Most computer users know how vital the Start menu is. It is a core component of the Windows GUI used for tasks such as launching programs, accessing settings, opening files, and more. Like many other Windows elements, the Start Menu may fail to work as expected, and users may encounter different problems with it. These problems may involve unresponsiveness, sluggishness, etc.
To add context, the Start menu is managed by the StartMenuExperienceHost.exe, a Microsoft Windows process responsible for managing the Start menu and its user interface. If Start menu issues arise, users may opt to restart their computer. However, resetting the Start menu process may help restore its functionality without requiring a full system reboot or user logoff.
In this guide, we will teach you the most effective methods for restarting the Start menu process in Windows 11. This should help you mitigate challenges with this key Windows GUI component.
| Click to Choose a Method | 💻 Best for Individual Users | 💻💻💻 Best for Enterprises |
| Method 1: Task Manager | ✓ | |
| Method 2: PowerShell | ✓ | ✓ |
| Method 3: Command Prompt | ✓ | |
| Method 4: Full Explorer shell | ✓ |
Method 1: Restart via Task Manager
📌 Use Case:
The Task Manager is a handy tool that casual Windows users can use to restart the Start menu process.
📌 Prerequisites:
- Applies to all editions of Windows 11: These steps work across Windows 11 Home, Pro, and Enterprise editions.
- Administrator privileges are not required: No administrator privileges are required for this method.
- Temporary UI interruption: Restarting the process will momentarily close the Start Menu if it’s open.
- No disruption to open apps: Your current session, including open windows and documents, remains unaffected.
- Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
- Click on the Details tab.
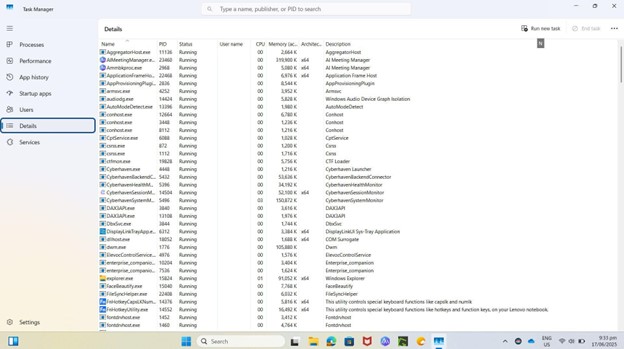
- Locate StartMenuExperienceHost.exe in the list of running processes.

- Right-click on the process and select End task.

Windows will automatically restart the process within a few seconds. If it doesn’t, you can:
- Try opening the Start menu again, or;
- Open a Run window by pressing the Windows key + R. Type explorer.exe and press Enter to relaunch the shell manually.
Method 2: Restart via PowerShell
📌 Use Cases:
This method best suits users or system administrators who want to restart the Start menu process using a command-line approach. It is also useful for script-based automation.
📌 Prerequisites:
- Applies to all editions of Windows 11: These steps work across Windows 11 Home, Pro, and Enterprise editions.
- Administrator privileges are not required: No administrator privileges are required for this method.
- Temporary UI interruption: Restarting the process will momentarily close the Start Menu if it’s open.
- No disruption to open apps: Your current session, including open windows and documents, remains unaffected.
- Open a Run window by pressing the Windows key + R. Type powershell in the dialog box and press Enter.

