Key points
- Intune manages cloud-based device updates through configuration policies, enabling BYOD and mobile device patching but without direct, granular control.
- WSUS handles direct update distribution; SCCM manages on-prem devices; Intune focuses on cloud-managed endpoints and mobile devices.
- Intune is best for organizations with Microsoft-only ecosystems seeking lightweight, cloud-based management for Windows and mobile devices already integrated with Microsoft services.
- Using Intune for mobile and Windows updates alongside NinjaOne for broader OS and application coverage ensures autonomous patch management and compliance protection.
Patching is a huge concern within IT environments since attacks on unpatched vulnerabilities make up 95% of all cyberattacks. IT teams want to ensure that the IT management tools they choose are capable of delivering reliable patch management.
Microsoft has a family of products called the Intune product family. Its focus is on endpoint management in the cloud (whereas Microsoft Configuration Manager is used for on-prem management). Intune is also a Microsoft’s mobile device management (MDM) and modern management solution.
→ Learn why NinjaOne is G2’s highest-rated patch management solution
Watch a free demo of the software in action.
Does Microsoft Intune have patch management?
Microsoft Intune does have patch management capabilities. But to help you better understand the product, let’s break down other Microsoft patch management products, like WSUS and Microsoft Endpoint Manager, so you can understand where Intune patch management fits into all this.
What is WSUS?
WSUS, which stands for Windows Server Update Services, is a free default role that enables you to distribute and deploy patches using push-style patching. It can be used on the cloud with Microsoft Azure.
What is SCCM?
SCCM, short for System Center Configuration Manager (and now part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager), is an endpoint management tool for the on-prem management of devices. It can also be cloud-hosted through Microsoft Azure, but it’s not used for the patch management of endpoints. WSUS fills that responsibility.
What is Intune?
Microsoft Intune is an endpoint management tool that works in the cloud and was designed for endpoint bring-your-own-device (BYOD) and MDM. In a roundabout way, it provides patch management using policies and configurations. Unlike WSUS, it operates through the cloud and doesn’t require an on-prem infrastructure, and it doesn’t offer any direct form of patching. It also differs from SCCM because it’s designed for mobile devices, not other endpoint devices.
The product enables you to configure an endpoint, whether it’s a server or a mobile device, and essentially give it directions on how to update itself. This is accomplished using Windows Update for Business. Instead of keeping track of individual updates, you would just need to configure update settings on devices and assign update policy assignments to software. The product doesn’t, however, give you granular control over patching. It would need to be integrated with WSUS and SCCM for robust patch management to happen.
Additionally, Intune focuses on device enrollment and further user management and control of each device. Though this isn’t related to patching, it’s another way to ensure the safety and security of endpoint devices.
Who should use Microsoft Intune’s patch management?
Businesses with an IT environment made up of entirely Microsoft Windows devices can benefit from the use of Intune patching for continual updates of their mobile devices through the cloud. Additionally, if you’re already using Microsoft tools to monitor and maintain your devices, your organization may find it to be less of a hassle to tack on an additional Microsoft product than finding and implementing a new MDM tool.
Advantages of Intune patch management:
- Updates BYODs and mobile devices
- Can set predefined policies for device updates
- Active user management and control of off-prem devices
However, it should be noted that the functionality of Intune’s patch management is fairly limited. Intune was designed for the management of remote mobile devices, so it doesn’t serve other types of endpoints as well as it could. With no direct control over how patches or updates are deployed and applied, there’s a lot left up to the configurations that were initially set up, and since the devices are mobile, the ability to have control over patches is crucial.
