A threat actor, also known as a malicious or bad actor, is any individual who intentionally harms a digital device or system. These people exploit weaknesses and vulnerabilities in your computers or networks to carry out disruptive attacks, whether for financial gain or idealistic purposes.
It’s worth noting that “threat actors” are not the same as “cyber criminals,” although both share similarities. As their names suggest, cybercriminals engage in illegal activities, such as spear phishing or ransomware-as-a-service. Threat actors, on the other hand, cover a broader range of people, including not only cybercriminals but terrorists, insiders, and even internet trolls. Thus, a threat actor is anyone intending to damage a specific computer system in various ways.
Who are the targets of threat actors?
Anyone can become a target for a threat actor. Some threat actors may want to harm an indiscriminate number of people, including strangers. This includes “cyber big game hunting”, where threat actors use ransomware to target large organizations or high-profile individuals for monetary gain, and “advanced persistent threats (APT)”, such as the ones sponsored by Russia, which are sustained cyberattacks to steal sensitive data over a prolonged period.
Similarly, threat actors may also target specific individuals or entities, such as trolls who spam social media posts on someone’s account or employees who steal privileged information from their organization.
As you can see, targets differ from case to case, depending on the threat actor’s ultimate goal.
Guard yourself against threat actors by learning the top 5 IT security fundamentals.
Types of threat actors
There are many different types of threat actors. While most fall under the standard cybercriminal umbrella, some do not. Keep in mind that a threat actor is someone who harms a computer system or device, whether that’s through malware or stealing sensitive data. Consequently, there are many types of threat actors to take note of:
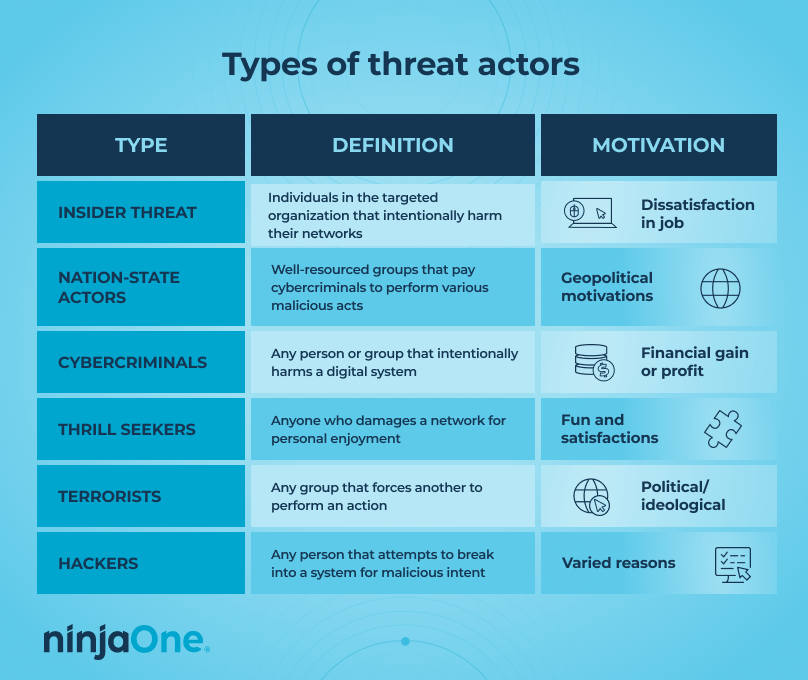
1. Insider threats
Insider threats are cyberattacks from authorized users, such as employees or business partners, who intentionally misuse their legitimate access. Insider threats can range from corruption to espionage to even unauthorized information disclosure.
Disturbingly, these types of threats are on the rise. According to a new report by Cybersecurity Insiders, insider attacks increased from 66% to 76% from 2019 to 2024, and this number is expected to rise even further in the next few years.
2. Nation-state
Nation-state actors fund cybercriminals to perform a series of malicious activities. The Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has declared that nation-state adversaries pose an “elevated threat” to national security, continually deploying sophisticated malicious cyber activity for prolonged network and system intrusion.
3. Cybercriminals
When we hear the term “threat actors,” cybercriminals are often what we think of. These actors are usually motivated by financial gain and employ various social engineering strategies, such as phishing emails or other more common cyber attacks, to get us to perform a desired action.
4. Thrill seekers
Thrill seekers are threat actors who damage computer systems or networks for their own enjoyment. These types of actors are often difficult to classify, as their motivations can differ, whether to see how much sensitive data they can steal or how “far” they can go with their malicious actions. Typically, thrill seekers do not intend to do much harm to their targets but may cause some network lagging or operational impact.
5. Terrorists
Extremist groups that use various cyber techniques to intimidate or force a group of people into performing specific actions are known as terrorist threat actors. These actors may intersect with other types, such as insiders and nation-state actors, to further their cause. Thus, understanding the motivations of the threat actor may help distinguish which type they fall under. Typically, terrorists are motivated by political or ideological gain rather than financial gain.
6. Hackers
Hackers are anyone who uses their technical skills to overcome a problem, such as being locked out of a system. This means that “good” or ethical hackers work with organizations to keep their IT networks healthy and identify vulnerabilities.
For the purposes of this article, however, we will focus on hackers (or black-hat hackers) who deliberately attempt to break into a computer network or system with malicious intent. Black-hat hackers use several techniques to reach their goal, such as hacking passwords, phreaking, or executing a distributed denial-of-service attack.
Keeping your IT network secure from threat actors
There is no one way to keep your IT network secure from threat actors. Because each threat actor is different and has various motivations for their attacks, IT experts cannot suggest a single, effective way to prevent these threats from happening in your organization.
That said, an all-in-one endpoint management software solution, such as NinjaOne, can make a significant difference. Boasting proactive IT support and many out-of-the-box features that immediately detect and resolve vulnerabilities, you can reduce the risk of any organizational impact caused by a threat actor.
NinjaOne’s IT management software has no forced commitments and no hidden fees. If you’re ready, request a free quote, sign up for a 14-day free trial, or watch a demo.