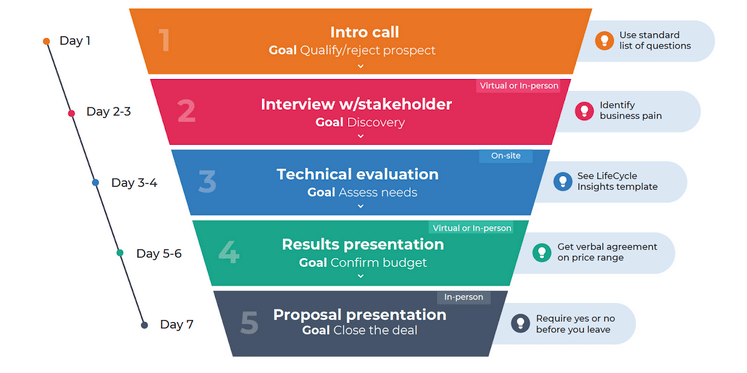
For instance, selling a mom-and-pop shop is going to be faster and way less convoluted than selling a medium-sized healthcare provider or large enterprise. That said, for many SMB clients, the magic number you should shoot for is completing the entire sales cycle — from first touch to quote — in 7-10 days.
Example of an MSP sales process
Benefits of having a consistent, documented sales process
Without a clear sales process, members of a sales department can feel lost or confused. A guide that clearly maps out the sales process provides valuable guidance for new and existing salespeople. As your sales department evolves, the sales process will also evolve and adapt, so it’s never set in stone.
It gets you organized as a business
Without a clear sales process, your efforts will be ad-hoc and quick to fall by the wayside the moment the next fire erupts needing your attention. It’s also a clear prerequisite to hiring and quickly onboarding salespeople.
It holds you accountable
As with your other SOPs, when reviewing performance it allows you to ask the simple question, “Did we follow the process?”
It helps you develop a baseline
Once you discover your typical conversation rates and sales cycle timelines, that gives you something to test improvements against and allows you to budget your sales and marketing spend accordingly.
It helps you identify bottlenecks
Regularly reviewing metrics can help you spot where in the funnel your process is stalling so that you can make adjustments to future cadences.
4 key MSP sales strategies and tips
1) Respond to lead interest early and often
Many times you can get a leg up on the competition simply by being quick to respond to inquiries. How quick do you need to be? According to InsideSales, the likelihood of contacting the lead drops 10x after the first 5 minutes.
That means developing automation around responding to form fills and “contact us” submissions is critical. If you don’t have a CRM, you may want to consider looking into CRM options geared toward SMBs and MSPs.
But what if you reach out and the lead doesn’t pick up or respond? How quickly and often should you try reaching out again?
InsideSales has stats to help guide your approach here, too.
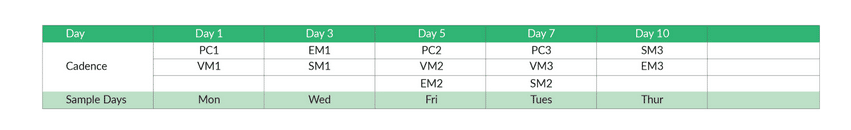
According to their research, an optimal cadence for inbound leads:
- Starts with a phone call that’s made as quickly as possible after the lead makes initial contact (downloads an eBook, fills out a form, etc.).
- Includes leaving voicemails — over 66% of business professionals are likely to respond to voicemails!
- Includes about 10 touches over 10 days, as shown by the graph below:
- PC = phone call + VM = voicemail (3)
- EM = email (3)
- SM = social media (3) — ex: LinkedIn InMail
- Total touches = 9
Their suggested cadence for outbound leads (cold leads who haven’t had any interaction with you) varies slightly and can be found in our post “MSP Sales Cadence Stats: When and How Often to Reach Out to Leads.”
At first glance, that can seem like a lot of touches, but the numbers don’t lie — the chance of making contact with a lead doubles (from under 10% to over 25%) if you use three different contact methods rather than just one.
Hence the suggestion for reaching out via phone calls, emails, and social media. Obviously, the more automated you can make this process using sales tools like a CRM, the better.
2) Disqualify bad-fit leads quickly
The only thing worse than losing out on a good lead is wasting time on a lead you never should have been talking with in the first place. Make it a priority to review your qualification criteria to ensure you’re asking the right questions and filter out bad fits as early on in your process as possible.
You can accomplish that by asking for things like location and number of employees on your web forms, or even using auto-responder emails to provide additional questions or prompts. The responses can help you prioritize your outreach accordingly.
3) Avoid the race to the bottom on price
Competition in the MSP world is on the rise, and being underbid by low-quality providers is unfortunately a scenario many owners are facing more and more often. It can be tempting to match prices when you’re in the midst of a bake-off, but it’s important to understand your costs and know your breaking point. As Lifecycle Insights founder Alex Farling puts it, “There will always be someone that’s willing to go into bankruptcy faster than you.” Don’t follow them down that path.
4) Make your offer stand out
While you should avoid dropping your prices to the bare minimum, that doesn’t mean you can’t use incentives (such as offering the first month free) to make your offer stand out. You should also mention what makes your business or services different from, or better than, your competitors. Keep in mind the goal of this is not to put down your competitors, but simply to mention how your services can better serve the potential client.
FAQs
What is MSP in business?
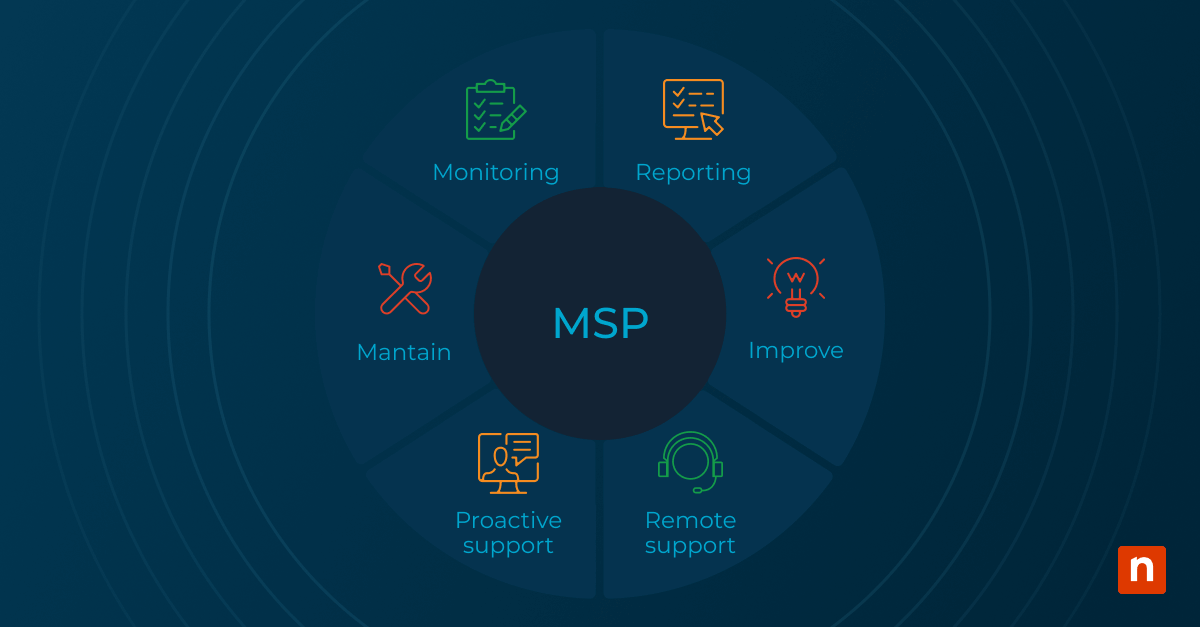
Businesses can partner with an MSP to remotely manage their IT infrastructure under a monthly subscription. This offloads IT \operations from businesses and ensures their IT assets run efficiently. MSPs offer various services, including endpoint management, network monitoring, patch management, and more. MPSs offer businesses reduced operational costs and improved IT service levels.
What is MSP in sales?
MSP sales refers to selling the IT management services of MSPs to prospective clients through monthly or annual subscription-based contracts.
What is the MSP sales funnel?
1. Lead generation and qualification
As the top-most level of the MSP sales funnel, lead generation is about promoting an MSP’s services to the right target audience. MSPs can reach potential customers through social media marketing, search engine optimization, email marketing, and other avenues for generating awareness. Once these marketing efforts have generated leads, MSPs have to qualify these leads so that MSP sales personnel can focus on leads more likely to become paying clients. MSPs should evaluate prospects based on their IT infrastructure, needs, and budget.
2. Free trials
Every business has unique requirements for its IT infrastructure, so giving them hands-on experience through a free trial allows them to see the value of your offered services. When a free trial is not feasible (for example, some MSPs require intensive hardware set-up), MSPs can also showcase customer success stories and case studies. The main goal of this stage of the MSP sales funnel is to demonstrate the value you can provide prospective clients.