- Enter the following command:
Stop-Process -Name StartMenuExperienceHost -Force
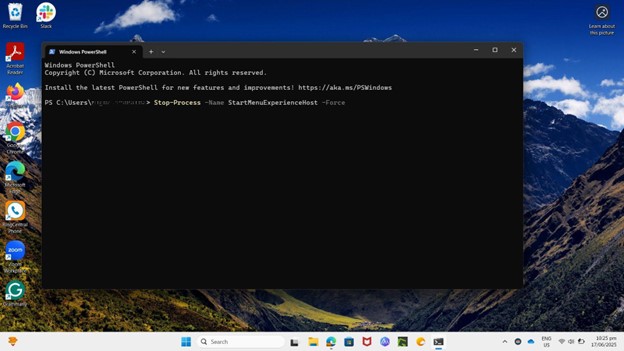
- Press Enter.
Using the command forces Windows to end the Start Menu process automatically. If the Start Menu does not reinitialize, you can:
- Run the following command on PowerShell:
Start-Process explorer.exe
Method 3: Restart using Command Prompt
📌 Use Case:
This is another method you can use if you prefer a command-line approach to restart the Start menu process.
📌 Prerequisites:
- Applies to all editions of Windows 11: These steps work across Windows 11 Home, Pro, and Enterprise editions.
- Administrator privileges are not required: No administrator privileges are required for this method.
- Temporary UI interruption: Restarting the process will momentarily close the Start Menu if it’s open.
- No disruption to open apps: Your current session, including open windows and documents, remains unaffected.
- Open the Command Prompt by pressing the Windows key + R. Type cmd and press Enter.

- Enter the following command:
taskkill /f /im StartMenuExperienceHost.exe
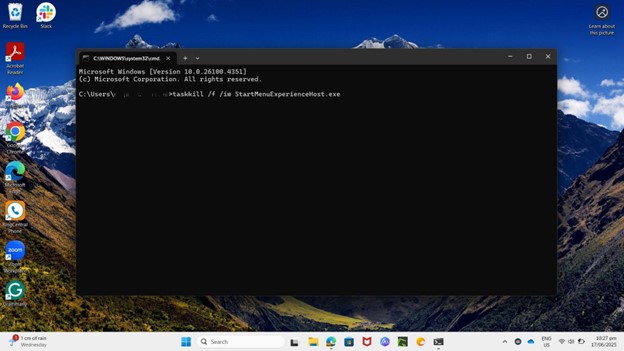
- Press Enter.
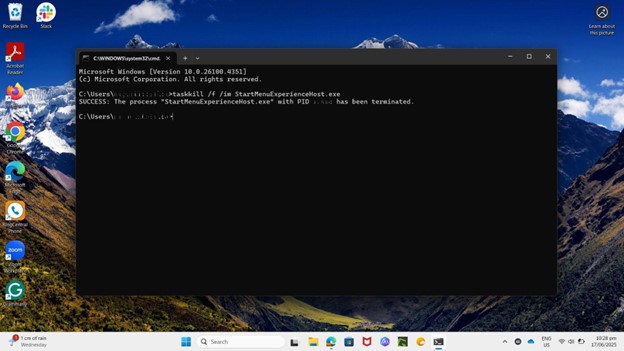
Windows will usually restart the process automatically. If it doesn’t, you can:
- Launch it manually by running start explorer.exe from the same Command Prompt window.
Method 4: Full Explorer shell restart (if needed)
📌 Use Cases:
This method is used when the Start Menu process fails to restart or if multiple UI elements are unresponsive.
📌 Prerequisites:
- Applies to all editions of Windows 11: These steps work across Windows 11 Home, Pro, and Enterprise editions.
- Administrator privileges are not required: No administrator privileges are required for this method.
- Temporary UI interruption: Restarting the process will momentarily close the Start Menu if it’s open.
- No disruption to open apps: Your current session, including open windows and documents, remains unaffected.
- Open Command Prompt or PowerShell.
- Run the following combined command:
- For Command Prompt:
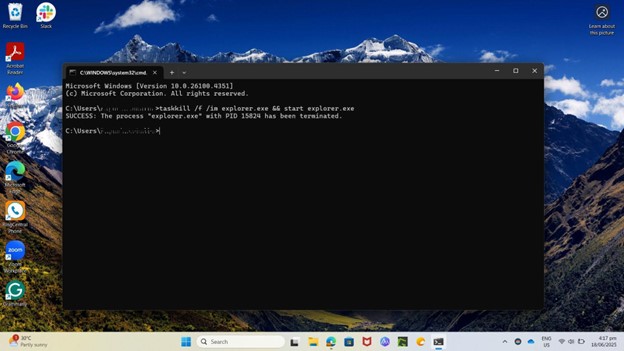
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe && start explorer.exe
- For Command Prompt:

