Key Points
- Server patching is a core part of enterprise patch management—protecting servers from security threats, reducing downtime, and optimizing IT performance
- 8 server patching best practices:
- Take inventory of servers to understand systems and dependencies.
- Use patch management software to automate and simplify patching.
- Establish a patch management policy to define procedures, compliance, and risk mitigation.
- Evaluate server risk to prioritize vulnerabilities based on impact and exploitability.
- Create a server patching schedule (weekly checks + critical patch alerts).
- Test patches in a sandbox environment to prevent system failures.
- Design a backup server environment (failover systems for recovery).
- Leverage automation to reduce manual work and improve efficiency
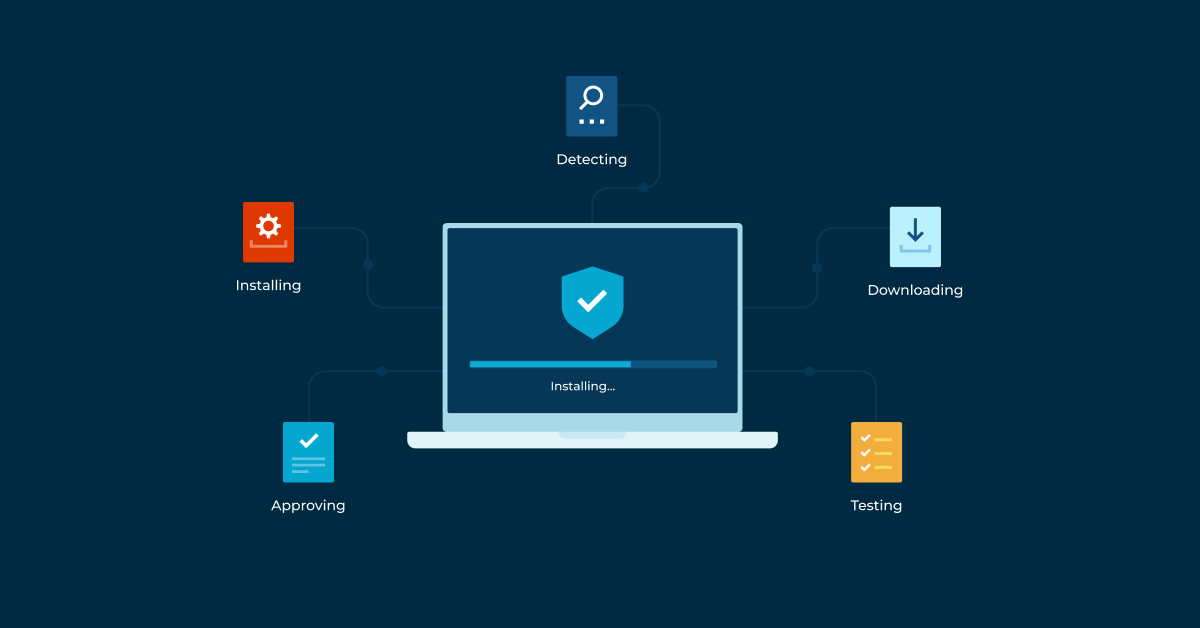
Patch management is the process that helps keep IT assets safe, protected, and functioning optimally. Server patching follows many general patch management best practices, but also includes tasks and processes specific to patching servers.
In this article, we will to discuss what patch management best practices apply to server patching in your IT environment, and how you can start improving your server patch management process.
→ Discover more about patching basics through NinjaOne’s definitive guide on patch management.
What is server patching?
Server patching is the specific process of managing patches and updates for your server. When done efficiently, server patching protects your server from outside threats and optimizes its performance.
Patch management vs change management
Change management is the process, framework, and methods used to manage any change or development within an organization.
Patch management is a type of change management. It involves finding, obtaining, verifying, and deploying patches to an organization’s IT assets.
Therefore, server patch management is a specific type of patch management focused on updating and fixing servers.
How to ensure your server is patched correctly and effectively
Server patching can be a large undertaking because of a server’s high impact on an organization. To ensure your server patch management process will effectively maintain updates on and keep your server safe, follow these eight patch management best practices:
NinjaOne server patching solution provides IT teams and administrators with extensive control over their server patch deployment process.
8 server patching best practices
Many of the best practices for server patching are included in general patch management best practices, but some are unique to server patch management. Here are six recommended server patching best practices:
1. Take inventory of your servers
Before you can start server patch management, it is crucial to know what type of servers your IT environment has. Understanding your servers provides a clearer perspective on your patch management strategy, including the necessary software and the policies to implement.
2. Obtain patch management software
Invest in patch management software to set a solid base for your server patching efforts.
Patch management software contains tools and features specifically designed to simplify and streamline your patch management process for all your IT systems.
Investing in patch management software will immediately improve your IT cybersecurity because you’ll be able to patch and protect your server and other endpoints more easily.
3. Establish a patch management policy
Establishing a patch management policy is key to your overall patch management process. A patch management policy includes your organization’s plans and procedures for executing patch management in your IT environment.
Within the patch management policy, make sure to include specific actions pertaining to identifying and applying valuable or necessary server patches. This helps to ensure your server is accounted for, server patching is structured, server risk is minimized, and server downtime is limited. Servers are important IT assets, and you want to ensure they remain protected and functioning optimally.
4. Evaluate server risk
One tried-and-true method for efficient server patch management is to take a risk-based approach to patching a server. A risk-based approach involves using risk assessments to identify any vulnerabilities in the server, evaluating how easily the vulnerability could be exploited and the impact that could have on the server, and determining other ways to manage the vulnerability besides patching.
It’s practically impossible to patch every single vulnerability that exists on servers. Thus, evaluating the risks and potential impacts helps determine which server patches to prioritize and effectively conduct server patch management.
5. Create a server patching schedule
A server patching schedule is a documented plan for how often a server will be patched, the method for obtaining patches, and the implementation of patches on the software.
It is generally recommended to check for server patches at least once a week. Additionally, it is wise to sign up to receive alerts for any critical patches released to ensure your server is secured as quickly as possible after an impactful vulnerability is identified.
6. Test your server patches
One of the most important steps, if not the most important, is to test your server patches. Sandbox testing allows you to test server patches in an isolated environment, separate from your own IT environment. You can implement a patch in the sandbox to determine its effects on the server system, thereby avoiding any potential damage the patch would cause to your actual server.
Because the state of a server affects a large number of people, any possible adverse effects of patching are more widespread. Sandbox testing is an essential practice and a preventative measure to check whether a patch be smoothly implemented.
7. Design a backup server environment
Backups are key to protecting data, software, and systems. Server failovers are essentially a backup environment you can revert to if the actual server fails, is damaged, or is abnormally functioning after implementing a patch.
Testing your patches before implementation often prevents the need for server failovers, but things can still go wrong when you apply a patch, so the backup server environment acts as a safety net.
8. Use automation in your server patch management process
Server patching can involve a lot of repetitive and time-consuming tasks. When manual intervention isn’t required, automation can streamline the server patch management process. This allows your technicians to move away from tedious patching tasks and focus on more critical aspects of server patching.
How to start efficiently patching your server
So, how do you actually patch your server? With these eightserver patching best practices, you are well-equipped to approach server patching within your own IT environment.
Invest in patch management software, such as NinjaOne’s patch management software. A solid patch management solution will simplify the server patching process and give you all the tools and features you need to execute proper server patch management.
Once you have the necessary tools and software, you can create a patch management policy that will lay out your server patching plan and guide your methods and procedures.
After these have been set up and established, you can begin identifying available server patches, testing them, and creating a patching schedule. Server failovers and sandbox testing are essential to guaranteeing your IT environment remains functional and in good health. Apply automation where possible to enhance the entire process and improve efficiency.
Optimize your patch management processes with NinjaOne’s Enterprise Patching solution.
Server patch management with NinjaOne
NinjaOne’s patch management software gives you the patching tools you need to secure and optimize your server. With features like patch automation, vulnerability data, instant patching alerts, and patch reporting, you can rest assured knowing your server is patched efficiently. To experience the benefits of these tools and more, sign up for a free trial today.