Disadvantages of Intune patch management:
- Lacks granular control for patching
- Focus on remote devices leaves more wanted for general endpoint management
Complement Intune with NinjaOne Patch Management
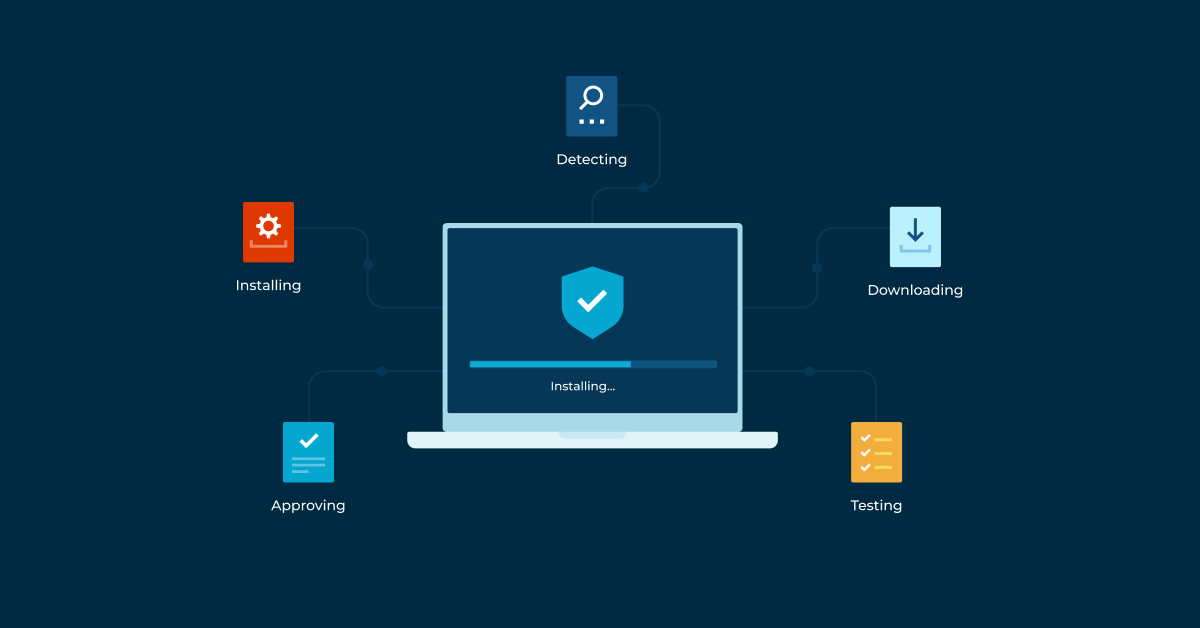
While Intune covers the patching needs of Windows devices in your IT environment, NinjaOne offers autonomous patch management to help you secure the rest of it—endpoints across different operating systems and over 6,000 third-party applications.
Through NinjaOne’s comprehensive and autonomous patching, organizations can
- reduce manual endpoint maintenance on the part of IT teams,
- ensure that their devices are not only secure from cyber threats but also compliant with the latest data protection regulations, and
- focus on more strategic tasks as a result of fewer disruptions and shorter (or even eliminated) downtime.
More notably, NinjaOne’s patching solution comes with Patch Intelligence AI, which detects and pauses unstable or risky updates before they’re deployed, providing further security and marking a step beyond the usual “set and forget” practice.
Patch management with NinjaOne also serves a different purpose from that of Microsoft patch management. NinjaOne focuses on the identification and remediation of endpoint vulnerabilities, while Intune focuses on keeping mobile device systems up to date.
Overall, major features that stand out about NinjaOne’s Patch Management are that it:
- identifies patches for you,
- lets you decide what you do and don’t want to patch in a direct manner,
- reports on patching outcomes, and
- gives you direct control of the overall patching process
In conjunction with Microsoft Intune, NinjaOne provides comprehensive patch management endpoint infrastructure.
Start your free trial of NinjaOne Patch Management today
Get started with NinjaOne Patch Management
Patch management is critical when it comes to protecting your IT environment from external cyber threats. Learn more in our patch management overview, and find out why it’s such a necessary process and component.
NinjaOne’s patch management solution helps you mitigate risk and harden your endpoints. With features like patch automation, patch reporting, remediation tools, and more, you can ensure that you’ve taken the necessary precautions against malware.
See for yourself how much smoother patch management can be with NinjaOne, and sign up for a free trial.