3. MSP sales process follow-up
At the end of a free trial, potential clients should want to sign up for your MSP’s services. MSPs should look to communicate with prospects to convert leads into clients. This can be at the end of a trial or within a few days following the trial. Strategic timing and communication are vital in this stage of the sales funnel. MSPs should focus on emphasizing the benefits of their services.
4. Closing a contract
This is the final stage of the MSP sales funnel, so it’s crucial for MSPs to present potential clients with a competitive MSP deal. MSPs need to show prospects a proposal that outlines all the services that will be provided and the pricing plan. Creating a proposal tailored to a potential client’s specific requirements will help close the deal. Once the contract has been signed, MSPs should provide a quick and easy setup to reduce downtime needed for training and implementation and also to maintain customer satisfaction.
What is the MSP model?
The MSP model is a framework for outsourcing the remote management of a client’s IT infrastructure via a subscription. Services such as endpoint management or network and server monitoring allow MSPs to ensure the security, stability, and performance of all the systems, servers, software, and hardware in a business’s IT environment. The difference between the MSP model and the break/fix model is that services are only provided when a problem arises in the break/fix model, whereas the MSP model offers a longer-term partnership between a business and an MSP. Through this partnership, MSPs can provide more consistent, stable, and holistic management of a business’s IT infrastructure.
What are the top MSP sales metrics?
-
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR)
MRR refers to the monthly recurring revenue generated by the ongoing support and services provided by the MSP to their customers. This is among the top metrics for MSPs to measure, as it provides decision-makers with
-
Earning before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA)
EBITDA measures a company’s profitability regarding operational performance that does not include debt, taxes, or operational costs. For MSPs, tracking EBITDA can help them understand their services’ profitability and make informed investment decisions or cost optimizations.
-
All-in seat price (AISP)
The All-In Seat Price refers to the comprehensive cost covering all IT support and services provided by an MSP, billed per user or per seat. It typically includes support, infrastructure, software licenses, and any other IT services required. Tracking AISP helps MSPs understand their pricing model’s competitiveness and profitability vis-a-vis the cost of delivering services.
-
First-time appointments (FTAs)
FTAs refer to the initial meetings or contacts made with potential clients. Monitoring FTAs helps MSPs gauge the performance of their lead generation and sales strategies.
-
First-Time Fix Percentage
This metric measures the percentage of issues or tickets resolved on the first visit without requiring follow-up action. This metric means that an MSP’s customer support is efficient and effective, which leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. MSPs can utilize ticketing software to improve this sales metric greatly.
-
Close ratio
The Close Ratio is the percentage of deals won from the total number of proposals sent. Tracking the Close Ratio helps MSPs assess the effectiveness of their sales team and strategies. Improving the Close Ratio directly impacts revenue and can indicate areas for training or process improvement.
-
Average deal size
The average deal size is the average revenue expected from each closed deal. This metric helps MSPs decide which market segments to target and how to structure service offerings.
-
Client effective rate (CER)
CER is the average hourly rate that an MSP earns from all billable services provided to a particular client. This metric can help MSPs identify which clients are most valuable and which services are the most lucrative, allowing decision-makers to allocate resources and set pricing plans strategically.
-
Cost of goods sold (COGS)
COGS refers to the direct costs of an MSP’s services, such as labor, software licenses, and IT infrastructure expenses. By keeping track of COGS, MSPs can ensure that their pricing structure remains profitable.
What is MSP sales automation?
Automation boosts productivity and efficiency by reducing the need for manual intervention, freeing up your personnel to focus on more strategic tasks. MSPs can leverage automation to handle repetitive sales tasks, speeding up their sales and customer relationship management processes.
Next steps for your MSP
Although there are plenty of MSP sales tips out there, the way to find the best ones is to choose tips that are relevant and will benefit you. Depending on where you’re starting from, standing up a well-running sales process can seem like a tall order, but the key is to start simple and stay consistent. Responding to leads early, disqualifying bad leads quickly, making your deals stand out, and understanding the importance of MSP sales cadences are a few examples of basic sales tips that can get you on your way.
When engaging with sales leads, remember to focus more on how your services can benefit them and less on making a sale. In our MSP breakthrough discussion regarding client relationships, successful MSP owners explained that building positive client relationships is the key to success. Most businesses want to work with people who act as partners rather than salespeople.
Download our MSP Sales Process Checklist for templates and tips you can use to make launching or improving your own sales process faster and easier.
Take your IT services to the next level with NinjaOne
All an MSP needs to profit in today’s market is reliable services and a thorough understanding of the sales process. Take a look at our NinjaOne MSP sales process checklist to ensure that your department is set up for success. To take your IT services to the top, get in touch with NinjaOne and begin your free trial.