Streamline Security and Permissions with Role Based Access Control
Managing IT access across growing environments doesn’t have to be complex or risky. Many organizations struggle with over-permissioned users, security gaps, and time-consuming admin tasks.
NinjaOne’s Role Based Access Control (RBAC) solution empowers IT teams to assign the right access to the right people—no more, no less. Gain total confidence in how users interact with systems, data, and devices while accelerating day-to-day operations.
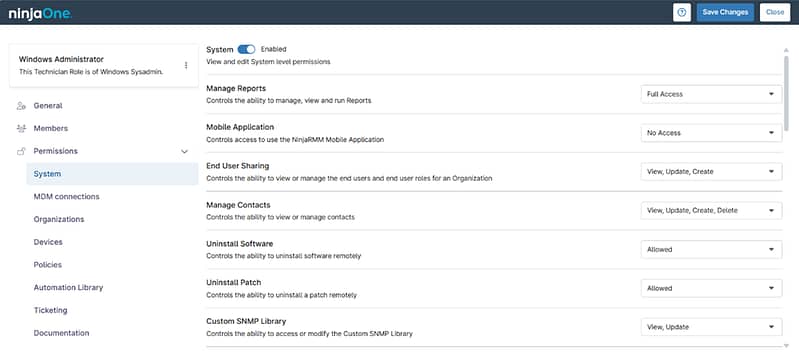
Precision and Protection Made Simple with NinjaOne RBAC
Tailored Access for Every Role
Security-Centric Permissions Management
Each access policy is designed to support zero trust best practices. With granular role configurations and time-limited permissions, NinjaOne reinforces RBAC security principles that align with today’s cybersecurity expectations.
Simplified Onboarding and Offboarding
Audit-Ready Compliance and Reporting
Multi-Tenant Friendly Role Management
Policy-Driven Operational Efficiency
Purpose-Built Features for Smarter Access Control
Centralized Role Assignment Dashboard
Granular Permission Sets per Role
Automated Role Inheritance for Sub-Roles
Flexible Role Editing with Instant Updates
Multi-Level Admin Access Policies
Seamless Integration with Audit Logs
Built for real teams solving real access challenges
Securing Hybrid Workforces with Tailored Access
Empowering MSP Technicians with Custom Permissions
Simplifying Compliance for Regulated Industries
Healthcare, finance, and legal organizations can use NinjaOne’s RBAC policy enforcement to meet strict regulatory standards. Access logs and granular permission control support HIPAA, SOC 2, and GDPR requirements. Auditors can quickly verify that access is role-based and tightly managed, easing the burden on IT teams during compliance reviews.
Take Control of Access with NinjaOne
NinjaOne’s Role Based Access Control empowers IT teams to enhance security, boost efficiency, and reduce risk by giving users exactly the access they need—nothing more.
With intuitive controls, audit-friendly transparency, and support for multi-tenant environments, NinjaOne simplifies what used to be a complex, manual task. Experience RBAC that scales with your operations, fits your security goals, and supports your team’s day-to-day success.
Role Based Access Control FAQs
What is role based access control?
Role Based Access Control, or RBAC, is a security model that restricts system access based on a user’s role within an organization. Instead of assigning permissions to individual users, RBAC groups users by roles—such as administrator, technician, or auditor—and grants access rights according to each role’s responsibilities. This streamlines permission management, reduces the risk of unauthorized access, and ensures consistent enforcement of security policies. To put it simply, the meaning of RBAC revolves around the principle of “least privilege,” allowing users to perform only the tasks necessary for their roles, which strengthens both operational efficiency and cybersecurity.
What is an example of Role-Based Access Control?
An example of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) can be seen in an IT service management platform where different team members have distinct responsibilities. For instance, a technician might be assigned a role that allows access to view and manage devices but not modify system-wide policies. Meanwhile, an administrator role would have full control over user management, automation scripts, and system settings. These differences are governed by RBAC permissions, which define exactly what each role can or cannot do within the system. By assigning roles rather than individual permissions, organizations can maintain a secure, scalable, and easily auditable access control structure.
Benefits of RBAC for your endpoint?
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for your endpoints offers several key advantages that directly enhance security and efficiency. By assigning access rights based on user roles, organizations can prevent unauthorized changes, reduce human error, and ensure only qualified personnel can perform sensitive tasks. This is especially important in environments where multiple users interact with devices and data daily. In the context of RBAC cyber security, this model reinforces endpoint protection by minimizing exposure to potential threats and supporting compliance with security frameworks like zero trust. Ultimately, RBAC helps IT teams enforce tighter control without slowing down operations.
How to implement RBAC?
To implement RBAC effectively, start by identifying and defining the various roles within your organization based on job responsibilities. Next, map out which resources or system functions each role should have access to, ensuring you follow the principle of least privilege. Once roles and associated permissions are established, assign users to their appropriate roles rather than granting access individually. A practical role based access control example would be giving a helpdesk technician access to device monitoring tools but restricting access to policy configuration settings, which remain reserved for administrators. This structured approach improves both security and operational efficiency by standardizing how access is granted and maintained.
What are the 4 types of access control?
The four main types of access control are discretionary, mandatory, role-based, and attribute-based. Discretionary Access Control (DAC) allows the data owner to decide who can access specific resources, offering flexibility but with potential security risks. Mandatory Access Control (MAC) enforces strict policies based on classifications and is commonly used in government or highly regulated environments. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) assigns permissions based on a user’s job role, streamlining access management across an organization. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) goes further by using policies that evaluate user attributes, environmental conditions, and resource types to make access decisions, allowing for highly granular and dynamic control.
Related Resources
Securing Company Data with Enterprise Access Control
How to Run Commands as a Different User in Windows 10
Configuring Windows Defender Exploit Guard Network Protection in Windows
