Key Points
How to Automate Patch Management
- Set Up a Patch Management Tool: Choose a solution like NinjaOne that simplifies patch discovery, deployment, and monitoring across all endpoints.
- Build an IT Inventory: Identify all devices and applications on your network to ensure complete patch coverage and prioritize critical systems.
- Automate Scheduling and Policies: Configure patch schedules, auto-approvals, and conditions to deploy updates with minimal disruption.
- Monitor and Verify Patching: Use dashboards and alerts to track patch success, resolve failures, and ensure compliance across your IT environment.
Patch management is a key component in any functional, successful IT environment, and you can automate it to keep your IT estate healthy and more secure. In this article, we’ll discuss how to automate the patch management process to improve not only your efficiency but also strengthen your IT security strategy.
We recommend using this guide along with our other resources on the patch management process to gain a more in-depth understanding of the concept.
What this article will cover:
- 5 steps to automate patch management
- Manual patching vs. automatic patching
- How does automated patch management work?
- How autonomous patch management makes IT resilient
🥷 NinjaOne automates patch processes for seamless security updates and maintenance.
Learn more about NinjaOne Automated Patch Deployment.
5 steps to automate patch management
With the right patch management tool and a comprehensive IT inventory, setting up an automated patch management system will be easier than you think. Here’s how to set up automated patching in five simple steps:
1) Set up a patch management tool
If you have previously patched all devices manually, setting up and becoming familiar with your patch management tool might take some time. However, the right patch management tool should be intuitive with an easy-to-use interface so that you can begin automation right away.
2) Build a comprehensive network inventory
To patch all the endpoints in your IT environment, you need to know some specific details, such as how many endpoints are on your network, what types of endpoints you use, how many require patching, etc. The best way to gather and organize all this information is to create a comprehensive network and IT inventory. MSPs and IT departments use this inventory to manage hardware and software assets and to provide information about the current state of their IT environments.
3) Identify areas that benefit from automation
With a network inventory in hand and a patch management solution, it’s time to begin the automation process. Although you might not be able to automate all the stages in the patch management process, you can automate the majority of the main steps, such as patch deployment/scheduling, policy creation, and testing.
4) Set conditions and schedule automated patching
Now, it’s time to set up conditions and schedule automated patching for your systems. As you set up the automated processes, be sure to keep patching best practices in mind. For instance, if you are setting up automated patching for servers, it’s best to schedule the patching for after-work hours so that your other teams are not affected by the updates.
5) Monitor and ensure all patching systems function correctly
Even after patches are deployed, there’s still work to be done. Your patch management tool should allow you to monitor your systems, ensure that all patches are deployed successfully, and alert you in case any systems experience issues after the process. Use unified endpoint management that includes patch management, such as the NinjaOne Platform.
Manual patching vs. automatic patching
It’s tempting to say that automated patching is “better” for larger organizations, but manually patching updates also has advantages. Let’s summarize the most salient points:
Pros | Cons | |
Manual | ● Greater control over patch deployment ● It can possibly be cheaper as users can patch on their own | ● Time-consuming ● Greater probability of inaccuracies and human error ● Requires constant vigilance |
Automatic | ● Streamlines patch management process ● Reduces IT workload ● Ensures consistent patching across all systems ● Automatically downloads and deploys patches based on a predetermined schedule | ● Requires safety checks to avoid deploying problematic patches, including controlled testing ● Requires regular reviews of patch deployment logs to avoid deploying incompatible patches |
Manual patching offers flexibility and control but tends to be labor-intensive and error-prone, especially as you scale. Meanwhile, automatic patching boosts efficiency and consistency but requires a bit more effort to set up and a stricter auditing framework to ensure safe, compatible autonomous updates. These patching challenges and benefits will also be less or more prevalent depending on the size of the IT stack.
How does automated patch management work?
Automated patching usually follows a simple 4-step process:
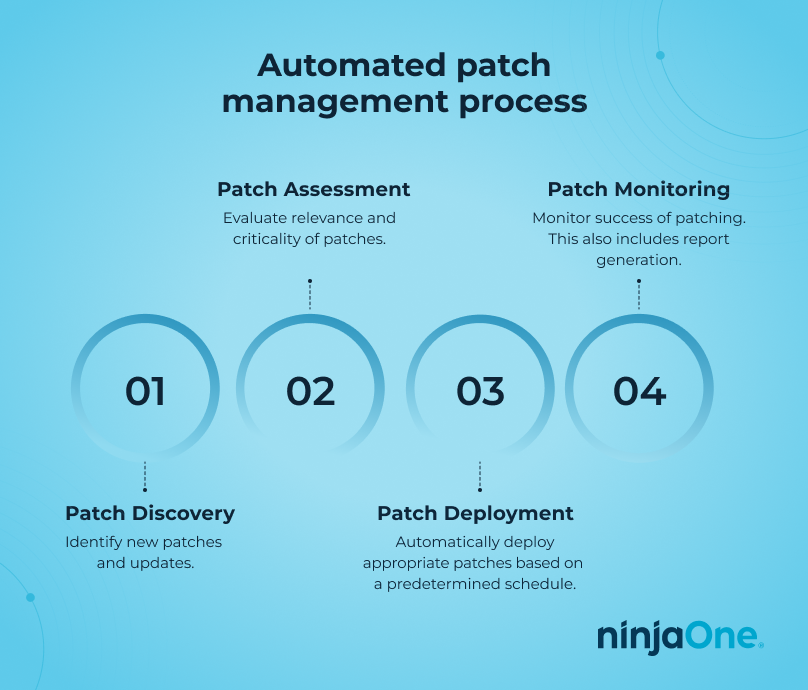
1. Patch discovery
Your automated patch management tool identifies new updates and patches from various sources. These updates can address everything from dangerous security flaws to small performance enhancements. For MSPs and growing IT enterprises, discovering all these patches across client environments—manually—is practically impossible.
The types of patches that are typically discovered are:
- Critical security patches: These are urgent updates that can be easily exploited by threat actors. If left unpatched, these flaws might allow malware infections, unauthorized access, or data breaches.
- Bug fixes: These patches resolve software glitches, errors, or faulty behaviors. While they may not be security-related, they can still disrupt productivity or cause systems to crash.
- Performance improvements: These patches optimize how software runs. They can include memory usage enhancements, speed improvements, or better compatibility with hardware. These updates contribute to your overall operational efficiency.
- Feature updates (optional): Sometimes, vendors release updates that add new functionality or features. These may not be necessary, but could be useful depending on the needs of your end users.
Patch discovery involves finding updates from multiple sources, including:
- Operating system vendors (like Microsoft or Apple)
- Third-party software providers (Adobe, Google, Zoom, etc.)
- Hardware drivers and firmware updates
How NinjaOne automates patching
NinjaOne takes the complexity out of patch discovery by centralizing it in a single dashboard. NinjaOne helps MSPs and IT enterprises patch discovery by:
- ✅ Continuous scanning for updates: NinjaOne can automatically scan all managed devices for missing patches across Windows, macOS, Linux, and third-party applications. Take note, however, that this is an optional feature that must first be enabled and correctly configured to work.
- ✅ Real-time visibility: NinjaOne’s single-pane environment means that you easily see all available patches across all endpoints and clients. This makes it easier to see what updates are pending and which systems are affected.
- ✅ No need for on-site infrastructure: Unlike legacy patching systems, NinjaOne is cloud-native. This means you can manage patch discovery remotely without needing VPN connections or servers.
2. Patch assessment
After discovering available patches, your automated patch management tool evaluates their relevance to your organization’s IT network. Remember: Not every update needs to be installed right away or at all. As its name suggests, patch assessment evaluates each patch to determine its relevance, urgency, and potential impact on your client environment.
