Key Points
- Modern Standby on Windows 11: Enables the device to remain connected to the Internet while in low-power mode.
- Four Methods to Turn On or Off Modern Standby:
- Method 1: Via Power Options: Open Power Options → select your active plan → Advanced settings → set Network connectivity in Standby to Enable, Disable, or Managed by Windows.
- Method 2: Via Windows Terminal: Open PowerShell or Command Prompt (CMD); Use powercfg /setdcvalueindex and powercfg /setacvalueindex to enable, disable, or let Windows manage connectivity for both battery (DC) and plugged-in (AC) modes.
- Method 3: Via Group Policy: Navigate to Computer Configuration → Administrative Templates → System → Power Management → Sleep Settings. Edit “Allow network connectivity during connected-standby” (plugged in / on battery).
- Method 4: Via .REG files: Create or deploy .reg scripts to control network connectivity policies for both ACSettingIndex and DCSettingIndex
Windows 11’s Modern Standby network connectivity (otherwise known as S0 low-power idle) allows your device to be partially active in a low-power state while remaining connected to Wi-Fi or Ethernet. Enabling Modern Standby allows you to sync emails, receive VoIP calls, or receive updates when needed.
This article will walk you through how to enable or disable Modern Standby in Windows 11, plus related considerations and answers to relevant questions.
Configure Windows power policies, network behavior, and device settings at scale with NinjaOne.
Methods to turn on or off Modern Standby network connectivity in Windows 11
You can turn on or off Windows 11’s Modern Standby network connectivity in Power Options, using Windows Terminal, with the Local Group Policy Editor, and by editing a REG file. These methods all have pros and cons, varying degrees of difficulty, and different requirements.
📌 Prerequisites:
- Laptop or tablet
- Windows 11
📌 Recommended deployment strategies:
| Click to Choose a Method | 💻 Best for Individual Users | 💻💻💻 Best for Enterprises |
| Method 1: Navigate Power Options | ✓ | |
| Method 2: Use Windows Terminal | ✓ | |
| Method 3: Local Group Policy Editor | ✓ | |
| Method 4: Edit a .reg file | ✓ | ✓ |
Method 1: Enable or disable in Power Options
📌 Use Cases: Straightforward and doesn’t require scripts or administrative rights, making it the easiest option for the everyday user
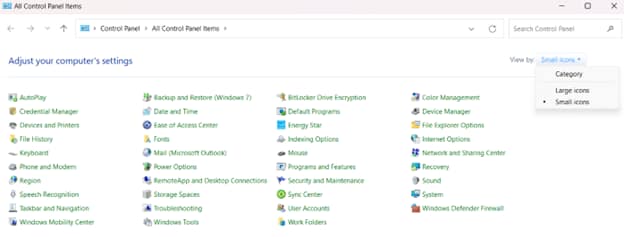
- Press the Win key or Start, type Control Panel, and press Enter.
- Ensure the Control Panel is in icons view (see image below). If not, click Category next to View by: and select one of the two icon options.
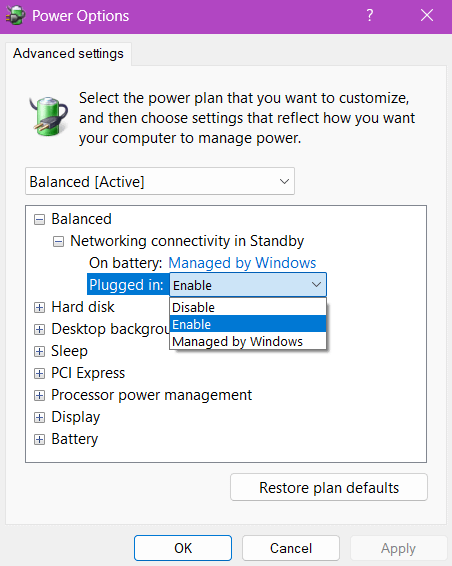
- Tap the Power Options icon and click the Change plan settings link on the right side of your active power plan. Ensure you change the active plan’s settings.
- Press Change advanced power settings.
- Select Enable, Disable, or Managed by Windows in both On battery and Plugged in drop menus below Network connectivity in Standby.
- Click on Ok to apply the changes.
⚠️ Warning: You won’t see this setting if your device isn’t capable of this mode or feature.
Method 2: Enable or disable using Windows Terminal
Using Windows Terminal lets you change how Modern Standby behaves under different power conditions (battery or plugged in).
📌 Use Cases: Recommended for configuring standby policies in managed environments
- Press the Win button or Start and type in either PowerShell or CMD. Hit Enter.
- Copy and paste the commands below into the command prompt and press Enter. Ensure you copy and paste the scripts correctly. Also, note that settings may not persist across sessions.
On Battery
| To enable | To disable | To be managed by Windows (Default) |
powercfg /setdcvalueindex scheme_current sub_none F15576E8-98B7-4186-B944-EAFA664402D9 1Or
| powercfg /setdcvalueindex scheme_current sub_none F15576E8-98B7-4186-B944-EAFA664402D9 0Or
| powercfg /setdcvalueindex scheme_current sub_none F15576E8-98B7-4186-B944-EAFA664402D9 2Or
|
Plugged in
| To enable (Default) | To disable | To be managed by Windows |
powercfg /setacvalueindex scheme_current sub_none F15576E8-98B7-4186-B944-EAFA664402D9 1Or
| powercfg /setacvalueindex scheme_current sub_none F15576E8-98B7-4186-B944-EAFA664402D9 0Or
| powercfg /setacvalueindex scheme_current sub_none F15576E8-98B7-4186-B944-EAFA664402D9 2Or
|
Method 3: Enable or disable with the Local Group Policy Editor
📌 Use Cases: Use this method if you want to override methods 1 and/or 2.