- For PowerShell:
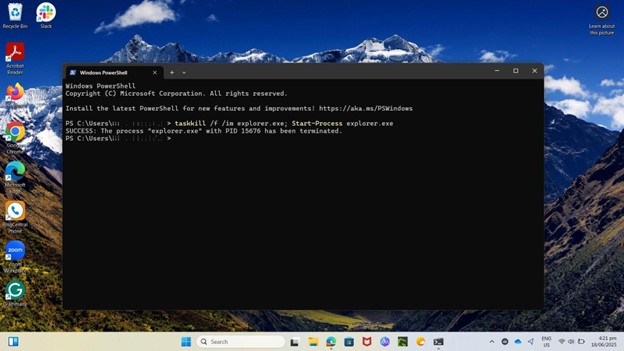
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe; Start-Process explorer.exe
- For PowerShell:

- Press Enter.
This is how it’s going to look in Command Prompt:
Meanwhile, this is how it’s going to look in PowerShell:
The command stops all Explorer processes and then immediately restarts them, reinitializing the UI components, including the Start Menu, taskbar, and desktop shell.
⚠️ Things to look out for
| Risks | Potential Consequences | Reversals |
| Ending explorer.exe but not restarting it | Your taskbar, desktop, and Start Menu will disappear. | Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc). Click File > Run new task, type explorer.exe, and press Enter |
| Persistent crashing of StartMenuExperienceHost.exe when restarted manually | Might result in flickering Start Menu behavior or brief reloading loops of the taskbar | Use Event Viewer.
Run DISM and SFC.
|
| Killing wrong or unrelated processes | System instability | Restart your computer or use Safe Mode |
Why restart the Start menu process?
There are several reasons why users may want to restart the Start menu process. Here are some of them:
Fix Start menu issues: Restarting the Start menu process can help fix issues like unresponsiveness or slow Start menu reactions.
Fix unresponsive UI: The methods presented above can help refresh graphical glitches or UI freezes.
Initiate fixes without rebooting: Some users may need to restart the Start menu without rebooting the entire system to resolve shell issues.
Remote management: The methods, specifically those that are done via Command Prompt or PowerShell, support remote or scripted troubleshooting in managed environments.
Additional considerations when restarting startmenuexperiencehost.exe
Aside from the methods outlined here for restarting the Start menu process, there are some factors you may need to consider:
- No data loss: Ending and restarting the Start Menu process doesn’t affect open programs or unsaved files. User data is safe when restarting the Start menu process because it operates independently from user data.
- Safe for remote execution: System administrators and IT teams can use commands to restart the Start menu and run them via remote desktop sessions or remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools.
- Scriptable and automatable: You can include these steps in login scripts, batch files, or PowerShell scripts to automatically recover from Start Menu issues.
- Diagnostic value: Start menu issues may become persistent due to deeper problems with user profiles, system updates, or third-party applications. If this is the case, there are tools you can use to monitor the StartMenuExperienceHost.exe process to investigate further.
Restore functionality by restarting the Start menu process
The Start menu is a core element that the majority of Windows users utilize. It is used to launch programs, search for files, access settings, and more. However, the Start menu is not immune to encountering issues such as unresponsiveness, glitches, sluggishness, and more. Restarting the StartMenuExperienceHost.exe process can restore normal functionality without requiring a system reboot.
Users can use the Task Manager for quick, visual intervention, PowerShell or Command Prompt for command-line control or scripting, and the Explorer shell restart for broader UI problems. These methods don’t require administrator privileges and can be utilized by IT professionals in scenarios where remote assistance or automated solutions are necessary.
Related topics:








