Turning disk write caching on or off is one common way to optimize disk write performance on high-throughput systems. However, while disk caching speeds up write operations by using additional memory resources, it also risks data loss when the process is interrupted by a power failure or improper system shutdown. If you lack the safeguard protocols for such scenarios, this guide provides several ways to disable disk write caching on managed networks.
Prerequisites and methods for managing disk write caching
Before you proceed, here are some key reminders and considerations when updating the disk write caching preferences:
✔️ Changing these settings requires administrative privileges.
✔️ These settings will affect internal drives (HDDs, SSDs, NVMe).
✔️ Separate policies may be required for USB and removable drives.
✔️ Write caching settings must apply to each individual disk.
✔️ Disabling write caching may reduce write performance.
Method 1: Enable or disable write caching via Device Manager (GUI)
This method is recommended for personal devices or limited deployment.
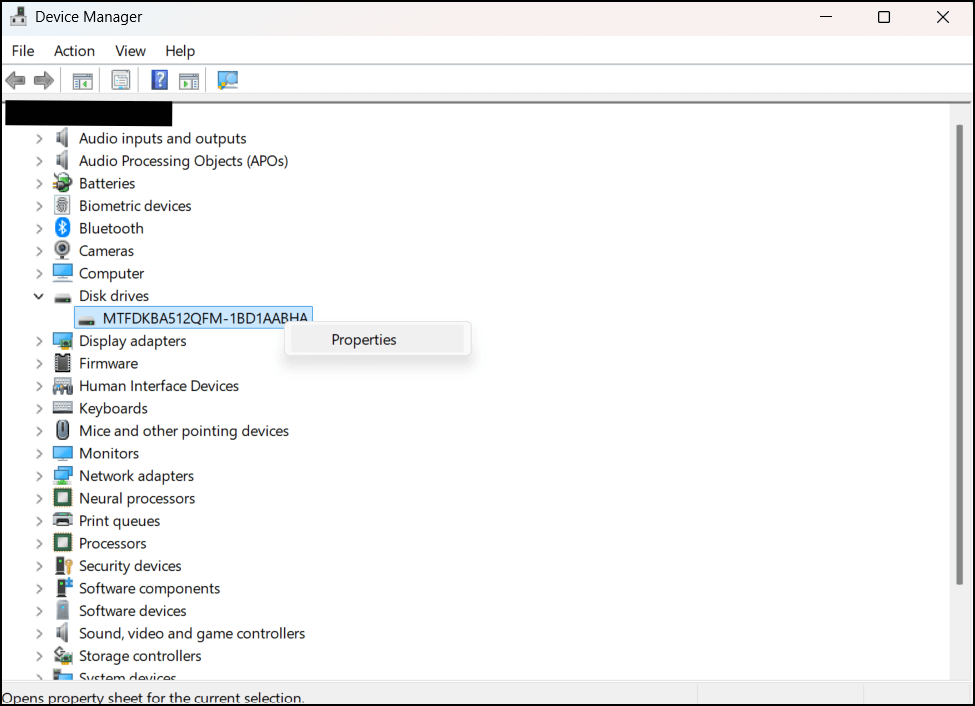
- Press Win + X and select Device Manager from the menu.
- Tap ➤ next to Disk drives to expand the list of active drives.
- Right-click on the target drive, select Properties → Policies tab.
- Toggle ✅ to enable or disable write caching on the selected drive.
- Click OK to save changes.
If you select Enable, you may toggle the additional Turn off Windows write-cache buffer flushing on the device option if you have data protection protocols in place and a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) for outages and crashes. Enabling it will further boost disk write performance but increase the risk of data loss.
Method 2: Check or modify write caching via PowerShell
First up, here’s the command to show the disk write caching status:
Get-WmiObject -Query "Select * from Win32_DiskDrive" | Select-Object Caption,
DeviceID, WriteCacheEnabled
Then, you may use this next command to modify the disk write caching settings.
Enable-StorageAdvancedProperty -PhysicalDisks (Get-PhysicalDisk) -Property
WriteCacheEnabled -Value $false
ℹ️ Note: Some storage devices do not expose or allow certain features or settings to be modified programmatically (e.g., PowerShell commands or scripts).
Additional considerations and tips for disk write caching
These additional tips may help with monitoring and testing the ideal disk write caching settings for your managed environment.
Group Policy and Registry
There is no direct Group Policy setting for disk write caching on internal disks. Instead, you can check cache behavior and settings via the following Registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\SCSI…\Device
Parameters\Disk
⚠️Warning: Making unintended changes to the Registry Editor can affect your system’s performance and stability. Learn how to back up the Windows Registry to save your database and create a restore point.
Windows Performance Monitor
For devices that are suspected to be struggling with disk write performance, you can test your settings by monitoring write cache behavior in Windows Performance Monitor. Here’s how:
- In Windows Search, type perfmon and select Performance Monitor.
- Add new counters for:
- PhysicalDisk → % Disk Write Time
- LogicalDisk → Disk Write Queue Length
This setup is useful for determining the live impact of enabling or disabling write caching settings on disk performance.
Set up a UPS
Disabling write-cache flushing without a UPS can lead to data loss following a power failure or process interruption.
With a UPS, power failures are less likely to cause severe setbacks. Many UPS systems can also signal the OS to shut off safely, ensuring the write cache is flushed to disk before power is cut.
NVMe devices
Enterprise-grade NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) devices deliver improved disk writing performance and may provide additional Advanced Power Loss Protection (PLP), which works well with a UPS.
File system caching
File system caching also improves performance, without being dependent on the physical disk for every operation. Instead, it uses the RAM for caching. However, you are still at risk of losing data when the system crashes or power is interrupted.
Best practices for managing disk write caching
Disk write caching can help speed up processes and reduce latency; however, not all devices or IT environments may be equipped to handle the trade-off.
When caching is enabled, you also need to account for the risk of losing crucial business data if the system crashes or power is interrupted. If you don’t have a UPS or data backup and protection protocols, it’s more practical to disable disk write caching for endpoints and storage devices.