📌 Prerequisite: Sign in as an administrator
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor.
- Look for Computer Configuration in the folder list on the right side.
- Click Administrative Templates > System > Power Management > Sleep Settings.
- Double-click Allow network connectivity during connected-standby (plugged in) on the right pane to edit it.
- Tick Enable or Disable (depending on your preference) on the top left side and tap OK.
- Repeat the process from step three to step five, but double-click Allow network connectivity during connected-standby (on battery) in step four instead.
- Close the Local Group Policy Editor.
Method 4: Enable or disable by editing a .reg file
📌 Use Cases: Ideal for enterprises looking to send solutions to employees and for individual users who want to create their own toggle
- Open Notepad, copy and paste the scripts below, and save them on your desktop. Save the scripts as the highlighted file name for it to work.
To enable or disable Modern Standby network connectivity (plugged-in)
| File name | Script |
| Always_Disable_Modern_Standby_network_connectivity_when_Plugged_In.reg | Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
|
| Always_Enable_Modern_Standby_network_connectivity_when_Plugged_In.reg | Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
|
| Default_Not_Configured_Modern_Standby_network_connectivity_when_Plugged_In.reg | Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
|
To Enable or Disable Modern Standby network connectivity (battery)
| File name | Script |
| Always_Disable_Modern_Standby_network_connectivity_On_Battery.reg | Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
|
| Always_Enable_Modern_Standby_network_connectivity_On_Battery.reg | Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
|
| Default_Not_Configured_Modern_Standby_network_connectivity_On_Battery.reg | Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
|
- Double-click the .reg files one at a time to merge them.
- Press Run, Yes, and/or OK to approve the merge when prompted.
- Restart your computer to apply the changes and avoid potential issues.
⚠️ Things to look out for when enabling or disabling Modern Standby network connectivity
Here are some risks and consequences you could encounter when turning Modern Standby on or off, as well as ways to resolve them.
| Risks | Possible consequences | Reversals |
| Overheating | Users reported that Modern Standby sometimes doesn’t sleep, resulting in an overheating device and a drained battery. Overheating could damage the device and/or the battery. | Monitor the device first to see if Modern Standby is functioning as intended. Otherwise, avoid enabling it. Alternatively, if you’re using a laptop, avoid keeping it plugged in to your charger so that the battery can discharge naturally, rather than overheating. |
| Accidental Wakeups | Accidental wakeups pose security risks as Modern Standby may not trigger a screen lock during wakeups. If you leave the device somewhere public, sensitive data is at risk. | Set up a laptop password and ensure your device is in a secure location when enabling Modern Standby. |
| Device Instability | Some users have reported issues with device instability including reboots after the device wakes up. In some instances, reboots can be a hassle, but it’s not as big an issue as the first two. | If you need to avoid reboots, turn on your device earlier than usual to give yourself some leeway. |
How to check if your computer supports Modern Standby
Before enabling or disabling network connectivity in Modern Standby, you must first check device support. Some computers, regardless of the operating system (OS), may not support Modern Standby. To do so, follow the steps below:
- Press the Win button or Start and type in either PowerShell or CMD. Hit Enter.
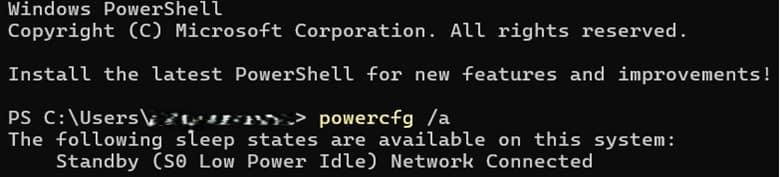
- Copy and paste the command below into the command prompt and press Enter:
powercfg /a
- You should see one of the following under The following sleep states are available on this system if your device supports Modern Standby:
- Standby (S0 Low Power Idle)
- Network Connected (image below)
- Standby (S0 Low Power Idle)
- Network Disconnected
- Standby (S0 Low Power Idle)
This video outlines ‘How to See Sleep States in Windows 10’ clearly.
- If not, you’ll see:
- Standby (S0 Low Power Idle)
- The system firmware does not support this standby state.
- Standby (S0 Low Power Idle)
Additional information regarding Modern Standby
Below is useful information about Windows 11’s Modern Standby. Please note these before turning the feature on or off, as they can affect functionality.
- Device Firmware: Some devices may override the Modern Standby settings, particularly those with BIOS and/or UEFI firmware.
- Connected vs Disconnected Standby: Some devices can only support connected or disconnected standby.
- Impact on Battery: Enabling Modern Standby increases background activity and power usage.
- Security Implications: With Modern Standby enabled, your device may be exposed to background network activity.
Manage power settings and network connectivity of your Windows debices with NinjaOne.
Ensure background apps are online by managing Modern Standby network connectivity
Windows 11’s Modern Standby is a power-saving feature that allows a device to enter a low-power sleep state while remaining connected to networks, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet. It’s useful for users who want to receive updates and emails while preserving battery life. The easiest way to enable it is by navigating the Power Options.
Other methods exist, such as using Windows Terminal, the Local Group Policy Editor, or creating and editing a .reg file. However, not all devices, regardless of OS, support Modern Standby.
Related topics: