If you’ve experienced a quick flash when a scheduled BAT file runs, that means the Command Prompt is popping up to run it, which is disruptive and frustrating. In this guide, we will help you run your BAT file quietly in the background with Task Scheduler, ensuring your automated tasks run smoothly without interruptions.
We recommend checking ⚠️ Things to look out for before proceeding.
📌Skip ahead to the recommended deployment strategies:
Configure Task Scheduler to run BAT file in the background
This method uses native Windows 11 settings to execute your BAT file as a background process, avoiding disruptive pop-ups.
📌Use case: Perfect for routine admin tasks, like log cleanup and backups, where silent operation matters the most.
📌Prerequisites: Ensure you are running on Windows 11 OS, have administrative rights, your existing batch file, and basic familiarity with the tool.
- Open Task Scheduler:
- Open the Run dialog (Win + R), type taskschd.msc, then hit Enter.
- Alternatively, you can search Task Scheduler in the taskbar.
- Open the Run dialog (Win + R), type taskschd.msc, then hit Enter.
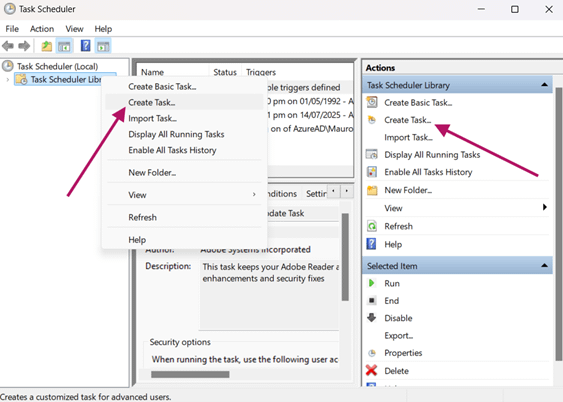
- Create a task:
- Right-click Task Scheduler Library, then select Create Task (not Basic Task). You can also select it in the Actions pane.
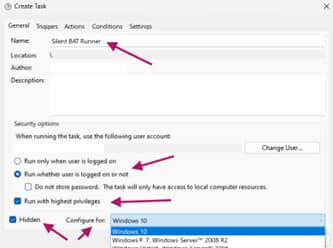
- Input the following in the General Tab (Critical Settings):
- Name: e.g., Silent BAT Runner”
- Select the Run whether user is logged on or not (This will have the task run in the system background).
- Select Run with highest privileges (if admin access is required).
- Select Hidden.
- In the Configure for dropdown, select Windows 11.
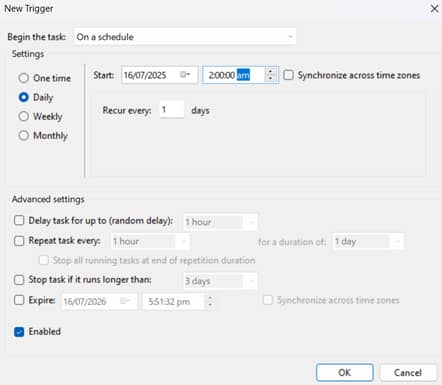
- Input the following in the Triggers Tab:
- Select New, then set the schedule (e.g., daily at 2 AM).
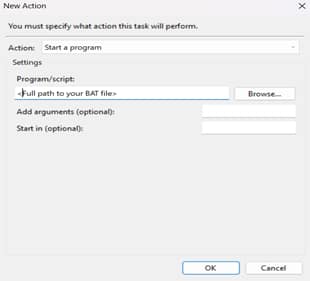
- Input the following in the Actions Tab:
- Select New, then set Action to Start a program.
- In Program/script: Paste the full path to your BAT file.
- Save and authorize:
- Click OK, then enter your password when prompted.
💡Note: A brief Command Prompt flash may still occur. For complete silence, follow the supporting procedures below.
Alternative methods to silently run a BAT file in the background
If you prefer completely stopping that split-second Command Prompt flash when a BAT file runs in the background, below are two procedures you can use to completely silence it.
Option 1: Use VBScript to suppress the CMD window
VBScript acts as a silent wrapper, executing your BAT file without any visual trace.
📌Use case: This is ideal when running the BAT file in Kiosks, presentation systems, or user workstations where zero visual interruption is critical.
- Create a .vbs file:
- Open Notepad (search in taskbar), then input this script:
Set WshShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")WshShell.Run Chr(34) & "C:\Path\To\Your\BatchFile.bat" & Chr(34), 0Set WshShell = Nothing
- Replace the path in the script (C:\Path\To\Your\BatchFile.bat) with your BAT file’s location.
- Save as Runner.vbs (ensure the extension is .vbs, not .txt).
- Schedule the VBScript:
- In Task Schedule, create another task, inputting the same details in the General and Triggers Tabs as the main procedure above.
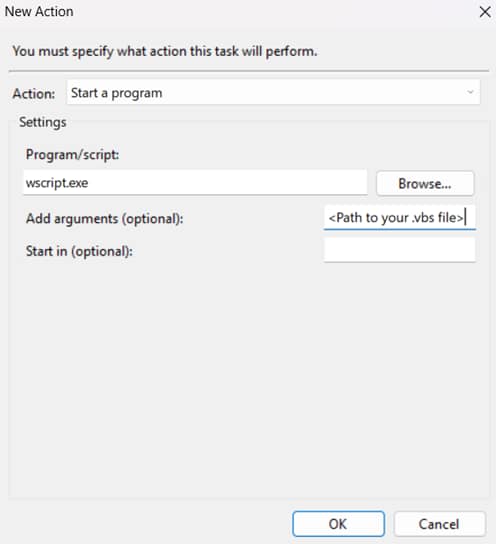
- In the Action Tab, input the following,
- Action: Start a program
- Program: wscript.exe
- Arguments: Path to your VBScript file
This procedure works to run your BAT file silently since the 0 flag in the script hides the flashing window completely. The VBScript executes this invisibly using Windows Script Host.
Option 2: Use PowerShell (.ps1) to hide the BAT execution
PowerShell offers modern, flexible control over process visibility with a single command.
📌Use case: This procedure is great for environments where PowerShell is already the ideal tool used, or for scripts that need additional logic before BAT execution.
- Create a .ps1 file:
- Open Notepad (search in taskbar), then input this script:
Start-Process "C:\Path\To\Your\BatchFile.bat" -WindowStyle Hidden
- Update the path with your BAT file location.
- Save it as StealthRunner.ps1.
- Schedule the PowerShell script in Task Scheduler:
- In Task Schedule, create another task, inputting the same details in the General and Triggers Tabs as the main procedure above.
- In the Action Tab, input the following,
- Action: Start a program
- Program: powershell.exe
- Arguments: Input this script:
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "C:\Path\To\StealthRunner.ps1"
The PowerShell approach has the -WindowStyle Hidden script, which suppresses the console at the kernel level.
Supporting Procedures to prevent focus stealing when running BAT file
Complementary adjustments can further minimize disruptions when running background BAT files and other tasks in Windows 11.
Option 1: Modify the Windows Registry to prevent focus stealing
This approach delays application focus shifts, reducing the impact of any residual window flashes.
📌Use case: This procedure is ideal when a user or an organization wants to avoid any task-triggered focus interruption.
⚠️ Warning: Editing the Registry incorrectly can lead to serious system instability. Always back up your Registry or create a system restore point before proceeding. Review the ⚠️ Things to look out for section to learn more.
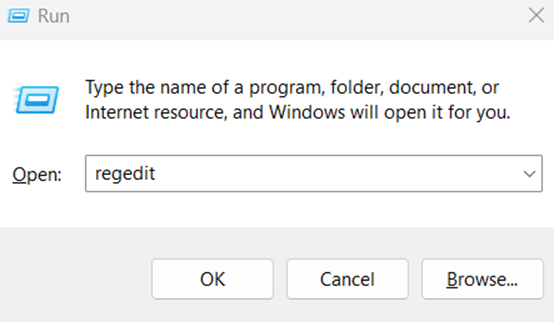
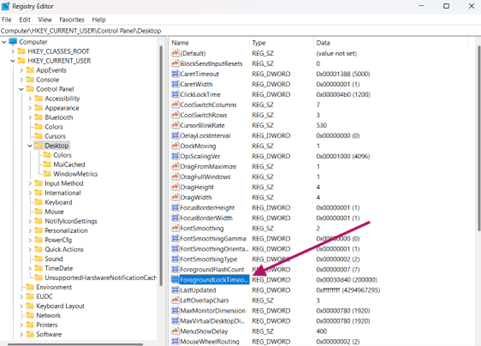
- Open Registry Editor:
- Open the Run dialog (Win + R), then type and enter regedit.
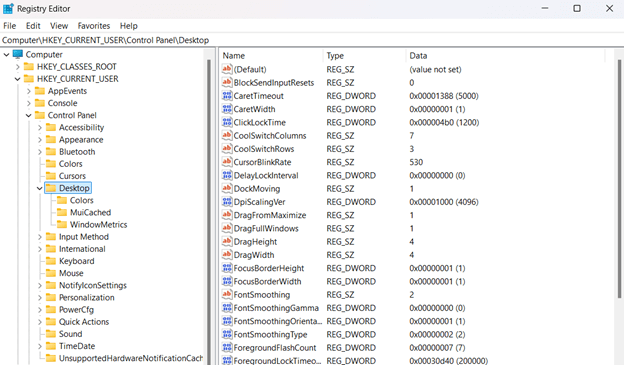
- Go to the address key:
- Navigate or paste this path: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop
- Create/modify the DWORD:
- Double-click the Foregroundlocktimeout DWORD.
- If it does not exist, right-click the right pane, then select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Name the DWORD as Foregroundlocktimeout.
- Double-click the Foregroundlocktimeout DWORD.
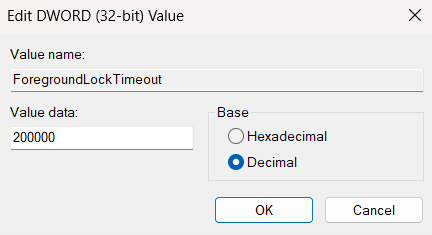
- Set the value data:
- Set the value of the DWORD to 200000 in decimal.
- Apply changes:
- Restart the device or run this in Command Prompt:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe && start explorer.exe
This will not prevent the CMD window from popping up, unlike the approaches in the previous section, but it will suppress focus stealing if a window manages to flash.
Option 2: Adjust Group Policy to limit prompt-based focus shifts
This policy suppresses security warnings that could interrupt workflows when executing scripts.
📌Use case: Enterprise environments where downloaded scripts trigger Open File Security Warning pop-ups during task execution.
💡Note: This approach can only be done in Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions. For Home edition users, we recommend using the Registry Editor method.
- Open Group Policy Editor:
- Open the Run dialog (Win + R), then type and enter gpedit.msc.
- Navigate to the policy:
- Follow this path: User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Attachment Manager
- Enable key policy:
- Double-click Do not preserve zone information in file attachments.
- Select Enabled, then click OK.
- Apply changes:
- Reboot your device or run gpupdate /force in Command Prompt.
How to verify the BAT file is running in the background
Confirm your batch file runs silently and flawlessly after setup with these quick checks.
- Trigger the task manually:
- In Task Scheduler, right-click the task you created, then select Run.
- Watch your screen if the Command Prompt flashes or steals focus.
- Check Task Scheduler history:
- In the Task Scheduler Library, right-click your task.
- Select Properties, then go to the History Tab, and check the Event ID:
- 100: This means the task was completed.
- 101: This means the task failed to start.
- 201: This means the action failed to execute.
- Validate logs and output:
- Check your BAT file’s log/output location (e.g., C:\Logs\output.txt).
- If no logs exist, add this to your BAT file temporarily:
echo %date% %time%: Task ran >> C:\Verify\log.txt
⚠️ Things to look out for
This section highlights potential challenges to keep in mind while following this guide.
| Risks | Potential Consequences | Reversals |
| 1. Incorrect “Run whether user logged on” setting or misconfigured triggers | Task fails silently or BAT file doesn’t execute | Reopen task, then verify the settings. Or test with echo log in BAT file |
| 2. Antivirus blocks wscript.exe or Syntax errors in VBS file | Script aborts silently or no error logs | Whitelist the wscript.exe in AV Or debug VBS via cscript Runner .vbs |
| 3. Execution policies block script or Paths with spaces unquoted | PowerShell exits with policy error | Run Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSignedOr wrap paths in quotes: “C:\My Scripts\file.bat” |
| 4. Making Registry errors like typos or editing the wrong key | System instability; Explorer crashes | Restore registry backup or delete erroneous DWORD, then reboot. Watch How to Back Up and Restore Windows Registry to learn more. |
| 5. Disabling security prompts system-wide | Malicious scripts execute without warnings | Revert Group policy to Disabled/Not Configured or run gpupdate /force. |
Key considerations for running BAT files in the background
Implement these best practices to ensure reliable and secure silent execution.
Permission management
Make sure your BAT file (and supporting VBS/PS1 script files) have Read/Execute rights to run the task for the user account and to log off the execution in the system. This will ensure the tasks run smoothly without errors.
💡Tip: You can run icacls "C:\Your\BatchFile.bat" in Command Prompt to verify if the file has the privileges.
Staged testing protocol
Ensure to test the procedure in a controlled environment first, before deploying it in the user’s device. This will allow you to check if the procedure can be done without errors, like compatibility issues or syntax errors, in the environment, preventing possible system instabilities.
System modification settings
As mentioned, before making Registry or Group Policy edits, create a restore point, export registry keys, and back up task configurations to safeguard your system.
Run BAT Files Silently in Windows 11 for uninterrupted focus
Optimize your background system executions using Windows 11’s Task Scheduler to eliminate disruptive CMD flashes. Use the methods in this guide for uninterrupted task operations. Reform how your backups, cleanups, or scripts run in the background powerfully and invisibly with this guide.
Related topics
Quick-Start Guide
NinjaOne supports running BAT files in the background through its Scheduled Automations feature. Here are the key details:
- You can create scheduled automations that run scripts or applications on devices under a policy.
- Scheduled automations can be set to run:
- On demand
- On a schedule (daily, weekly, monthly)
- On system startup
- On user login
To run a BAT file in the background:
- Go to Administration > Policies
- Select Agent Policy
- Click Scheduled Automations
- Click “Add a Scheduled Automation”
- Configure:
- Name and description for the automation
- Schedule (daily, weekly, etc.)
- Select your BAT file from the Automation Library
- Choose to run as System, current user, or specific credentials
Important notes:
- If fast boot/quick startup is enabled, it may prevent scheduled tasks from running on system startup
- You can add multiple scripts/applications that will run in order
- You can set up notifications or tickets when the automation runs