Hibernate mode can be practical for power-saving users and those in the middle of an important project. Booting takes less time, so you can jump back into your task without significant interruption. Likewise, this power option saves your session to the hard drive, so you don’t lose files when the power is cut.
In some cases, the hiberfil.sys size can be a concern if a device runs low on storage. As such, you may want to configure the hibernation file type from Full to Reduced to save crucial disk space. We’ll break this down further in this guide.
For a visual guide, watch How to Specify Hibernation File Type as Full or Reduced in Windows 10.
How to specify the hiberfile type
We have the Command Prompt as the ideal console for this task. But before we proceed, here’s an overview of the hibernation settings:
✔️ Full: Enables Hibernate power option and fast start-up; takes 40% default of installed physical memory.
✔️Reduced: Hides Hibernate power option but retains fast start-up; takes 20% default of installed physical memory.
With that in mind, you can now choose the ideal power options for an IT environment or even a personal device. Here’s how to do it via an elevated Command Prompt.
Using elevated Command Prompt
- In Windows Search, select Command Prompt → Run as Administrator.
- Type powercfg /a to show your device’s supported sleep or power options.
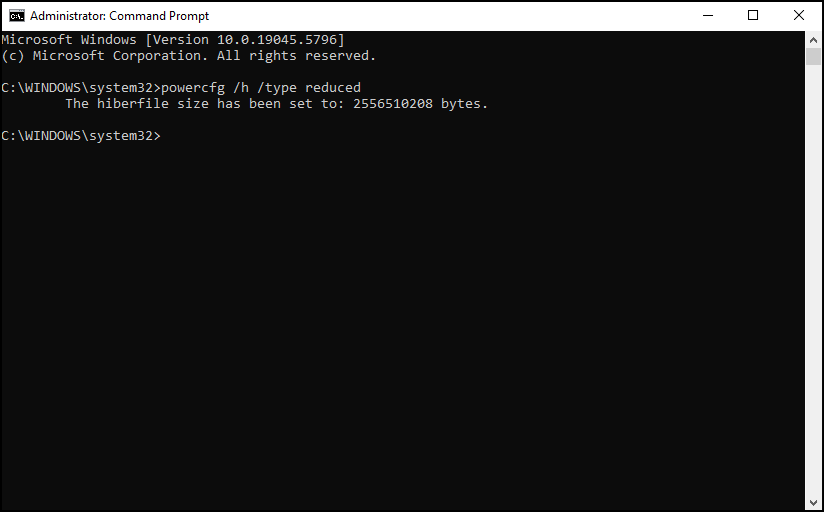
- To select Full, type powercfg /h /type full
- To select Reduced, type powercfg /h /type reduced
- (Optional) Run powercfg /a to confirm the updated sleep or power settings.
Selecting the reduced hiberfile type is an excellent way to free up some disk space, but if you want to take it further, you can also disable hibernation mode altogether.
Alternative ways to manage hibernation files and storage
If the Hibernate power option isn’t essential to the workspace or personal device, you may consider switching it off to free up storage.
Disabling Hibernation to save more disk space
- In Windows Search, select Command Prompt → Run as Administrator.
- Type powercfg.exe /hibernate off to disable and remove Hibernation in the power options.
Should you need to re-enable it, use the powercfg.exe /hibernate on command.
Adjusting hiberfil.sys size
Reducing the default hiberfil.sys size can lead to mixed results, as it may not function as intended. With that said, this command is used for older versions of Windows:
- In Windows Search, select Command Prompt → Run as Administrator.
- Type powercfg /h /size [percentage], and set the value between 50 and 100.
→ Need more disk space? For more storage-saving tips, check out our guide on freeing up disk space in Windows 10.
Hibernation file type FAQs
What happens if I switch from Full to Reduced hiberfile type?
Switching to Reduced will disable Hibernate mode in the settings, but fast startup will remain enabled on boot-up.
How much disk space does hiberfil.sys use?
When set in Full mode, the hibernation file takes 40% of the system’s memory and 20% in Reduced mode.
Can I delete hiberfil.sys?
Yes. Hibernation files will be removed when you run the powercfg.exe /hibernate off command, which completely disables Hibernation mode.
Is it safe to delete hiberfil.sys?
Yes. If you are not actively using Hibernate, you can disable it and fast-start up via the powercfg.exe /hibernate off method outlined above, which will also delete the hibernation files.
Can I reduce the hiberfil.sys size?
The hiberfil.sys size can be kept to a minimum by setting the hibernation file type to Reduced.
Do the hibernation file commands work on Windows 11?
Yes. These commands will run safely and function the same when deployed on a Windows 11 device.
Troubleshooting hibernation files
Issue: Command not working
Ensure you are running the Command Prompt as an Administrator, and try again. If you don’t have elevated access, report it to the appropriate IT personnel so they can facilitate the changes on your behalf.
Issue: Hibernation is still using too much space
Consider disabling Hibernation mode instead. Take note, however, that doing so removes any hibernation file.
Issue: Fast Startup option missing
If you want to keep the Turn on fast startup in Power Options, you have to enable Hibernate and at least set it to Reduced.
Quick-Start Guide
NinjaOne does have some related power management scripts that might be helpful:
– There’s a “Change Power and Sleep Settings” script that can adjust power-related configurations
– Scripts to enable/disable fast startup and modify various power-related settings
For the specific hibernation file type configuration, you might need to use Windows built-in tools or PowerShell commands directly
Summing up hiberfil.sys settings
Hibernate is enabled and even recommended on most Windows devices. However, it can also be customized or disabled to free up storage space. With SSDs, we can almost always expect a smooth boot process in modern devices, which makes Hibernate mode more of a practical power option for specific situations.