Here’s what patch assessment typically involves:
- Identifying patch severity: Your automated patch management tool determines how urgently patches need to be applied. Some are labeled as “critical” or “high severity,” while others are considered “low priority.”
- Evaluating compatibility: Some patches might conflict with legacy systems or applications your clients rely on.
- Understanding the purpose of the patch: Is it a new feature? A bug fix? Or behind-the-scenes improvement?
- Client-specific needs: If you’re an MSP, you need to assess which patches are most suitable for your clients. For example, a healthcare client would need security patches to stay HIPAA-compliant.
- Risk of downtime: Some patches may cause issues, especially if an endpoint does not have sufficient storage space or features conflicting apps. As an MSP, you need to evaluate patches to minimize disruptions to your end users.
How NinjaOne automates patching
NinjaOne gives MSPs and organizations the tools and flexibility they need to assess patches efficiently.
- ✅ Patch severity filters: NinjaOne clearly labels each patch with vendor-supplied severity levels.
- ✅ Granular device and group controls: NinjaOne automated patch management can assess and apply updates based on client, device group, or individual endpoint basis.
- ✅ Custom patch approval: You can configure rules to automatically approve certain types of patches (like critical security fixes), while holding others (like optional feature updates) for manual review.
3. Patch deployment
The patch management tool automatically deploys the appropriate patches based on a predetermined schedule. This is a critical moment. It’s where all the planning and assessment become real-world action. For MSPs and IT enterprises, reliably deploying patches across hundreds (or even thousands!) of devices without disrupting the end user is the primary goal.
Patch deployment typically involves:
- Scheduling: You want to make sure that updates are applied during off-hours (as much as possible) to avoid disrupting work. This can be a little more complicated for globally distributed teams, as “off-hours” can vary. All the same, an automated patch management tool makes the deployment as frictionless as possible. We recommend reading this guide, “How to Minimize Downtime in IT Operations”, for further information.
- Managing reboots: Many patches, especially updates to an operating system, require system reboots. You need a strategy for optimizing your patch management tool´s handling of reboot timing, warnings, and user prompts.
- Coordinating across environments: If you’re an MSP, you often need to patch a mix of desktops, laptops, servers, and VMs, each running different OS versions and software stacks.
- Fallback options: Sometimes, a patch fails mid-deployment or causes unexpected issues. You must be able to roll back or re-deploy quickly.
How NinjaOne automates patching
NinjaOne handles patch deployment with a focus on reliability, customization, and automation.
- ✅ Automated deployment schedule: NinjaOne automated patch management allows you to schedule patches at the most convenient times for you and your end users.
- ✅ On-demand patching: NinjaOne lets you deploy updates manually to specific endpoints.
- ✅ Third-party app patching: NinjaOne supports patch deployment for popular third-party apps.
Simplify patch deployment with NinjaOne for seamless security updates.
→ Learn more about NinjaOne Automated Patch Deployment.
4. Patch monitoring
Patch monitoring is the final step and arguably the most important. It’s important that you continuously monitor the success of your patches and detect any inconsistencies or abnormalities. Monitoring ensures your process is working, lets you catch issues early on, and gives you proof of compliance for your clients.
Effective patch monitoring involves:
- Verifying successful installations: Did the patch install correctly? Were there any errors during the process?
- Tracking failures and issues: If a patch fails, you need to know why. From there, you would know whether the same patch needs to be retried, skipped, or further investigated.
- Watching for post-deployment issues: Even if a patch installs correctly, it might cause system instability, app crashes, or user complaints.
- Reporting for compliance: Many clients, especially those in highly regulated industries, need reports showing patch status across systems. You need reliable patch reports of what has been updated, when, and where.
- Alerting and escalation: If something does go wrong, you need to know immediately so your IT team can respond before it becomes a bigger issue.
How NinjaOne automates patching
NinjaOne offers real-time and reliable patch monitoring, so you’re never in the dark and always ready to respond.
- ✅Real-time patch status dashboards: You immediately see the status of applied patches across all devices and clients, including what is still pending, what has been installed, what has failed, or what is overdue.
- ✅ Detailed audit trails and logs: All patch management activities are logged, so your team can track when scans are performed or patches are installed and the outcome.
- ✅ Multi-client monitoring: With NinjaOne, you can monitor and manage all your customers on a single dashboard.
How autonomous patch management makes IT resilient
Traditional patch management has its advantages in terms of flexibility, particularly within moderately-sized IT networks. That said, the speed and volume of modern threat actors can overwhelm hands-on patch management over time.
Below, you can explore more about the benefits and challenges of automated and traditional patching strategies.
Automated patch management benefits
While manual patching can work for smaller environments, automation unlocks significant advantages that directly improve IT operations. Here are the four core benefits of automated patch management in various IT stacks:
Better security
Without a doubt, an automated patch management tool immediately takes your security to the next level. Using the advantages of automation, a patching tool ensures that every device in your IT infrastructure receives the security patches they need in a timely manner.
Reduce manual errors
Manual errors happen when patching is left entirely in human hands. Automated patch management allows users to set up patching schedules and ensure that updates are pushed uniformly to all endpoints without significant human intervention.
Greater efficiency & productivity
No one really wants to spend hours patching. It’s tedious work that’s better handled by an automated system. After setting up an automated patch management tool, users notice an impressive boost in IT efficiency and productivity.
Simplify compliance reporting
For organizations that qualify for SOC compliance audits, such as MSPs, automated patch management is a great help since the automated systems produce patch reports. These reports are used in compliance audits to ensure that IT teams follow IT and security best practices.
Unpatched software risks and past incidents
No organization is safe from the risks of unpatched software, from small businesses to large enterprises. A significant number of cyberattacks exploit known software vulnerabilities, many of which can be mitigated through an effective patch management program.
Some of the worst cyberattacks of 2025 and 2024 include:
- Hundreds of US military and defense credentials were compromised in February 2025 due to malware. Experts warn that even partner organizations, suppliers, and vendors of affected sites could still be compromised as well (Infosecurity Magazine).
- In February 2025, Mars Hydro, a China-based IoT grow light company, suffered a massive IoT data breach that exposed more than 2 billion records, including WiFi network names, passwords, IP addresses, and device IDs (Infosecurity Magazine).
- Change Healthcare fell victim to a massive ransomware attack, described as the “most serious incident of its kind” in modern history (NBC News).
- Ascension Healthcare admitted that several files containing protected health information (PHI) and personally identifiable information (PII) were exfiltrated, with several of its servers being compromised in a ransomware attack (HIPAA Journal).
- CDK Global “almost certainly” paid a $25 million ransom after a “cyber incident” with BlackSuit disrupted thousands of data points (CNN).
- CrowdStrike experienced a major outage related to an oversight in its software update, affecting around 8.5 million Microsoft devices On July 19, 2024, millions encountered an error known as the “blue screen of death”, disrupting dozens of companies ranging from banks to airlines.
Experts predict that threat actors will continue targeting as many security vulnerabilities as possible in the near future. That said, it’s worth noting that this also includes vulnerabilities caused by human error.
According to Cyber Security Hub, nine major cyberattacks and data breaches have already occurred in the first quarter of 2025 alone. These include a WhatsApp spyware hack on Meta and the active exploitation of firewalls in Palo Alto Networks.
While patch management cannot completely eliminate these risks, it can create more efficient, successful, and productive programs, giving you more confidence to continue delivering quality services to your customers.
Why NinjaOne is your #1 solution for patch management
NinjaOne is an automated endpoint management software solution with a natively built-in patch management tool that helps IT departments and MSPs create a safer, more unified IT environment.
Trusted by 30,000+ customers worldwide, NinjaOne automatically patches Windows, Mac, Linux OSs, and third-party apps and offers flexible patching schedules to ensure all endpoints are patched exactly when you want.
If you’re ready, request a free quote, sign up for a 14-day free trial, or take a tour.